Maharashtra
Dharavi Redevelopment Project (DRP)
- 12 Apr 2025
- 4 min read
Why in News?
The Maharashtra government approved the allocation of 256 acres of salt pan land in Mulund, Kanjurmarg, and Bhandup for the Dharavi Redevelopment Project (DRP) to rehabilitate ineligible slum dwellers.
- Environmental concerns were raised as this violated the Internal Policy Guidelines (IPG) of 2012, which prohibited construction activities on salt pan land.
Key Points
- About the Land:
- The Officials clarified that the sea has not reached these plots since the construction of the Eastern Express Highway.
- It was emphasized that the land is no longer designated as a flood buffer zone nor falls under Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) restrictions.
- All necessary environmental clearances will be obtained before initiating construction activities.
- The land lies west of the expressway and is away from ecologically sensitive wetlands visited by flamingos.
- It was assured that the location poses no risk to wildlife or the surrounding ecosystem.
- The allocation of salt pan lands for affordable housing aligns with Mumbai’s Development Plan 2034.
- Salt Pan Lands:
- About:
- Salt pans are low-lying tracts of land where seawater periodically flows in, leaving behind deposits of salt and minerals.
- This natural process plays a critical role in maintaining the balance of coastal ecosystems.
- Protection Status:
- Under the CRZ Notification of 2011, these ecologically sensitive areas are classified under CRZ-1B and restrict economic activities except salt extraction and natural gas exploration.
- Salt Pans in India:
- In Mumbai, a total of 5,378 acres have been designated as salt pan lands.
- On a national scale, around 60,000 acres of salt pan lands are identified, distributed across states like Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, and Karnataka.
- Andhra Pradesh has the largest expanse (20,716 acres), followed by Tamil Nadu (17,095 acres) and Maharashtra (12,662 acres).
- About:
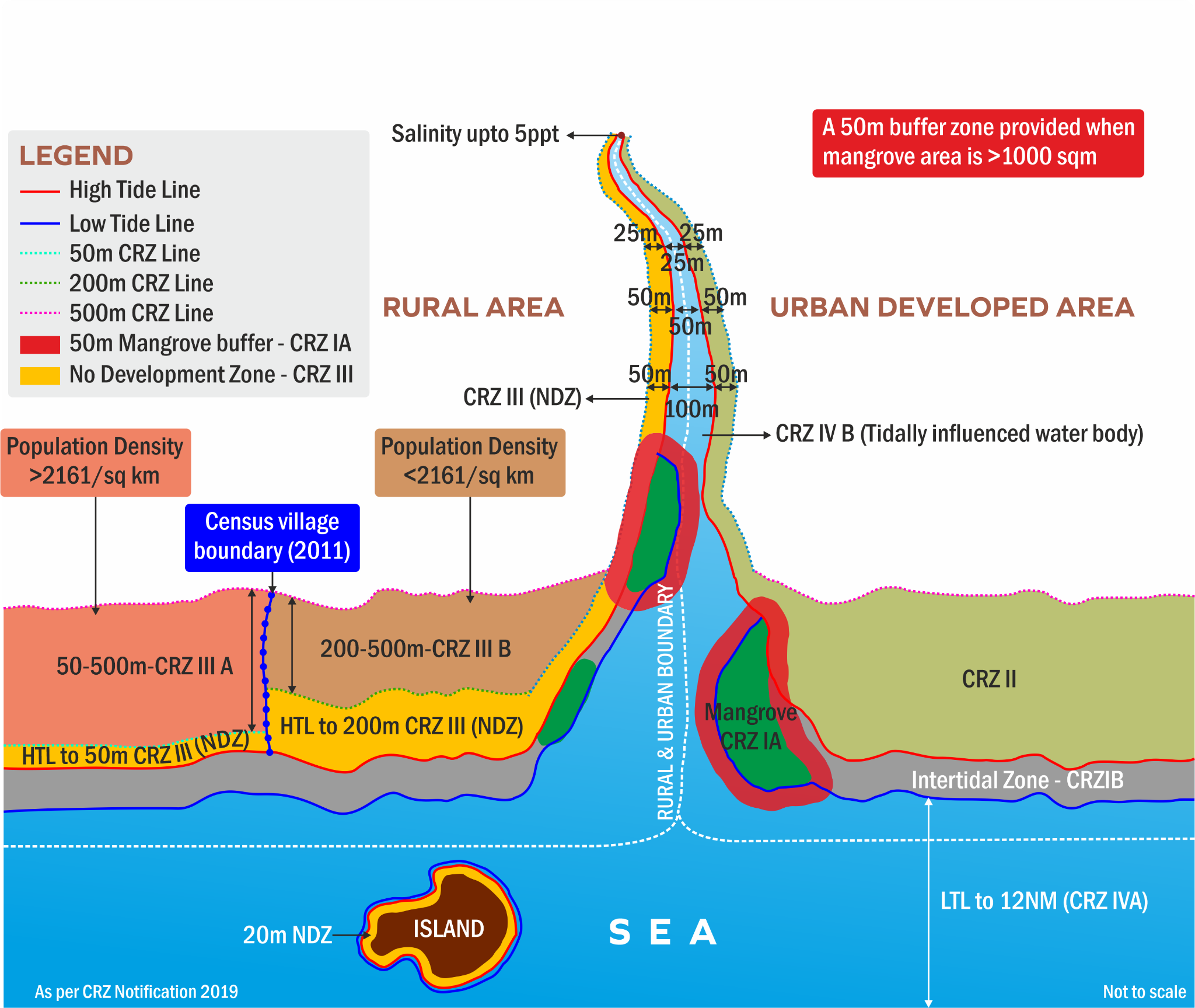
Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ)
- The CRZ was first notified in 1991 by the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEF) under the Environment Protection Act of 1986. The CRZ is categorized into five zones: CRZ-I, CRZ-II, CRZ-III, CRZ-IV, and CRZ-V.
- CRZ-I are ecologically sensitive areas like mangroves, coral reefs, biosphere reserves etc.
- CRZ-II includes built-up areas – villages and towns that are already well established.
- CRZ-III are areas that are undisturbed and do not fall under either in Category I or II.
- CRZ-IV is the aquatic area from low tide line up to territorial limits.
- CRZ is an area near the coastline that's governed by rules to protect the environment and promote sustainable development. The CRZ includes:
- It is the land between the high tide line (HTL) and the low tide line (LTL).
- A 100-metre stretch along the banks of rivers, estuaries, backwaters, and creeks that are affected by tides.
- The river banks on either side of estuaries.