Madhya Pradesh
MPPSC Exam Syllabus – Mains
- 09 Jan 2025
- 24 min read
The Mains examination of the Madhya Pradesh Public Service Commission (MPPSC) SSE delves deeper into candidates’ analytical abilities and understanding of various subjects relevant to administration. It evaluates knowledge across various disciplines. This phase plays a crucial role in determining a candidate's suitability for higher responsibilities in public administration.
A detailed outline of the MPPSC Mains syllabus is provided below for reference.
|
Question Paper |
Part |
Subject |
Marks |
Duration |
Medium of Examination |
General Studies - Paper I |
A |
History |
150 |
03 hours |
Hindi or English |
|
B |
Geography |
150 |
03 hours |
Hindi or English |
|
General Studies - Paper II |
A |
Political Science |
150 |
03 hours |
Hindi or English |
|
B |
Sociology |
150 |
03 hours |
Hindi or English |
|
General Studies - Paper III |
A |
Economics |
150 |
03 hours |
Hindi or English |
|
B |
Science, Technology, and Public Health |
150 |
03 hours |
Hindi or English |
|
General Studies - Paper IV |
A |
Philosophy, Psychology, Public Administration, and Case Study |
150 |
03 hours |
Hindi or English |
|
B |
Management, Personality Development, and Case Study |
150 |
03 hours |
Hindi or English |
|
|
Fifth Question Paper |
- |
सामान्य हिन्दी एवं व्याकरण |
200 |
02 hours |
Hindi |
|
Sixth Question Paper |
- |
हिन्दी निबंध एवं प्रारूप लेखन |
100 |
02 hours 30 minutes |
Hindi |
General Studies Paper-I
Part (A) – History
|
Unit |
Subcategory and Details |
|
Unit-I |
|
|
Unit-II |
|
|
Unit-III |
|
|
Unit-IV |
|
|
Unit-V |
|
Part (B) – Geography
- Unit-I Physical Features and Climate of India
- Geographical Knowledge in Ancient India.
- Major Physiographic (Physical) Divisions of India- the Himalayan Mountains, The Great Plain of North India, the Peninsular Plateau.
- Major Hills, Plateaus, Rivers and Lakes.
- Soils of India- Types and distribution.
- Climate- Seasons, Temperature, Rainfall, Origin of Monsoon, Upper Air Circulation- Jet Stream.
- Climatic Phenomena- El-Nino, La-Nina, Southern Oscillation, Western Disturbances, Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), Consequences of Climate Change.
- Unit-II India- Agriculture and Water Resources
- Agriculture- Production and Distribution of Major crops and Millets.
- Irrigation- Types of Irrigation Techniques, Sources of Irrigation and Multipurpose Projects.
- Food Security, Green Revolution, Strategies for Second Green Revolution and Sustainable Agriculture.
- Conservation and Augmentation of Water Resources- Rainwater Harvesting, Methods of Water Conservation, Interlinking the Rivers, National Water Policy.
- Unit-III India- Natural Resources and Industries
- Forest Resources- Their Types and Distribution.
- Major Minerals and Energy Resources.
- Energy Crises and Non-Conventional Sources of Energy.
- Major industries- Iron and Steel, Cement, Paper, Sugar, Cotton Textile Industry.
- Major Food Processing Industries.
- Unit-IV Disasters and Techniques
- Natural Hazards and Disasters in India~ Earthquake, Tsunamis, Droughts, Floods, Hailstorm, Fog, Cloud burst, Thunderstorm, Tropical Cyclones in India.
- Environmental Pollution- Air Pollution, Water Pollution, Soil or Land Pollution and their Prevention, Control and Management, Measures to Mitigate Pollution.
- Population Growth in India, Population Pressure on -Resources, Rural-urban Migration.
- Advanced Techniques in Geography- Remote Sensing, Geographical Information System (GIS), Global Positioning System (GPS) and their Applications. Types of Satellites.
- Unit-V Geography of Madhya Pradesh
- Major Physiographic (Physical) Divisions- Malwa Plateau, Madhya Bharat Plateau, Bundelkhand Plateau, Vindhyachal Range, Baghelkhand Plateau, Narmada-Son Valley, Satpura Range.
- Major Rivers and Their Tributaries.
- Climate- Seasons, Temperature, Rainfall.
- Soils of Madhya Pradesh- Types and Distribution, Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation.
- Natural Vegetation- Types and Distribution of Forests, Major Forest Produce.
