Van Mahotsav Programme | 21 Aug 2024
Why in News?
Recently, The Chhattisgarh Forest Department organised a Van Mahotsav programme in the Manendragarh-Chirmiri-Bharatpur (MCB) district by planting saplings using the Miyawaki method.
Key Points
- Around 6,000 seedlings were planted at five distinct locations. The primary aim behind adopting the Miyawaki technique is to mitigate urban heat islands and pollution.
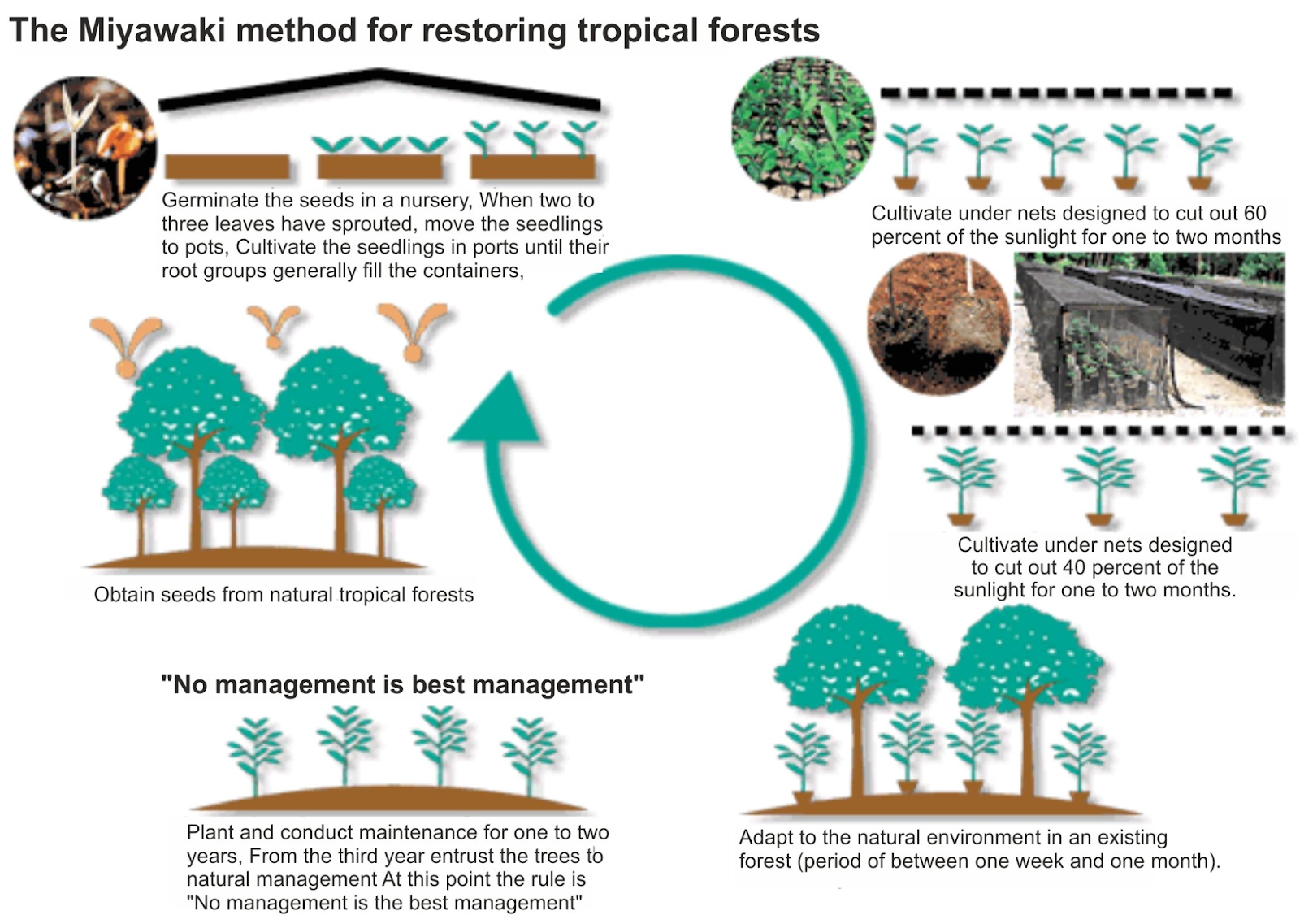
- Miyawaki method:
- It was named after Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki, this method involves planting two to four different types of indigenous trees within every square metre.
- The methodology was developed in the 1970s, with the basic objective to densify green cover within a small parcel of land.
- In this method, the trees become self-sustaining and they grow to their full length within three years.
- The plants used in the Miyawaki method are mostly self-sustaining and don’t require regular maintenance like manuring and watering.
- Significance:
- The dense green cover of indigenous trees plays a key role in absorbing the dust particles of the area where the garden has been set up. The plants also help in regulating surface temperature.
- Some of the common indigenous plants that are used for these forests include Anjan, Amala, Bel, Arjun and Gunj.
- These forests encourage new biodiversity and an ecosystem which in turn increases the fertility of the soil.
- The dense green cover of indigenous trees plays a key role in absorbing the dust particles of the area where the garden has been set up. The plants also help in regulating surface temperature.