-
10 Feb 2023
GS Paper 1
Geography
Day 81
Question 1: The connection between agriculture and the market is crucial. Analyze the immediate and long-term effects on relevant parties caused by the relationship between agriculture and the market. (250 words)
Question 2: Discuss the Agro-Climatic Regions in India. How the cultivation of indigenous crops as per local agro-climate can benefit the farmers and consumers. Discuss. (150 words)Answer 1
Approach
- Write an introduction that shows how the connection between agriculture and the market is crucial.
- Analyze the long term and short-term impact on relevant parties of relationship between agriculture and market.
- Write a holistic and effective conclusion.
Introduction
- The connection between agriculture and the market is crucial because agriculture is a major source of food and other agricultural products, which are essential for human consumption and trade.
- The market provides a platform for the exchange of these products between producers and consumers, determining their prices and creating demand for them.
- The market also influences the decisions made by farmers, such as what crops to grow and how to produce them, based on consumer preferences and economic conditions.
- Thus, the connection between agriculture and the market is essential for ensuring the availability and affordability of food and other agricultural products, and for driving economic growth and development.
Body
- The relationship between agriculture and the market has both immediate and long-term effects on relevant parties. Some of these effects include:
- Immediate effects:
- Farmers: Farmers are directly affected by the market through the prices they receive for their crops and livestock. Market conditions can determine whether farming is a profitable venture or not, affecting farmers' income and livelihoods.
- Consumers: Consumers are also directly impacted by the market through the prices they pay for agricultural products. Market conditions can influence the availability and affordability of food and other agricultural products, affecting consumers' purchasing power and dietary choices.
- Agribusinesses: Agribusinesses, such as processors, wholesalers, and retailers, are also impacted by the market. Market conditions can determine the demand for their products and services, affecting their sales and profits.
- Long-term effects:
- Agricultural development: The relationship between agriculture and the market can drive agricultural development through the creation of new technologies and production methods. This can lead to increased efficiency and productivity, and lower costs, ultimately benefiting both farmers and consumers.
- Economic growth: Agriculture is a key sector of many economies, and the relationship between agriculture and the market can drive economic growth through increased trade and investment in the sector. This can lead to job creation and improved living standards.
- Food security: The relationship between agriculture and the market is crucial for ensuring food security, as it provides a mechanism for the efficient distribution of food and other agricultural products to consumers. This can help to alleviate hunger and malnutrition, especially in developing countries.
- Immediate effects:
Conclusion
Agriculture and the market are closely connected, and this connection has an impact on various parties in both the short-term and long-term. The market acts as a hub for the trade of agricultural products and sets their prices, impacting the choices made by farmers and the well-being of farmers, consumers, and agribusinesses. This relationship plays a key role in advancing agriculture, boosting the economy, and guaranteeing food security. As a result, it is crucial to regularly evaluate the relationship between agriculture and the market to make sure it continues to have positive outcomes for all involved parties.
Answer 2
Approach
- Write a brief introduction about Agro-Climatic regions in India.
- Discuss the benefits of cultivation of indigenous crops as per local agro-climatic conditions.
- Write a holistic and effective conclusion.
Introduction
- Agro-climatic regions in India refer to the different areas of the country with distinct agro-climatic conditions, such as temperature, rainfall, and soil type, that influence the type of crops that can be grown successfully.
- These regions are defined based on the climatic and soil conditions, which determine the growing conditions for crops, including the length of the growing season, the amount of rainfall, and the soil type.
- There are various agro-climatic regions in India, including the tropical wet region, tropical dry region, sub-tropical humid region, subtropical arid region, and temperate region.
Body
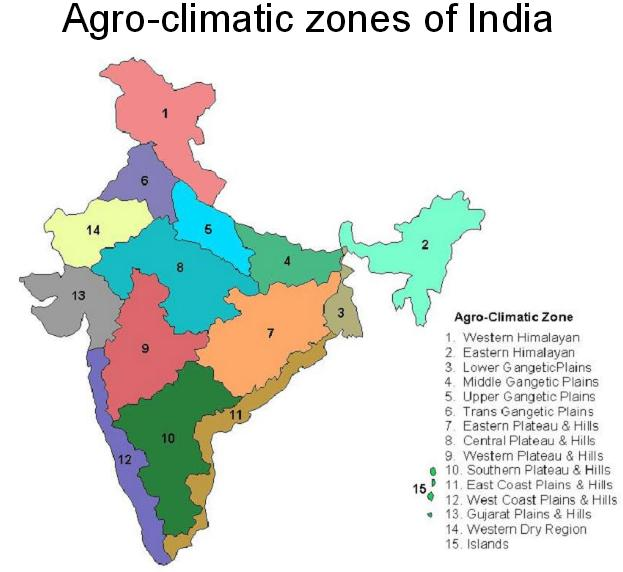
- There are 15 main agro-climatic regions in India, which are:
- Western Himalayan:
- This Agro-Climatic Zone is a region located in the western part of the Himalayan Mountain range, covering the states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand in India.
