Farm Fires Rise Across Haryana | 30 May 2024
Why in News?
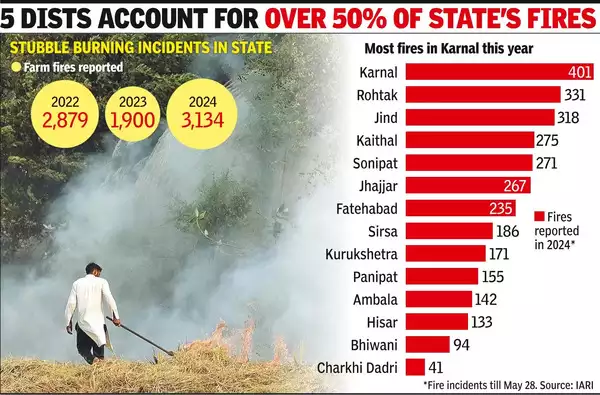
Farm fires that are used to clear land after wheat harvesting in the summer months reached 3,134 cases in Haryana in April and May, making it the highest number recorded in the state during this period in the last three years.
Key Points
- As per satellite data analyzed by the Indian Agricultural Research Institute in 2023, there was a 42% reduction in farm fires during April-May, with only 1,900 incidents recorded.
- The decrease in figures for 2023 was attributed to a higher number of pre-monsoon showers in the area.
- The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) recently stated that the increased occurrences of burning crop residue in and around the National Capital Region (NCR) and forest fires in neighboring states may be contributing to the poor air quality in Delhi-NCR, alongside dry weather conditions causing dust to linger over the area.
- Public awareness initiatives have been initiated to inform both farmers and the public about the adverse effects of burning crop residue and the significance of embracing environmentally friendly alternatives.
- According to the Center for Study of Science, Technology and Policy (CSTEP), authorities must not only focus on combating air pollution in winter but also address the issue throughout the year.
- Although the negative impact of farm fires causing poor air quality is usually highlighted during October–November, the burning of Rabi stubble in April and May is equally detrimental.
- Even though stubble burning may not significantly affect Delhi's air quality in the summer due to monsoon winds, it does contribute to a decline in air quality in Punjab and nearby regions.
- This situation worsens when stagnant winds persist for several days, hindering the dispersion of pollutants.
Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI)
- Indian agricultural Research Institute (IARI), popularly known as Pusa Institute, began in 1905 at Pusa (Bihar) with the generous grant from an American philanthropist, Mr. Henry Phipps.
- Following a devastating earthquake in 1934, the institute was shifted to Delhi on 29th July 1936. Post independence, the institute has been renamed as Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI).
- The green revolution that brought smiles to millions of Indians bloomed from the fields of IARI with the development of famous wheat varieties which contributed to massive production.
- IARI continues to be the leading institution for agricultural research, education and extension in the country.
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
- It is a statutory mechanism to coordinate and oversee diverse efforts to improve air quality in Delhi, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and UP, with the underlying remedial approach.
- The establishment of CAQM has the potential to address the problem of air pollution but an institution by itself is not a solution.