Haryana
Low Water Supply in Haryana and UP
- 19 Dec 2024
- 3 min read
Why in News?
The water level of the Yamuna has significantly decreased due to lack of rain in the upper hills of Himachal Pradesh, causing a severe shortfall in water supply in Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
Key Points
- Water Level at Hathnikund Barrage:
- The water level at Hathnikund Barrage rose but despite the rise, the current supply remains far below demand, impacting irrigation, drinking water supply, and hydropower generation.
- Western Jamuna Canal (WJC) Shortfall:
- The WJC has a water demand of 9,000 cusecs, but only 1,756 cusecs were released.
- The canal provides drinking water to Delhi and irrigates crops in southern Haryana, both of which have been severely affected by the shortfall.
- Eastern Jamuna Canal (EJC) Shortfall:
- The EJC, which caters to Uttar Pradesh, requires 1,500 cusecs but received only 182 cusecs.
- Water supply to the EJC was stopped due to low flow in the river, which dropped to 1,142 cusecs.
- Impact on Hydropower Projects:
- Hydropower projects in Naino Wali, Bhudkalan, Begampur, and Dadupur villages have been impacted by the Yamuna's water shortage.
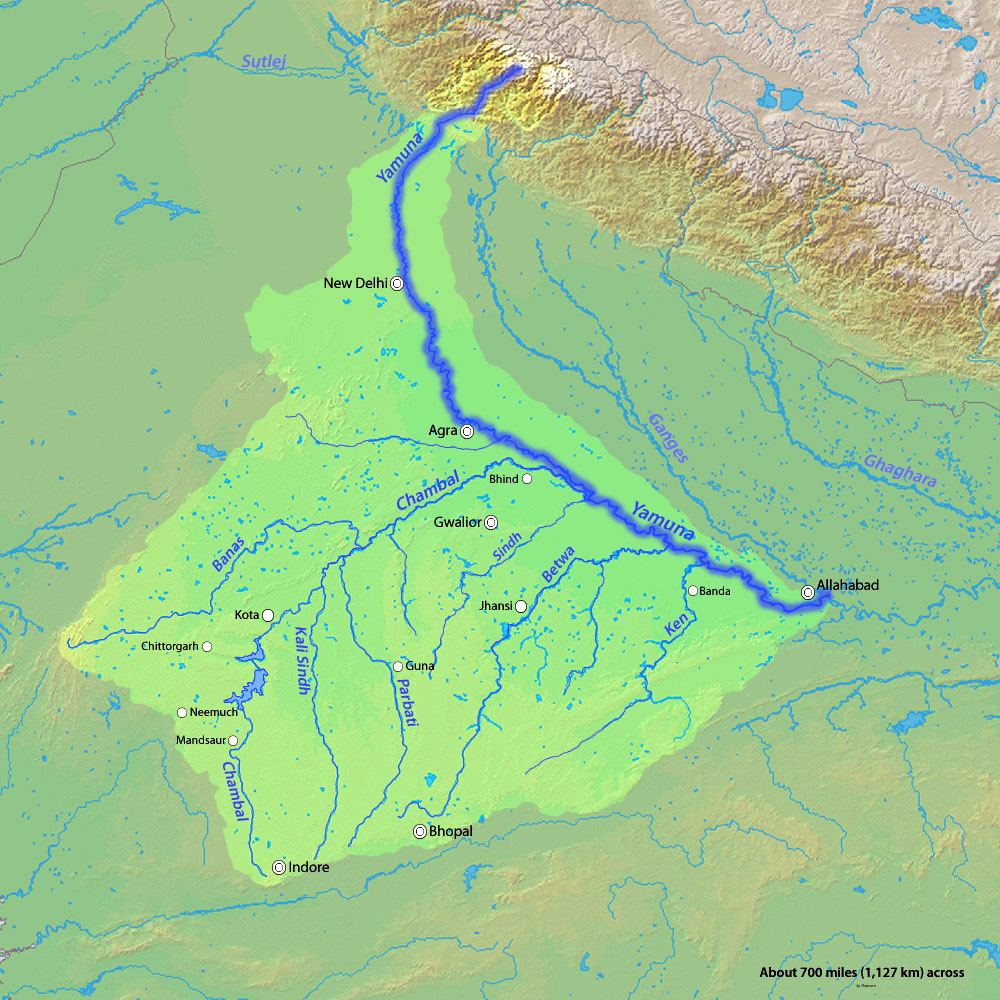
Yamuna River
- About:
- The Yamuna River is one of the major tributaries of the Ganges in Northern India.
- It forms an integral part of the Yamuna-Ganga Plain, one of the world's most extensive alluvial plains.
- Source:
- It has its source in the Yamunotri Glacier at an elevation of 6,387 meters on the southwestern sides of Banderpooch crests in the lower Himalayan ranges.
- Basin:
- It meets the Ganges at the Sangam (where Kumbh mela is held) in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh after flowing through Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana and Delhi.
- Important Dam:
- Lakhwar-Vyasi Dam (Uttarakhand), Tajewala Barrage Dam (Haryana) etc.
- Important Tributaries: Chambal, Sindh, Betwa and Ken.





-min.jpg)