-
26 Jan 2024
GS Paper 1
Geography
Day 59: Explain the process of cloud formation and categorize the various types of clouds. (150 words)
- Start the answer by introducing the cloud and its formation.
- Discuss the process of cloud formation.
- Also explain the categorization of the various types of clouds.
- Conclude as per the requirement of keywords.
Introduction
Clouds are visible accumulations of tiny water droplets or ice crystals in the Earth’s atmosphere. Their formation is a complex meteorological process that involves the transformation of water vapor into visible water droplets or ice crystals in the Earth's atmosphere. It plays a crucial role in the water cycle and has significant implications for weather patterns.
Body
Process of Cloud Formation:
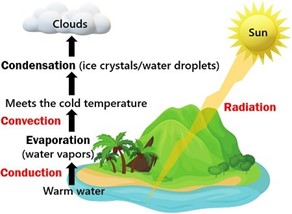
- Evaporation and Condensation:
- Cloud formation begins with the evaporation of water from Earth's surface, such as oceans, lakes, and rivers.
- The risen water vapor then undergoes condensation as it ascends into higher altitudes, where temperatures are lower.
- Nucleation:
- Microscopic particles called aerosols serve as nucleation sites for water vapor to condense around. These aerosols can be dust, pollution particles, or even salt crystals.
- The process of nucleation forms tiny droplets or ice crystals.
- Cloud Droplet Growth:
- Once nucleation occurs, cloud droplets continue to grow as more water vapor condenses onto them.
- Collision and coalescence contribute to the growth, as larger droplets combine with smaller ones.
- Cloud Formation Altitudes:
- Clouds can form at various altitudes, depending on factors like temperature and humidity.
- Low-altitude clouds, such as stratus and cumulus, form in the troposphere, the lowest layer of the atmosphere.
- High-altitude clouds, like cirrus clouds, form in the upper troposphere and even extend into the stratosphere.
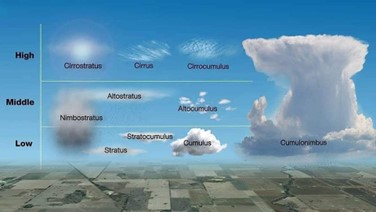
Types of Clouds:
- Cirrus Clouds:
- High-altitude clouds with feathery and wispy appearances.
- Composed of ice crystals due to their formation in the colder upper troposphere.
- Cumulus Clouds:
- Puffy, white clouds with a flat base.
- Often associated with fair weather but can develop into larger storm clouds.
- Stratus Clouds:
- Form in uniform layers covering the sky, creating overcast conditions.
- Can bring light rain or drizzle.
- Nimbostratus Clouds:
- Thick, dark clouds covering the sky, often associated with continuous rain or snow.
- Stratocumulus Clouds:
- Low, lumpy clouds with a mix of elements from stratus and cumulus clouds.
- May bring light precipitation.
- Altostratus Clouds:
- Gray or blue-gray clouds covering the sky at mid-altitudes.
- Often precede storms with continuous rain or snow.
Conclusion
Cloud formation is a dynamic process influenced by atmospheric conditions and the presence of aerosols. Categorizing clouds based on their appearance and altitude helps meteorologists predict weather patterns, contributing to a better understanding of the Earth's complex climate system.