-
10 Dec 2024
GS Paper 1
Indian Heritage & Culture
Day 8: Buddhism and Jainism integrated religious doctrines with progressive social ideals.Comment.(150 words)
Approach
- Briefly define Buddhism and Jainism as religious-philosophical systems
- Describe their role in integrating religious doctrines with progressive social ideals.
- To conclude,reflect on their relevance in contemporary times
Introduction
Buddhism and Jainism, which emerged in the 6th century BCE, were revolutionary in their ability to blend spiritual doctrines with progressive social ideals. Rooted in ethical and philosophical teachings, these traditions challenged the societal norms of their time, offering an alternative vision of an egalitarian and harmonious society.
Body
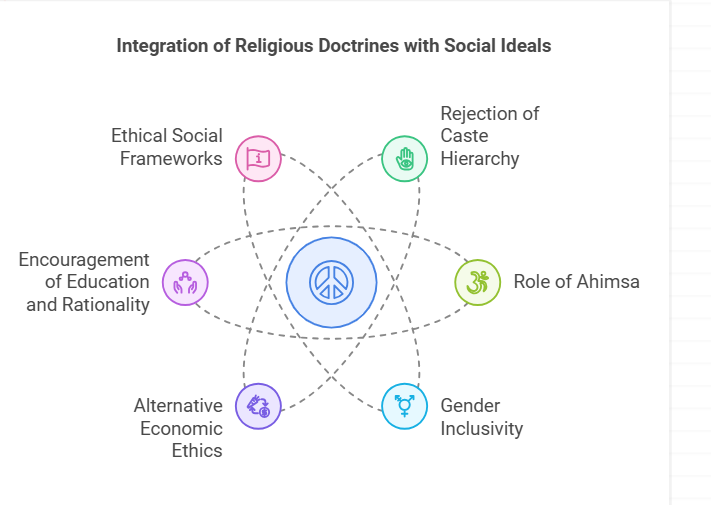
Integration of Religious Doctrines with Progressive Social Ideals
- Rejection of Caste Hierarchy : Both religions strongly opposed the rigid caste-based inequalities prevalent in Vedic society.
- The Buddhist Sangha was an inclusive community where individuals from all castes, including women and untouchables, could attain spiritual liberation.
- Jain monks and nuns often come from various social backgrounds, emphasizing that spiritual progress is not determined by caste, but by one's actions and intentions.
- Role of Ahimsa : Non-violence was a cornerstone of both philosophies.
- Buddhism promoted compassion and kindness to all living beings.
- Jainism prescribed strict vegetarianism and careful action to avoid harm even to the smallest creatures.
- Gender Inclusivity :
- Buddhism took a progressive step by allowing women to join the monastic order (Bhikkhuni Sangha), thus offering them spiritual autonomy.
- Jainism also acknowledged women’s potential for spiritual progress, particularly in the Shwetambara sect, reflecting gender inclusivity in religious and social spheres.
- Alternative Economic Ethics : Buddhism and Jainism critiqued materialism and greed.
- They advocated for simple living and self-restraint, promoting the ethical use of resources and a sense of social responsibility.
- Jainism, in particular, emphasized aparigraha (non-accumulation), encouraging a balanced relationship with material possessions.
- Encouragement of Education and Rationality : Both movements prioritized rational discourse and philosophical inquiry, fostering intellectual growth.
- Buddhist monasteries like Nalanda became centers of learning, attracting scholars from across Asia, promoting education and debate.
- Ethical Social Frameworks : Both Buddhism and Jainism emphasized moral living as the foundation of their teachings.
- The Eightfold Path in Buddhism provided a practical guide for ethical behavior, right speech, and compassion toward all beings.
- Jainism, with its core principles of Ahimsa (non-violence), Anekantavada (multiple perspectives), and Syadvada (conditional truth), also advocates for the removal of suffering and the promotion of social justice
Conclusion
The ideals of these religions remain pertinent in addressing contemporary issues like inequality, environmental sustainability, and ethical governance. Leaders like Mahatma Gandhi, who championed non-violent resistance, Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, who fought against caste discrimination, and the Dalai Lama, who advocated for love and compassion, were profoundly influenced by these teachings, demonstrating their timeless impact for justice and peace.