-
03 Mar 2025
GS Paper 3
Economy
Day 79: How has the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) impacted the resolution of stressed assets in India? Examine its effectiveness and challenges. (150 words)
Approach
- Briefly introduce the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC).
- Discuss the impact of IBC on Stressed Asset Resolution.
- Examine its effectiveness and challenges.
- To conclude, suggest reforms.
Introduction
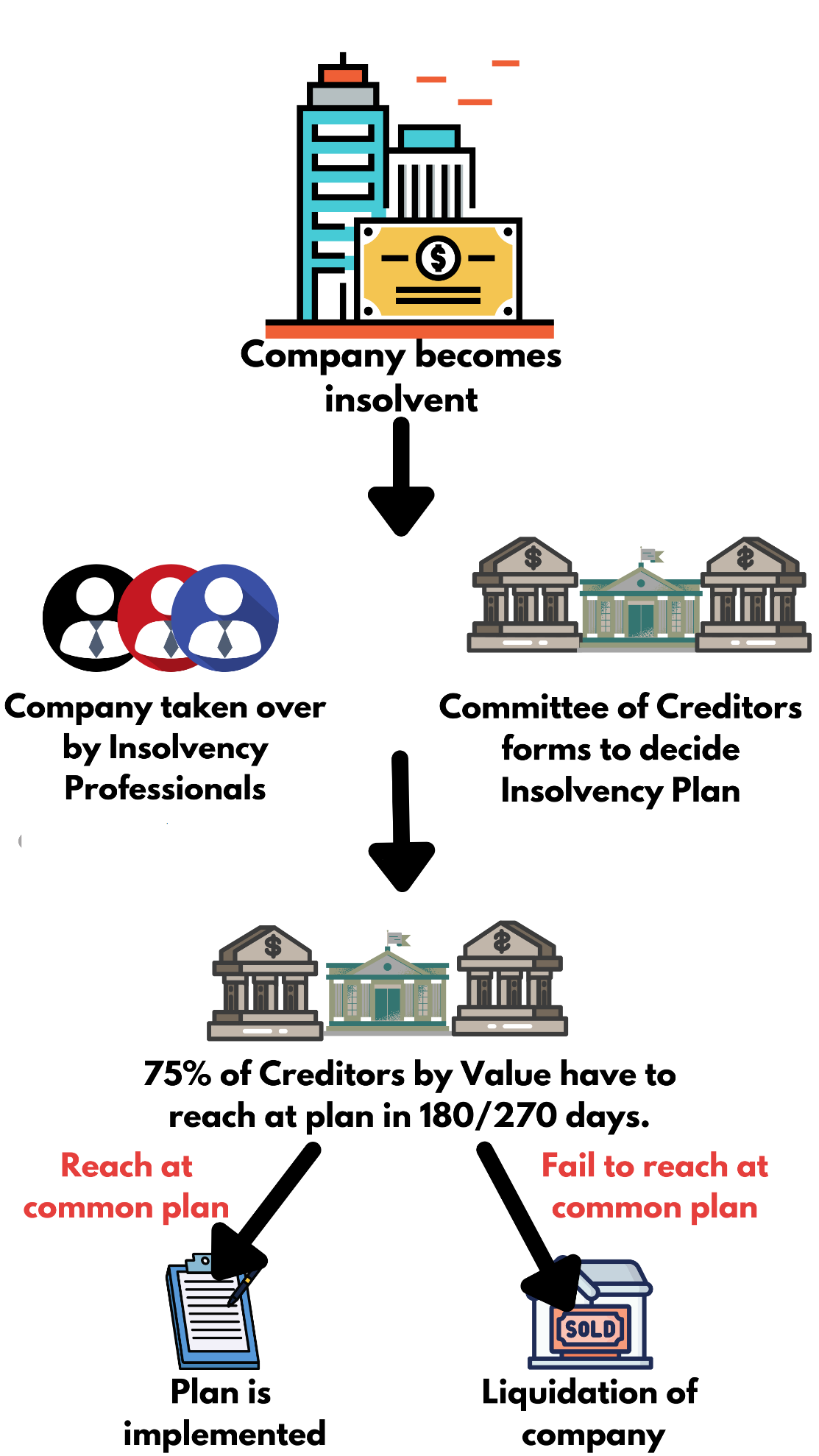
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), introduced in 2016, has been a transformative tool in resolving stressed assets and improving the credit culture in India. This was enacted for the reorganization and insolvency resolution of corporate persons, partnership firms and individuals in a time-bound manner for maximization of the value of assets of such persons.
Body
Impact of IBC on Stressed Asset Resolution
- Faster Resolution of Stressed Assets
- The IBC mandates a time-bound resolution process of 180 days, extendable up to a maximum of 330 days, reducing delays significantly compared to the pre-IBC framework.
- Before IBC, average recovery under the SARFAESI Act was 26% in 4.3 years, whereas under IBC, the recovery rate has improved.
- Improved Recovery Rates for Creditors
- According to the RBI Financial Stability Report (2023), the average recovery rate under IBC is 32.9% of admitted claims.
- IBC has facilitated resolutions of major defaulters such as Essar Steel, where creditors recovered 92% of dues (~₹42,000 crore).
- Strengthening Credit Discipline and Business Environment
- IBC has improved India’s ranking in the World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business Index, jumping from 136th (2016) to 63rd (2020) in resolving insolvency.
- Promotes a creditor-friendly environment, discouraging willful defaults and improving bank asset quality.
Effectiveness of IBC
- Success in Resolving Large Corporate Defaults: The National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) has successfully resolved cases like Bhushan Steel (₹35,200 crore recovered by Tata Steel) and Alok Industries (₹5,000 crore recovered by Reliance and JM Financial).
- Reduction in NPAs : Gross NPAs of banks declined from 11.2% (2018) to 3.9% (2023), reflecting improved resolution mechanisms.
- Strengthening the Financial System: IBC has created a transparent and predictable insolvency process, enhancing investor confidence and attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) in stressed assets.
Challenges in Implementation
- Delays in Resolution Process: Despite the prescribed 330-day resolution timeline, many remained unresolved for years.
- As of 2023, over 65% of cases exceed the deadline due to litigation and procedural delays.
- High Haircuts for Creditors: The average haircut for lenders under IBC is 67% (as per Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India reports).
- Overburdened NCLT and Delays in Case Disposal: As of 2023, more than 24,000 cases are pending before the NCLT, leading to bottlenecks in case resolution.
- MSMEs and Operational Creditors at a Disadvantage: Small businesses and operational creditors often receive lower priority in repayment under IBC.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Judicial and Institutional Capacity :
- Increase the number of NCLT benches and streamline case management to reduce backlog.
- Digitization of insolvency proceedings for faster resolution.
- Addressing the Haircut Issue :
- Introduce pre-pack insolvency resolution for MSMEs to reduce losses.
- Encourage financial institutions to explore alternative debt restructuring mechanisms.
- Enhancing Creditor Rights and Pre-IBC Settlements
- Promote out-of-court settlements to reduce litigation burden.
- Strengthen the role of Resolution Professionals (RPs) for better case management.
Conclusion
The IBC has significantly transformed India’s insolvency resolution framework, leading to better creditor recoveries, improved NPA management, and a stronger financial ecosystem. However, challenges such as delays, high haircuts, and overburdened tribunals need to be addressed for greater effectiveness. Strengthening institutional capacity and ensuring faster resolution processes will help balance financial stability with economic growth.