-
08 Jan 2025
GS Paper 1
Geography
Day 33: What is the significance of ozone in the atmosphere? Discuss the causes and consequences of ozone layer depletion. (250 words)
Approach
- Define ozone and its role in the atmosphere.
- Discuss the significance of Ozone in the atmosphere.
- Discuss the causes and consequences of ozone layer depletion.
- To conclude, suggest measures to address ozone layer depletion.
Introduction
Ozone (O₃) is a triatomic molecule present in the Earth's atmosphere, primarily concentrated in the stratosphere, forming the ozone layer. It plays a crucial role in protecting life on Earth by absorbing harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. However, human activities and certain natural factors have led to its depletion, raising significant environmental and health concerns.
Body
Significance of Ozone in the Atmosphere
- Protection from UV Radiation:
- The ozone layer absorbs most UV-B and UV-C rays, preventing them from reaching the Earth's surface. This protection reduces the risk of skin cancer, cataracts, and genetic damage in living organisms.
- Climate Regulation:
- Ozone regulates temperature in the stratosphere, influencing atmospheric circulation and stability.
- Ecosystem Support:
- By blocking harmful radiation, the ozone layer helps maintain biodiversity and supports ecosystems, including marine life dependent on phytoplankton.
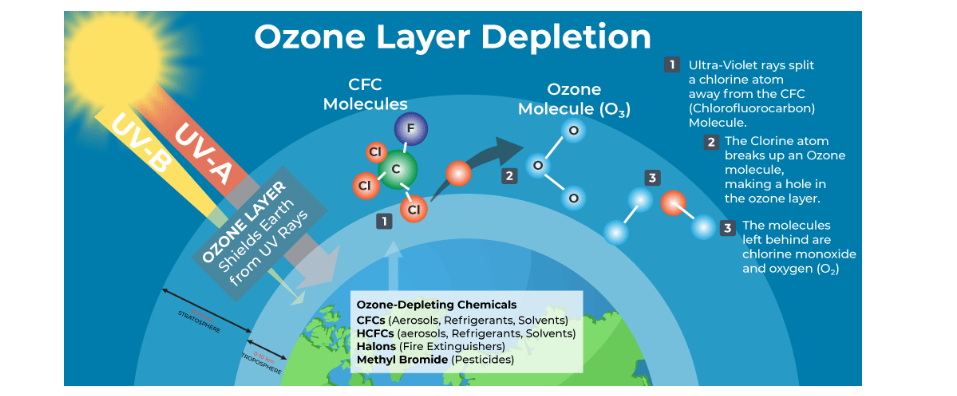
Causes of Ozone Layer Depletion
- Natural Causes:
- Volcanic Eruptions: Release chlorine-containing gases, which contribute to ozone destruction.
- Solar Activity: Variations in the Sun’s energy output can temporarily affect ozone levels.
- Anthropogenic Causes:
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs): Used in refrigeration, air conditioning, and aerosol sprays, these release chlorine atoms that destroy ozone molecules.
- Halons and Other Ozone-depleting substances (ODS): Found in fire extinguishers and solvents, these substances accelerate ozone depletion.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Emitted from supersonic aircraft and some fertilizers, these compounds break down ozone.
Consequences of Ozone Layer Depletion
- Health Impacts:
- Increased UV radiation exposure leads to higher rates of skin cancer, cataracts, and immune system suppression.
- Environmental Effects:
- Marine Ecosystems: UV radiation damages phytoplankton, the base of the oceanic food chain, impacting fisheries and biodiversity.
- Agriculture: UV exposure reduces crop yields, especially in sensitive plants like soybeans and wheat.
Measures to Address Ozone Layer Depletion
- International Efforts:
- Montreal Protocol (1987): A landmark treaty aimed at phasing out the production and use of ozone-depleting substances. Its success has led to significant recovery of the ozone layer.
- Technological Innovations:
- Development of eco-friendly alternatives to CFCs, such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and natural refrigerants.
- Public Awareness and Advocacy:
- Global campaigns like International Ozone Day (September 16) emphasize the importance of protecting the ozone layer.
- Policy and Regulation:
- India's efforts are further supported by the National Ozone Cell (NOC), which coordinates and monitors activities related to the phase-out of ODS.
Conclusion
The ozone layer is vital for life on Earth, shielding it from harmful UV radiation. While significant progress has been made through international cooperation like the Montreal Protocol, continued efforts are essential to fully restore the ozone layer and mitigate its depletion's harmful effects.