-
10 Mar 2025
GS Paper 3
Bio-diversity & Environment
Day 85: Explain the concept of a nutrient cycle in an ecosystem. How do the carbon and nitrogen cycles contribute to ecosystem sustainability? (150 words)
Approach
- Briefly explain the general process of nutrient recycling.
- Discuss the contribution of carbon and nitrogen cycles to ecosystem sustainability.
- Conclude Suitably.
Introduction
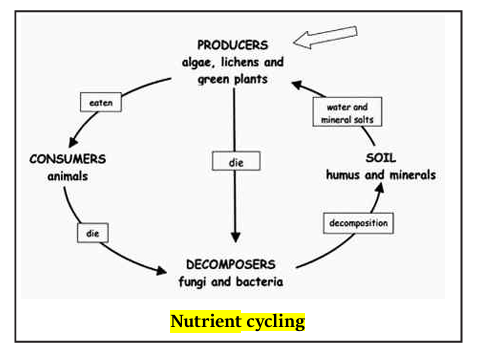
The nutrient cycle is the process through which essential elements, such as carbon and nitrogen, move between biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components of an ecosystem. This cycle ensures the continuous availability of nutrients necessary for life, maintaining ecological balance, and supporting biodiversity.
Body
The contribution of Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles :
- Carbon Cycle: The carbon cycle regulates the movement of carbon through the environment, facilitating energy flow and climate regulation.
- Key Processes:
- Photosynthesis: Plants absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere and convert it into glucose, which is used as an energy source.
- Respiration: Both plants and animals release CO₂ back into the atmosphere through respiration.
- Decomposition: Dead organisms decompose, releasing carbon into the soil and atmosphere.
- Combustion: The burning of fossil fuels releases significant amounts of carbon into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
- Contribution to Sustainability:
- The carbon cycle is essential for climate regulation, as it controls the amount of carbon in the atmosphere, preventing extreme global temperature changes.
- Oceans absorb around 30% of human-caused CO₂ emissions, playing a significant role in regulating the carbon balance.
- The Amazon rainforest, often referred to as the "lungs of the Earth," absorbs approximately 2 billion metric tons of CO₂ annually, underscoring its critical role in carbon sequestration.
- It also supports biomass production, which forms the base of food webs in ecosystems.
- However, deforestation contributes nearly 10% of global CO₂ emissions, as trees store large amounts of carbon that are released when trees are cut down.
- Key Processes:
- The nitrogen cycle: It ensures the availability of nitrogen, an essential nutrient for plants and animals, particularly for building proteins and nucleic acids.
- Key Processes:
- Nitrogen Fixation: Microorganisms like Rhizobium bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) into ammonia (NH₃), making it usable by plants.
- Nitrification: Ammonia is converted to nitrates (NO₃⁻) by nitrifying bacteria, which plants then absorb.
- Assimilation: Plants absorb nitrates and convert them into organic compounds.
- Ammonification & Denitrification: Decomposers break down organic matter, returning nitrogen to the soil, and bacteria convert nitrates back into nitrogen gas (N₂), completing the cycle.
- Contribution to Sustainability:
- The nitrogen cycle maintains soil fertility and supports plant growth, which in turn sustains the entire food web.
- It helps in agricultural productivity, ensuring the availability of food for humans and animals.
- The Green Revolution in the 1960s increased agricultural productivity through the use of nitrogen-based fertilizers, feeding billions of people worldwide.
- However, the overuse of nitrogen-based fertilizers has led to soil acidification, water pollution, and eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems.
- Key Processes:
Conclusion
The carbon and nitrogen cycles are fundamental to maintaining ecosystem sustainability. They regulate key processes like climate control, food production, and soil fertility. To ensure long-term sustainability, it is crucial to adopt sustainable practices such as reducing emissions, protecting forests, and using fertilizers efficiently to maintain these essential cycles for future generations.