Haryana-Delhi Yamuna Water Dispute | 29 Jan 2025
Why in News?
The Haryana-Delhi dispute over the Yamuna river has once again become a key political issue. Delhi Chief Minister (CM) has accused the Haryana government of contaminating the Yamuna with untreated sewage and industrial waste.
Key Points
- Water Contamination Allegations:
- Delhi Chief Minister termed Haryana’s actions as "water terrorism" and wrote to the Election Commission, citing a Delhi Jal Board (DJB) report that claimed ammonia levels in the Yamuna had surged beyond treatable limits.
- The ammonia levels have steadily increased in the water coming from Haryana to Delhi via River Yamuna due to mixing of untreated sewage or industrial waste from Haryana.
- Delhi Chief Minister termed Haryana’s actions as "water terrorism" and wrote to the Election Commission, citing a Delhi Jal Board (DJB) report that claimed ammonia levels in the Yamuna had surged beyond treatable limits.
- Legal and Political History:
- The Yamuna water-sharing dispute is a long-standing dispute, ongoing since 1995.
- 1994 Memorandum of Understanding (MoU): Five states (Delhi, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Himachal Pradesh) signed an MoU in 1994 to regulate Yamuna water distribution.
- The Supreme Court had intervened in 1995 and 1996 to ensure Delhi’s water supply from Haryana. Despite multiple petitions and legal battles, the issue remains unresolved.
- The Supreme Court has ruled multiple times that Haryana must ensure Delhi’s rightful share of water.
- Recent Developments:
- In 2018, the Supreme Court directed the Chief Secretaries of Delhi and Haryana to resolve water disputes.
- In 2021, the Delhi government accused Haryana of withholding Yamuna water, Haryana countered that Delhi’s crisis was due to "internal mismanagement."
- In July 2023, floods in Delhi led to fresh accusations, with the Delhi Government claiming Haryana deliberately released excess water from the Hathnikund Barrage.
- In June 2024, Delhi CM accused Haryana of "conspiring against Delhi" and launched an indefinite hunger strike, which she ended after five days due to health concerns.
- Impact on Delhi Residents:
- The dispute has led to severe water shortages in Delhi, particularly in summer months.
- Elevated ammonia levels pose a threat to public health, complicating water treatment processes.
- Future Outlook:
- The dispute remains unresolved despite legal interventions.
- The upcoming elections could further intensify political rhetoric around the issue.
- A long-term sustainable solution is needed to address Delhi’s water security concerns.
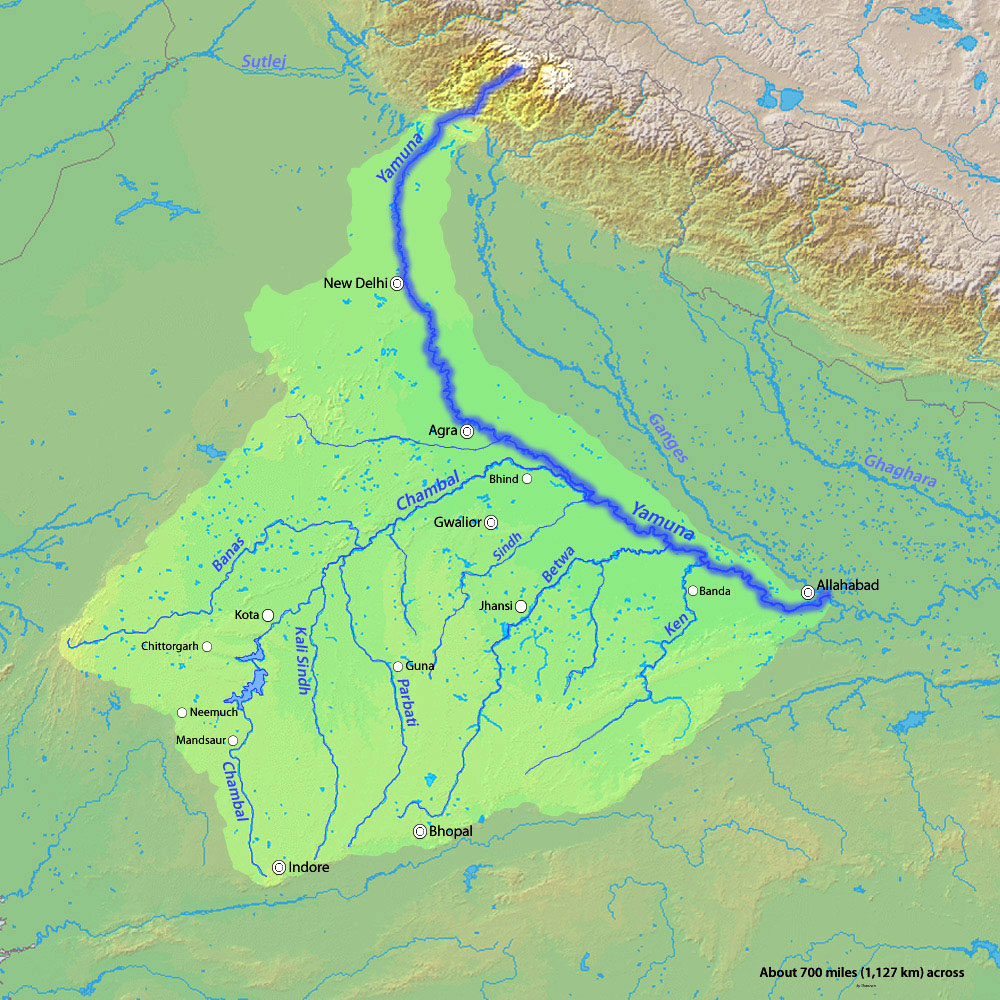
Yamuna
- The river Yamuna, a major tributary of river Ganges, originates from the Yamunotri glacier near Bandarpoonch peaks in the Mussoorie range of the lower Himalayas in Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand.
- It meets the Ganges at the Sangam in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh after flowing through Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana and Delhi.
- Length: 1376 km
- Important Dam: Lakhwar-Vyasi Dam (Uttarakhand), Tajewala Barrage Dam (Haryana) etc.
- Important Tributaries: Chambal, Sindh, Betwa and Ken.