Digital Transformation of Mahakumbh | 01 Jan 2025
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government is going to use the Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled cameras, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) wristbands and mobile app tracking to track the headcount of pilgrims at the Mahakumbh 2025.
Key Points
- Overview of Mahakumbh 2025:
- The government anticipates a footfall of approximately 450 million devotees during the Mahakumbh, a UNESCO-recognized Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- It is the world’s largest peaceful congregation, where pilgrims take a sacred dip in the river.
- Digital Transformation of Mahakumbh:
- Digital and AI-Based Initiatives:
- Launch of a dedicated website and app for event information.
- AI-powered chatbot available in 11 languages.
- QR code-based passes for people and vehicles.
- Multilingual digital lost-and-found centres for visitors.
- ICT and Monitoring Systems:
- ICT monitoring for cleanliness and tent accommodations.
- Software for land and facility allocation and multilingual digital signage.
- Automated ration supply system and drone-based surveillance and disaster management.
- Real-time monitoring software for 530 projects and an inventory tracking system.
- Integration of all event locations on Google Maps.
- Digital and AI-Based Initiatives:
- Infrastructure and Facilities:
- Ghats for Devotees:
- 35 permanent ghats and nine new ghats constructed to facilitate bathing.
- Aerial flower showers planned across all 44 ghats, covering a 12-km area.
- Enhanced Visitor Experience:
- Multilingual digital signage and other technological aids to enhance crowd management and convenience.
- Ghats for Devotees:
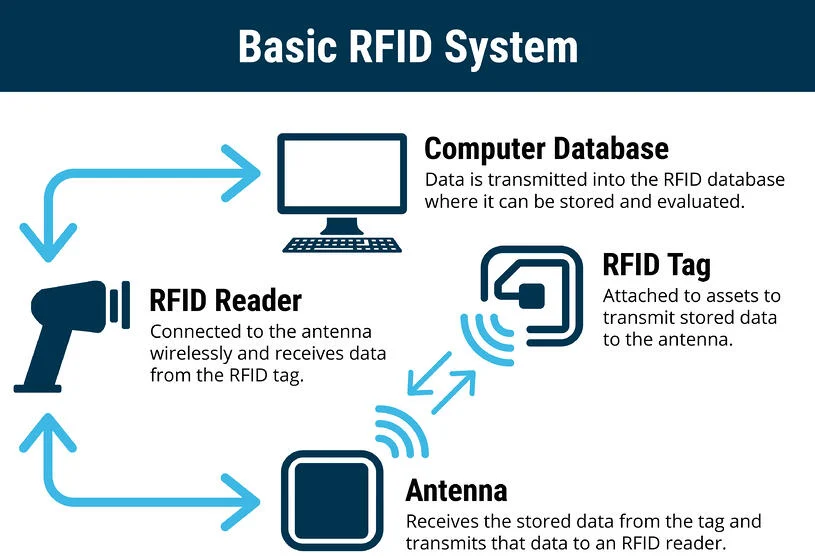
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
- RFID is a type of passive wireless technology that allows for tracking or matching of an item or individual.
- The system has two basic parts: Tags and Readers.
- The reader gives off radio waves and gets signals back from the RFID tag, while the tag uses radio waves to communicate its identity and other information.
- A tag can be read from up to several feet away and does not need to be within the direct line-of-sight of the reader to be tracked.
- The technology has been approved since before the 1970s but has become much more prevalent in recent years due to its usages in things like global supply chain management and pet microchipping.