-
02 Dec 2024
GS Paper 1
Indian Heritage & Culture
Day 1: Analyze the architectural features of rock-cut structures in India and their significance in early Indian art.(250 words)
Approach
- Provide a brief definition of rock-cut architecture.
- Analyze the architectural features of rock-cut structures in India.
- Discuss their significance in early Indian art.
- To conclude, reinforce that these structures represent invaluable artistic heritage deserving of preservation.
Introduction
Rock-cut architecture refers to a style of construction where structures are carved directly into solid rock formations. Originating in ancient times, particularly around the 3rd century BCE, rock-cut architecture is characterized by its intricate carvings, elaborate façades, and thoughtful interior design.
Body
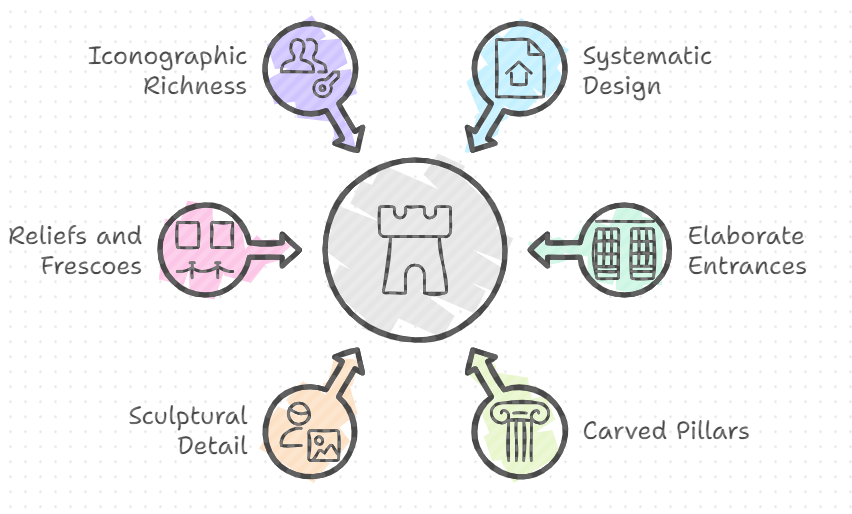
Architectural features of rock-cut structures in India:
- Systematic Design: Rock-cut structures typically include chaityas (prayer halls) and viharas (monasteries). The layout often follows a systematic plan to accommodate worship, meditation, and communal activities.
- Elaborate Entrances: The façades of rock-cut structures often feature intricately carved entranceways, depicting religious figures, floral patterns, and symbolic motifs.
- Intricately carved pillars: The interiors of rock-cut structures often contain rows of intricately carved pillars that support vaulted ceilings. These pillars can vary in design, from simple to highly ornate.
- Sculptural Detail: These carvings serve both decorative and narrative purposes, illustrating stories from religious texts and the cultural beliefs of the time.
- Reliefs and Frescoes: Walls and ceilings are often adorned with intricate sculptures and frescoes that depict religious narratives, such as the life of the Buddha or Hindu deities.
- Iconographic Richness: The sculptural art serves as an important form of expression, showcasing the religious and cultural values of the time.
Significance of Rock-Cut Structures in Early Indian Art :
- Chronological Significance: Rock-cut structures serve as historical records of the artistic trends, religious beliefs, and socio-political contexts of ancient India. .
- Centers of Worship: Many rock-cut structures, such as the Ajanta and Ellora Caves, served as important centers of worship for Buddhism, Hinduism, and Jainism.
- Reflection of Societal Values: The themes and narratives depicted in the sculptures often reflect the religious and cultural values of the time.
- For example, the Ajanta Caves feature numerous frescoes and sculptures illustrating Buddhist teachings and Jataka tales, providing insight into the spiritual life of early Indian society.
- Artistic Innovation: Rock-cut architecture displays sophisticated stone-carving techniques, reflecting the artisans' high level of skill and creativity.
- The intricacies of the sculptures and reliefs illustrate a deep understanding of proportion, depth, and detail.
- Cultural Exchange: Rock-cut architecture exemplifies the cultural interactions between different regions and communities in ancient India.
- The incorporation of elements from other cultures, such as Greco-Roman influences, highlights the dynamic nature of artistic exchange during this period.
- Tourism and Economic Benefits: Sites like the Ajanta and Ellora caves attract millions of tourists each year, contributing significantly to local economies.
Conclusion
As part of the world’s cultural heritage, the rock-cut structures of India hold significance that transcends national boundaries. Their recognition as UNESCO World Heritage Sites underscores their universal value. Their preservation is essential for understanding the rich artistic heritage of India and its impact on subsequent generations.