Maharashtra
Solar Water Desalination
- 18 Apr 2025
- 4 min read
Why in News?
Indian Institutes of Technology (IIT)- Bombay scientists have developed a new material to enable water desalination and address global freshwater scarcity. 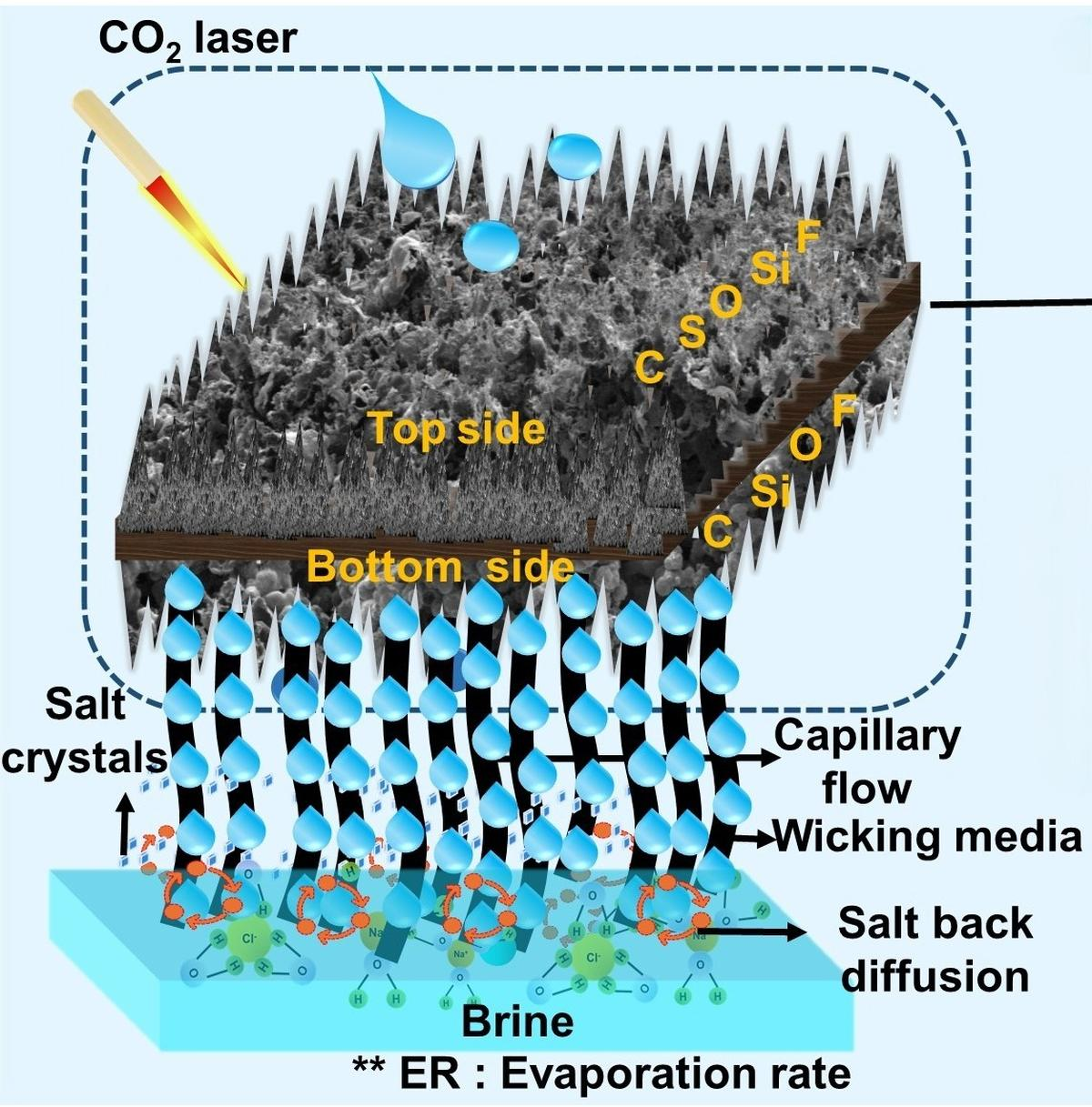
Key Points
- About the Innovation:
- Researchers have developed a Dual-Sided Superhydrophobic Laser-Induced Graphene (DSLIG) evaporator.
- The DSLIG addresses limitations of traditional evaporators and shows promise for large-scale desalination and wastewater treatment.
- The Freshwater Challenge:
- Only 3% of Earth’s water is freshwater, and less than 0.05% is easily accessible.
- Desalination of seawater and brackish water is a key solution to this scarcity.
- However, desalination produces brine, a concentrated salt byproduct, which poses disposal challenges, especially in landlocked areas.
- Industries now aim for zero liquid discharge systems to avoid environmental harm.
- Solar Desalination:
- Solar energy-based desalination offers a low-carbon solution.
- Yet, sunlight variability and poor light absorption reduce efficiency.
- Interfacial evaporation systems help by heating a thin surface layer of water instead of the whole volume, enhancing efficiency.
- Challenges in Interfacial Evaporation:
- Cloud cover and fluctuating solar intensity hamper consistent performance.
- Evaporation peaks around 2 pm, when solar radiation is highest.
- Salt deposition on the evaporator surface blocks water contact, reducing long-term efficiency.
- DSLIG Overcomes the Challenges:
- DSLIG allows dual heating—solar and Joule heating (electric)—ensuring performance even in low sunlight.
- Superhydrophobic properties (lotus effect) prevent salt from sticking to the evaporator surface.
- Solar energy-based desalination offers a low-carbon solution.
- Fabrication of DSLIG:
- Researchers coated PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) on one side of PES (polyether sulfone) polymer.
- PDVF are polymers that can generate electric charges on the surface under pressure/strain thus converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- PES is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high thermal stability, excellent chemical resistance, and biocompatibility.
- They used laser engraving to inscribe graphene onto the PVDF layer.
- PES ensures mechanical strength, while PVDF contributes to dual-sided water repellency.
- The result is a durable, superhydrophobic surface effective in both electric and solar modes.
- Applications:
- It is suitable for treating industrial wastewater and brine from desalination plants.
- Researchers observed improved performance by stacking multiple evaporators.
- DSLIG is low-cost, non-toxic, and sustainable, making it ideal for large-scale applications.
- Researchers coated PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) on one side of PES (polyether sulfone) polymer.
Desalination
- A desalination plant turns salt water into water that is fit to drink.
- Desalination is the process of removing salts from water to produce water that meets the quality (salinity) requirements of different human uses.
- The most commonly used technology for the process is reverse osmosis.
- An external pressure is applied to push solvents from an area of high-solute concentration to an area of low-solute concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
- The microscopic pores in the membranes allow water molecules through but leave salt and most other impurities behind, releasing clean water from the other side.
- These plants are mostly set up in areas that have access to sea water.





