Haryana
Aravali Safari Park
- 12 Feb 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
Recently, several retired Indian Forest Service officers from across the country submitted a representation to the Prime Minister, opposing the proposed 10,000-acre Aravali Safari Park project in parts of Gurugram and Nuh.
- They emphasized that any intervention in an eco-sensitive zone should prioritize "conservation and restoration" rather than destruction.
Key Points
- Aravali Safari Park:
- This project will be the largest such project in the world. Currently the largest curated safari park outside Africa is in Sharjah, which opened in February 2022, with an area of about two thousand acres.
- It aims to boost tourism and employment opportunities for the local people.
- Ecological Concerns:
- The project would increase vehicular traffic and construction in an eco-sensitive zone, harming the environment.
- They highlighted that the Aravali hills serve as critical water reserves for the water-scarce regions of Gurugram and Nuh.
- The proposed “underwater zone” in the park could alter water levels, exacerbating water scarcity in an area already classified as “overexploited” by the Central Ground Water Board.
- Legal and Environmental Restrictions:
- It is emphasized that the Safari Park falls under a "forest" category, where environmental laws strictly prohibit deforestation, land clearing, and construction.
- They cited multiple Supreme Court and National Green Tribunal (NGT) orders under the Forest Conservation Act, 1980, that restrict such activities.
- Impact on Haryana’s Forest Cover and Sustainability:
- Haryana has the lowest forest cover in India, and the Aravali range serves as a crucial ecological buffer.
- The officers warned that mining and human settlement in the area would disrupt environmental balance, violate Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and threaten long-term ecological sustainability.
Eco Sensitive Zones
- The National Wildlife Action Plan (2002-2016) of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) stipulated that state governments should declare land falling within 10 km of the boundaries of national parks and wildlife sanctuaries as eco-fragile zones or Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs) under the Environmental (Protection) Act, 1986.
- While the 10-km rule is implemented as a general principle, the extent of its application can vary. Areas beyond 10 km can also be notified by the Union government as ESZs, if they hold larger ecologically important “sensitive corridors”.
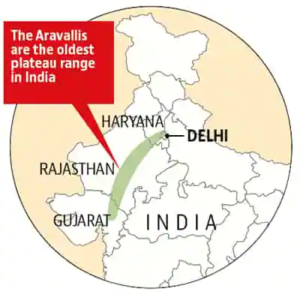
Aravali Mountain Range
- The Aravallis of Northwestern India, one of the oldest fold mountains of the world, now form residual mountains with an elevation of 300m. to 900m.
- This range starts from Himmatnagar in Gujarat and extends up to Haryana, Rajasthan, and Delhi (about 720 km).
- The mountains are divided into two main ranges – the Sambhar Sirohi Range and the Sambhar Khetri Range in Rajasthan, where their extension is about 560 km.
- The hidden limb of the Aravallis that extends from Delhi to Haridwar creates a divide between the drainage of rivers of the Ganga and the Indus
- These are fold mountains of which rocks are formed primarily of folded crust, when two convergent plates move towards each other by the process called orogenic movement.
- The Aravallis date back to millions of years when a pre-Indian sub-continent collided with the mainland Eurasian Plate. Carbon dating has shown that copper and other metals mined in the ranges date back to at least 5th century BC.