- Eastern Himalayan:
- The Eastern Himalayan Agro-Climatic Zone is a region located in the eastern part of the Himalayan Mountain range, covering the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, and parts of Assam and West Bengal in India.
- Lower Gangetic Plain:
- The Lower Gangetic Plain Agro-Climatic Zone is a region located in the northern part of India, covering the states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal. The region is characterized by its flat terrain, fertile soil, and favorable climate for agriculture, which support the production of a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, sugarcane, and potatoes.
- Middle Gangetic Plain:
- The Middle Gangetic Plain is a region located in the northern part of India, covering the states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and parts of Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. The region is characterized by its flat terrain, fertile soil, and favorable climate for agriculture, which support the production of a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, sugarcane, and potatoes.
- Upper Gangetic Plain:
- The Upper Gangetic Plain is a region located in the northern part of India, covering the states of Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and parts of Haryana and Delhi. The region is characterized by its flat terrain, fertile soil, and favorable climate for agriculture, which support the production of a variety of crops including rice, wheat, sugarcane, and potatoes.
- Trans Gangetic Plain:
- The Trans-Gangetic Plain is a region located in the northern part of India, covering parts of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, and Assam. The region is characterized by its flat terrain and fertile soil, which support the production of a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, sugarcane, and potatoes.
- Eastern Plateau and hill:
- The Eastern Plateau and Hill region is a geographic region located in the eastern part of India, covering parts of the states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal. The region is characterized by its rolling hills and plateaus, with elevations ranging from 300 to 1,000 meters above sea level.
- The Central Plateau and Hill:
- The Central Plateau and Hill region is a geographic region located in the central part of India, covering parts of the states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, and Odisha. The region is characterized by its rolling hills and plateaus, with elevations ranging from 300 to 1,000 meters above sea level.
- The Western Plateau and Hill:
- The Western Plateau and Hill region is a geographic region located in the western part of India, covering parts of the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Rajasthan. The region is characterized by its rolling hills and plateaus, with elevations ranging from 300 to 1,000 meters above sea level.
- The Southern Plateau and Hill:
- The Southern Plateau and Hill region is a geographic region located in the southern part of India, covering parts of the states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh. The region is characterized by its rolling hills and plateaus, with elevations ranging from 300 to 1,000 meters above sea level.
- The East Coast Plain and Hill:
- The East Coast Plain and Hill region is a geographic region located in the eastern part of India, covering parts of the states of Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and Tamil Nadu. The region is characterized by its rolling hills and fertile coastal plains, with elevations ranging from sea level to 1,000 meters above sea level.
- The West Coast Plains and Hill:
- The West Coast Plains and Hill region is a geographic region located in the western part of India, covering parts of the states of Gujarat, Karnataka, and Maharashtra. The region is characterized by its rolling hills and fertile coastal plains, with elevations ranging from sea level to 1,000 meters above sea level.
- The Gujarat Plains and Hill:
- The Gujarat Plains and Hill region is a geographic region located in the western state of Gujarat, India. The region is characterized by its rolling hills and fertile coastal plains, with elevations ranging from sea level to 1,000 meters above sea level.
- The Western Dry Region:
- The Western Dry Region is a geographic region located in the western part of India, covering parts of the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Maharashtra. The region is characterized by its arid and semi-arid climate, with low rainfall and high temperatures, making it one of the most drought-prone areas in India.
- The Islands:
- The Island region in India refers to the region consisting of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands, located in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea, respectively. The region has a tropical maritime climate, characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and abundant rainfall.
- Western Himalayan:
- The agro-climatic regions in India play a crucial role in determining the type of crops that can be grown in a specific area and supporting sustainable agriculture and food security in the country. Cultivating indigenous crops that are well-suited to the local agro-climate can have several benefits for both farmers and consumers:
- Increased profitability for farmers: Indigenous crops are often well-adapted to local growing conditions, which reduces the risk of crop failure and increases yields. This can lead to improved profitability for farmers as they can produce more crops with less inputs.
- Better food security: Cultivating indigenous crops can provide better food security as these crops are often well-suited to local growing conditions and are less susceptible to pests and diseases, reducing the risk of crop failure.
- Preservation of local food culture: Cultivating indigenous crops helps preserve local food culture and traditions, which are an important part of a community's identity.
- Improved health outcomes: Indigenous crops are often more nutritious than imported crops and can provide better health outcomes for consumers.
- Reduced dependence on imported crops: Cultivating indigenous crops can reduce a community's dependence on imported crops, which can be more expensive and less well-suited to local growing conditions.
- Reduced environmental impact: Indigenous crops are often well-adapted to local growing conditions and require fewer inputs, such as fertilizers and pesticides, reducing the environmental impact of agriculture.
Conclusion
The agro-climatic regions in India play a crucial role in determining the type of crops that can be grown in a specific area. Each agro-climatic region has its unique growing conditions, such as temperature, rainfall, and soil type, which influence the type of crops that can be grown successfully. It is important to recognize the value of these agro-climatic regions and the role they play in supporting sustainable agriculture and promoting food security in India.





-min.jpg)