-
27 Jan 2024
GS Paper 1
Geography
Day 60: What are the key characteristics and impacts of monsoon climate in India? (150 words)
- Give a brief introduction to the monsoon climate in India.
- Discuss the key characteristics of the monsoon climate in India.
- Discuss the impacts of the monsoon climate in India.
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction
The monsoon climate in India is a major meteorological event that defines the country's weather patterns and has a significant impact on the environment, agriculture, and society.
Body
Key Characteristics of Indian Monsoon:
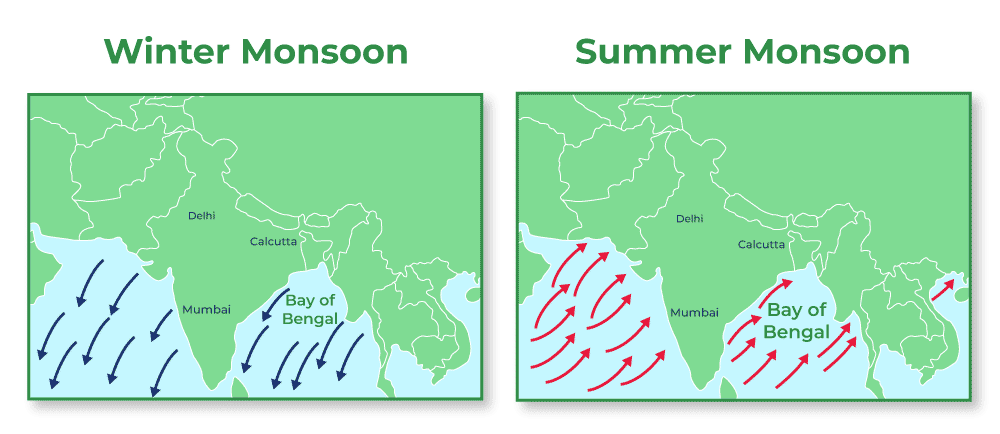
- Seasonal Reversal of Winds:
- Southwest Monsoon: During summer, hot air masses over the Indian subcontinent create a low-pressure area that draws in moist air from the Indian Ocean, resulting in the southwest monsoon which typically begins in June and lasts until September.
- It brings heavy rainfall to various parts of the country, especially the western coast and northeastern regions.
- Northeast Monsoon: In the winter months, from October to December, the landmass cools down, creating a high-pressure area over the Indian subcontinent, leading to the northeast flow of winds. These winds are known as the northeast monsoon or retreating monsoon.
- The retreating monsoon winds bring rainfall to the southeastern parts of the country, including Tamil Nadu and parts of Andhra Pradesh.
- Southwest Monsoon: During summer, hot air masses over the Indian subcontinent create a low-pressure area that draws in moist air from the Indian Ocean, resulting in the southwest monsoon which typically begins in June and lasts until September.
- Differential Rainfall Distribution: The monsoon is not uniform across India. The western coast, northeastern states, and the Himalayan foothills receive substantial rainfall, while the northwestern regions, such as Rajasthan, witness arid conditions.
- Cooling Effect: The monsoon helps in moderating temperatures, bringing relief from the scorching summer heat. The cooling effect is particularly pronounced in regions receiving heavy rainfall.
Impacts of Monsoon Climate in India:
- Positive Impacts:
- Agricultural Prosperity: Adequate and well-distributed rainfall during the monsoon season is vital for agriculture. It ensures proper soil moisture, fostering the growth of crops and boosting agricultural productivity.
- Water Reservoir Replenishment: Monsoon rains contribute significantly to the filling of water reservoirs, lakes, and rivers. This replenishment is essential for maintaining water levels and meeting the water demands for irrigation, domestic use, and industrial purposes.
- Biodiversity Support: The monsoon season supports biodiversity by providing the necessary water for plants, animals, and ecosystems. It sustains diverse habitats, contributing to the richness of flora and fauna in various regions.
- Cultural and Social Influence: The monsoon is deeply ingrained in Indian culture, influencing festivals such as Onam, traditions, and art. The arrival of the monsoon is often celebrated as a symbol of renewal and prosperity.
- Negative Impacts:
- Economic Dependency: Indian agriculture is heavily dependent on the monsoon. Monsoon failures can have severe economic consequences, affecting sectors like agriculture, fisheries, and forestry.
- Former President Pranab Mukherjee has aptly described monsoon as the real finance minister of India.
- Seasonal Flooding: Intense and prolonged rainfall during the monsoon often leads to flooding, especially in low-lying areas and river plains. This can result in significant economic and human losses.
- Environmental Concerns: Excessive rainfall can lead to soil erosion and waterlogging, impacting the health of the soil. Moreover, increased runoff may contribute to the depletion of nutrients in the soil.
- Economic Dependency: Indian agriculture is heavily dependent on the monsoon. Monsoon failures can have severe economic consequences, affecting sectors like agriculture, fisheries, and forestry.
Conclusion
A harmonious understanding and effective management of the multifaceted impacts of the monsoon climate in India is crucial for ensuring sustainable development, resilience to climate variability, and the overall prosperity of the country.