- Major Crops, Irrigation and Irrigation Projects.
- Major Minerals and Energy Resources, Non-Conventional Sources of Energy.
- Major Industries, Small and Cottage Industries.
- Population Growth, Distribution and Density, Urbanisation.
General Studies Paper-II
Part (A) – Constitution, Governance, Political and Administrative Structure
|
Topic |
Details |
|
Unit-I |
|
|
Unit-II |
|
|
Unit-III |
|
|
Unit-IV |
|
|
Unit-V |
|
Part (B) – Sociology
- Unit-I Basic Concepts of Sociology
- Indian Concept of Society- Joint Family, Family, Kinship, Lineage, Clan, Gotra tradition.
- Community, Institution, Association, Culture, Norms and Values.
- Elements of Social Harmony, Concept of Civilisation and Culture. Salient Features of Indian Culture.
- Social Institutions- Family, Education, Religion, Varna, Rin, Yagya, Sanskar.
- Rituals- Various references, Caste system. Ashram, Purushartha, Impact of Religion and Sects on society and marriage.
- Unit-II Diversity and Challenges in Indian Society
- Conceptualizing Indian Society- People of India, Unity in diversity.
- Cultural diversity- Regional, Linguistic, Religious, and Tribal.
- Changing scenario of Crime- Drug addiction, Suicide, Cyber Crime, Crimes against Women and Domestic Violence.
- Current Debate- Tradition and Modernity in India.
- Problems of Nation Building- Secularism, Pluralism and Nation building.
- Unit-III Rural and Urban Sociology
- Approaches to the study of Rural Society- Rural-Urban differences, Ruralism, and Urbanism.
- Peasant studies, Panchayati Raj System before and after the 73rd Amendment, Rural Leadership, Factionalism, Empowerment of People.
- Social issues and Strategies for Rural Development- Bonded and Migrant labours, Trends of changes in rural society.
- Characteristics of Urban Community, Changes in Urban Community, Causes and Impact of Urbanization.
- Concept of Town Planning, Factors affecting Urban Planning, Problems of Urban Management in India.
- Unit-IV Industrialization, Globalization, Social Development and Population
- Industrialization and Social Change in India- Impact on Family, Education, Stratification. Class and Class Conflict in Industrial Society.
- The Challenges of Globalization, Indianization of Sociology, Privatization of Education.
- Social Structure and Development, Facilitators, Inhibitors, Development and Socio-Economic disparities.
- Culture and Development- Culture as aid and impediment, Post-Modernization, Westernization.
- Population Growth and Distribution in India- Growth since 1901, Causes and Effects.
- Concepts- Fertility, Mortality, Morbidity, Migration, Age and Sex composition.
- Unit-V Human Resource Development and Social Welfare Schemes
- National Education Policy 2020- Vision, Principles, School Education, Higher Education, Professional Education, Online and Digital Education, Adult Education and Lifelong learning.
- Issues related to Social Classes and their Welfare Programmes- Senior Citizens, Children, Women, UnderPrivileged Classes and Displaced groups arising out of Developmental Projects. Issues related to Girl's Education.
- Community Development Programme, Extension Education, Panchayati Raj, Role of Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) in Community Development.
- Status of Tribes in Madhya Pradesh and their Social Structure, Customs.
- Beliefs, Marriage, Kinship, Religious Beliefs, Traditions, Festivals and Celebrations.
- Folk Culture of Madhya Pradesh.
General Studies Paper-III
Part (A) – Economics
|
Units |
Topics |
|
Unit-I |
Fundamental Aspects of the Indian Economy:
|
|
Unit-II |
Taxation and Policy Landscape:
|
|
Unit-III |
Overview of Madhya Pradesh Economy:
|
|
Unit-IV |
Social and Economic Development in Madhya Pradesh:
|
|
Unit-V |
Statistics, Data Analysis, and Probability:
|
Part (B) – Science, Technology and Public Health
- Unit-I General Science
- Simple Application of Science.
- Micro-organism- structure and types and Organic Farming.
- Cell— Structure, Types, Division and Function, Classification of Animals and Plants.
- Nutrition in Plants, Animals and Human beings, Balanced Diet, Vitamins, Deficiency Diseases, Hormones, Body Organs of Human Beings- Structure and Functioning.
- Biotechnology- Definition and its uses in sectors like Health and Medicine, Agriculture, Horticulture, Animal Husbandry, Industry and Environment.
- Application of Ethnobiology.
