-
06 Jan 2025
GS Paper 1
Geography
Day 31: Discuss how the concept of plate tectonics provides a unifying framework for understanding the origin and evolution of Earth's surface and its interior.(150 Words)
Approach
- Introduce the concept of plate tectonics and its relevance.
- Explain how it links surface and interior processes.
- Provide examples and conclude suitably.
Introduction
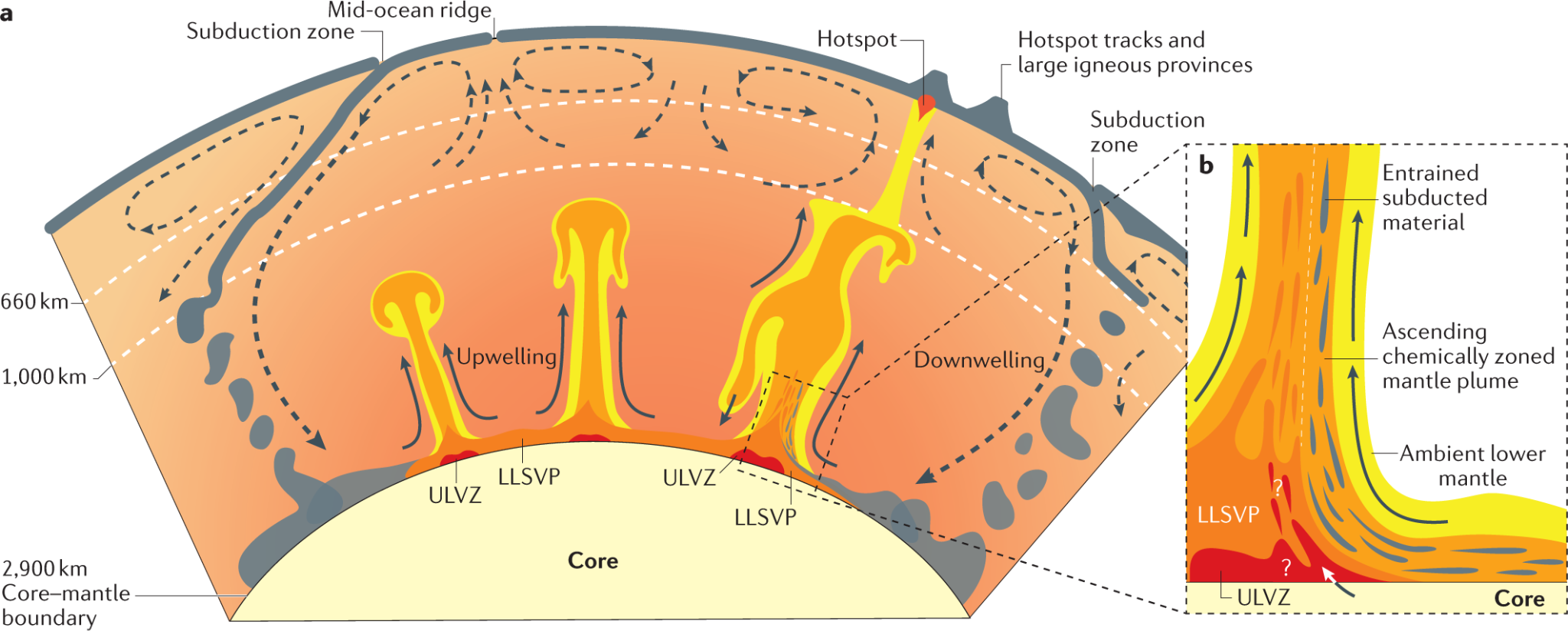
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory propounded by McKenzie and Parker that explains the movement and interaction of Earth's lithospheric plates. It provides a unifying framework for understanding geological processes both at Earth's surface and within its interior. This theory links surface phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanism, and mountain formation with deeper processes like mantle convection and core heat transfer.
Body
- Unified Framework:
- Plate tectonics explains diverse geological phenomena, such as continental drift, seafloor spreading, and mountain building.
- It establishes connections between surface processes (e.g., earthquakes, volcanism) and subsurface mantle convection and core heat dynamics.
- Role in Origin and Evolution:
- Major and Minor Plates: Large plates like the Pacific Plate interact with smaller ones like the Nazca Plate, leading to different geological features.
- For example, the Pacific Plate’s interaction with the North American Plate leads to significant earthquake activity along the San Andreas Fault.
- Formation of Continents and Oceans: Divergent plate boundaries (e.g., Mid-Atlantic Ridge) result in ocean basins, while convergent boundaries (e.g., Himalayas) lead to continental uplift and mountain formation.
- Subduction and Recycling: The descent of oceanic plates at subduction zones recycles crustal materials, contributing to mantle melting and the formation of volcanic arcs (e.g., the Andes).
- Supercontinent Cycles: Periodic assembly and fragmentation of supercontinents like Pangaea significantly impacted Earth's geological, climatic, and biological evolution.
- Major and Minor Plates: Large plates like the Pacific Plate interact with smaller ones like the Nazca Plate, leading to different geological features.
- Earth's Interior Processes:
- Mantle Plumes, such as those responsible for the Hawaiian Islands, show how rising material from the mantle can form surface landforms. The Earth’s internal heat drives the motion of tectonic plates, influencing volcanic and seismic activities.
- Examples:
- Ring of Fire: Volcanic and seismic activity around the Pacific Plate is a prime example of tectonic interactions.
- East African Rift: This rift marks a divergent boundary where the African continent is slowly splitting, illustrating the process of continental break-up. time.
- Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau: Formed by the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates, showcasing the interplay between tectonics and topography.
Conclusion
Plate tectonics links Earth's surface and interior processes, offering insights into the planet’s origin, evolution, and ongoing geological activity. It also has contemporary implications for resource distribution and environmental impacts, such as the localization of minerals and the effects of volcanic eruptions on climate.