-
18 Jan 2025
GS Paper 1
Geography
Day 42: Population Migration is a complex phenomenon shaped by interrelated factors and carrying diverse consequences in India.Comment. (150 Words)
Approach
- Begin with a brief introduction defining population migration and its significance.
- Use the body to address causes and consequences, with examples and data.
- Conclude by summarizing key impacts and suggesting balanced measures.
Introduction
Migration, the movement of people across regions or countries, is a result of various push and pull factors. It plays a critical role in shaping economies and societies, impacting both origin and destination areas.
Body
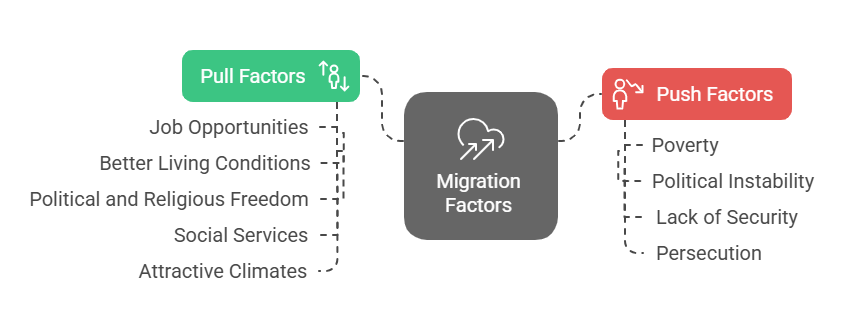
Causes of Population Migration
- Economic Factors: Economic factors, such as job opportunities and better living standards, drive population migration.
- High out-migration from Bihar and Uttar Pradesh has been highlighted, with limited employment opportunities being a significant factor.
- Migration to states like Delhi, Maharashtra, and Gujarat continues to be driven by better job prospects and infrastructure, as evidenced by the EAC-PM Report on Domestic Migration 2023.
- In 2023, districts like Mumbai, Bengaluru Urban, and Howrah accounted for the highest levels of migration, underlining their role as major economic hubs.
- Social Factors:
- Improved access to education and healthcare facilities in urban areas remains a key driver.
- Marriage is the predominant cause of female migration, with 86.8% of female migrants moving for this reason, as per the Migration in India Report 2020-21.
- Political Factors:
- Displacement due to conflicts remains relevant globally, such as the Syrian refugee crisis or Rohingya migration.
- Environmental Factors:
- Climate change, including sea-level rise and flooding, continues to drive migration from vulnerable areas like the Sundarbans in West Bengal.
- Seasonal migration patterns show peaks in April-June and November-December, influenced by agriculture, festivals, and marriages, while January has the lowest migration activity.
Consequences of Population Migration
- Positive Impacts:
- Economic growth in recipient states, such as West Bengal, Rajasthan, and Karnataka, as noted in the EAC-PM report.
- Remittances remain vital for rural economies in states like Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
- Negative Impacts:
- Brain drain from states like Bihar and Uttar Pradesh hampers their development.
- Migration can lead to regional discrimination and violence, often fueled by the "son of the soil" doctrine.
- Overcrowding and infrastructure strain in cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru are significant challenges, with urban areas continuing to absorb the majority of migrants.
- Gender disparities persist, with migration dominated by marriage-related reasons for females (47.9%) compared to employment-driven male migration (49.6%).
- Environmental Effects:
- Unplanned urbanization contributes to pollution and loss of green spaces in major urban centers.
- Agricultural lands in origin areas are abandoned, leading to reduced productivity and food security concerns.
Conclusion
Migration, a multifaceted phenomenon, is driven by economic, social, and environmental factors. While it facilitates economic development and cultural exchange, challenges like urban overcrowding and regional disparities necessitate targeted policies. A balanced approach that promotes equitable development and migration-friendly infrastructure is vital for achieving sustainable outcomes.