- Contribution in Astronomy by Arya Bhatta, Varahmihir, Brahmagupta and Bhaskar First and Second. Initial Information on Ancient and Modern Observatories.
- Patents and Intellectual Property Rights (Trips, Trims).
- Unit-II Computer Science
- Types of Computers, Characteristics and Generation.
- Memory, Input and Output Devices, Storage Devices, Software and Hardware, Operating systems, Windows, Uses of Microsoft office.
- Fundamental Knowledge of Computer Languages (C, C++, Java), Translators, Interpreters and Assemblers.
- Internet and E-mail.
- Social Media.
- E -Governance.
- Fundamental Knowledge of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Cloud Computing, Different useful Portals, Websites and Webpages.
- Mathematical Science
- Numbers and its type, Methods of Unit Measurement, Equations and Factors, Profit Loss, Percentage, Simple and Compound Interest, Ratio Proportion.
- Area and Volume of Geometric shapes and Surface area.
- Unit-III
- AYUSH- Basic Principle of Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, Sowa-rigpa, Basic Principles of Homeopathic Treatment.
- One Nation One Health System/Policy-2030.
- Ayurveda- Basic knowledge of Tridosh, Panchamahabhut, (Aakash, Vayu, Agni, Jal, Prathvi) Dincharya, Ritucharaya, Panchkarma. Biological Clock. Health Management including AYUSH at the Central, State, District and Village level. National Health Policy (NHP) and scope of Ayurveda in NHP.
- Yoga - Preliminary knowledge of Panchkosh Principles, Ashtanga Yoga, Shatkarma, Mudra. Naturopathy- Therapeutic effect of Soil treatment, Sun Bath, Hydrotherapy and its types.
- Shodasha Sanskar- General Knowledge of Namkarana, Nishkramana, Karnavedha etc and its scientific importance.
- Unit-IV
- National Health Programme- Health Hygiene and Disease, Leprosy (NLEP), AIDS (NACP), Blindness (NPCB), Polio, National TB Elimination Program, Vector Born Disease Control Program, Reproductive and Child Health (RCH) Program, Integrated Child Development Scheme (ICDS), Universal and National Immunization Program, National Ayush Mission (NAM), National Family Health Survey (NFHS).
- Swachh Bharat Mission, Ayushman Bharat Yojana, National Health Mission (NRHM and NUHM), Maternal Mortality Rate in Madhya Pradesh.
- Different Biomarkers such as- normal range of Hematology, Biochemistry, Serology.
- Primary Health Care- Principles and Elements of Primary Health Care, levels of Health Care, Structure of Primary Health Care at Village and Sub center, Primary Health Center (PHC), Community Health Center (CHC) and levels of Rural Hospitals.
- Unit-V
- Concept of Environment in Indian Tradition and Culture. JanapadodhvanshDistortions of Air, Water, land, Time.
- Impact of Human activities on Environment, Ethics and Values related to environment, bio-diversity (especially in the context of Madhya Pradesh), Environment- Pollution, Climate change. Endangered and Extinct Species.
- Problems and Challenges Related to Environment, Causes and Effects of Environmental Degradation.
- Environmental Education- Public Awareness Programs, Environmental Education and its Relationship with Health and Safety.
- Environment friendly Technology, Constitutional Provisions for Environmental Protection. Environmental Protection Policies and Regulatory Framework.
- Role of tribes of Madhya Pradesh (Baiga, Sahariya, Bhariya, Bhil, Gond. etc.) in Environmental Conservation.
- Solid Waste Management- Causes, Effects and Control measures of Urban and Industrial Waste.
- Cleanliness Survey Campaign- Objective, Various Stages, Achievements and Future.
- Water Security.
- Various efforts in the field of Water Conservation.
General Studies Paper-IV
Part (A) – Philosophy, Psychology, Public Administration and Case Study
|
Units |
Topics |
|
Unit-I |
Indian Shaddarshan, Philosophers/Thinkers, Social Reformers:
|
|
Unit-II |
Nation Building and Moral Concepts:
|
|
Unit-III |
Human Behaviour and Psychotherapy:
|
|
Unit-IV |
Moral Value in Public Administration:
|
|
Unit-V |
Case Study:
|
Part (B) – Entrepreneurship, Management, Personality Development and Case Study
- Unit- I Entrepreneurship Concept and Development
- Concept and Significance of Entrepreneurship.
- Symptoms of Entrepreneurship, Principles, Characteristics and Importance of Innovation.
- Process of Entrepreneurship – Creativity, Idea Generation, Analysis and Business Plan.
- Important factors and statutory requirements for new Enterprise Management, Challenges faced by Women Entrepreneurs.
- Development of Entrepreneurship in India- Startup India, Make in India, Organizations for promoting Entrepreneurial development in India.
- Unit-II Business Organizations and Management
- Business – Concept and Significance, Scope, Administration and Management, Purchase and Material, Management.
- Management Process, Resource Management and functions of Management- Plan, Organization, Direction, Control, Coordination, Decision Making, Motivation, Leadership and Communication.
- Time Management and Organization.
- Branding, Marketing and Networking.
- Unit-III Administration and Management
- Important dimensions of Management in Public Administration. Human Resource Management.
- Financial Management- Its scope and significance in Public Administration.
- Stress and Conflict Management Techniques and their significance in Public Service Domain.
- Administration and Management of Plurality, Opportunities and Challenges in Public Administration.
- Disaster Management.
- Unit-IV Overall Personality Development
- Overall Personality and National Development.
- Different components of Personality Development.
- Concepts of successfulness.
- Impediments in achieving success.
- Factors responsible for success.
- Learning from failure- accepting failure as an opportunity for continuous improvement and valuable introspection
- Implementation of Government Programme- Planning effective strategy to ensure successful implementation of Government Programme.
- Approach and facts regarding following issues- Civic Sense, Loyalty to the Institution, Voter Awareness Programme. Transport Management, Trend of Drug abuse, Adulteration in food items, Night Culture, Value based life and Legal Awareness Programme.
- Unit-V Case Study
- Based on the Contents of the Syllabus in Part-B (Entrepreneurship, Management and Personality Development) Question Paper.
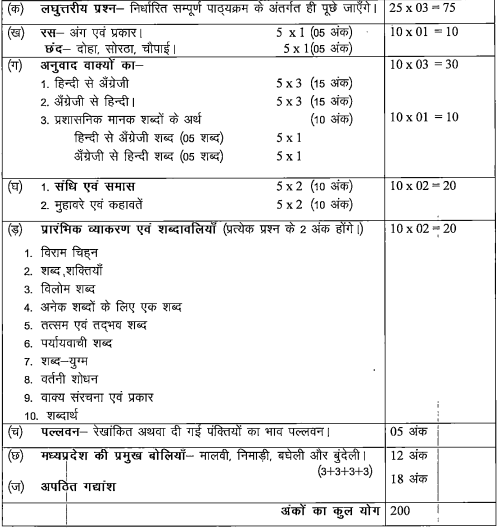
सामान्य हिन्दी एवं व्याकरण (General Hindi and Grammar)
(Total Marks: 200)
- इस प्रश्नपत्र का स्तर स्नातक परीक्षा उत्तीर्ण छात्रों के समक्ष होगा। इसका उद्देश्य उम्मीदवार की पढ़ने व समझने, भाषायी दक्षता, लेखन की योग्यता एवं हिंदी में स्पष्ट तथा सही विवेचन प्रस्तुत करने की क्षमता का मूल्यांकन करना है।
-
निम्नलिखित विषय-सामग्री पर प्रश्न पूछे जाएंगे। प्रत्येक प्रश्न की अंक योजना निर्दिष्ट है-"
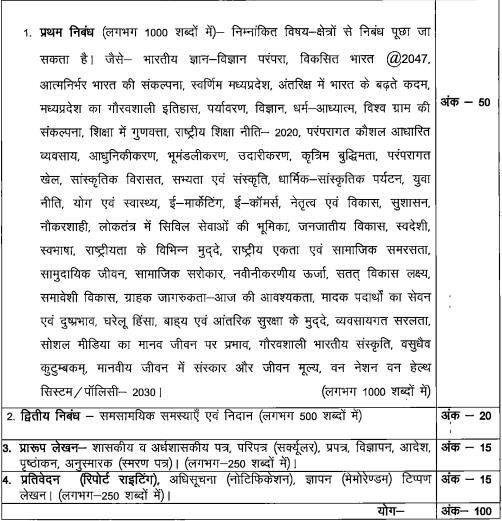
हिन्दी निबंध एवं प्रारूप लेखन (Hindi Essay and Draft Writing)
Note: Since the purpose of this question paper is to evaluate the candidate's expression in the Hindi language and their general knowledge of Hindi, the medium of answering this question paper has been kept exclusively in Hindi.

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)