PRS Capsule - June 2024 | 31 Jul 2024
Key Highlights of PRS
- Polity and Governance
- New Union government formed after general elections to Lok Sabha
- President’s Address highlights achievements of the government
- Cinematograph (Adjudication of Penalty) Rules, 2024 notified
- Cabinet approves scheme to enhance forensic infrastructure in India
- Economy
- Rules to identify offshore mineral areas for granting concessions notified
- CERC notifies new regulations for grant of inter-state transmission licences
- Education
- UGC releases curriculum and credit framework for postgraduate programmes
- High-level Committee constituted to suggest reforms in examination process
- Environment
- Cabinet approves viability gap funding for offshore wind energy projects
Polity and Governance
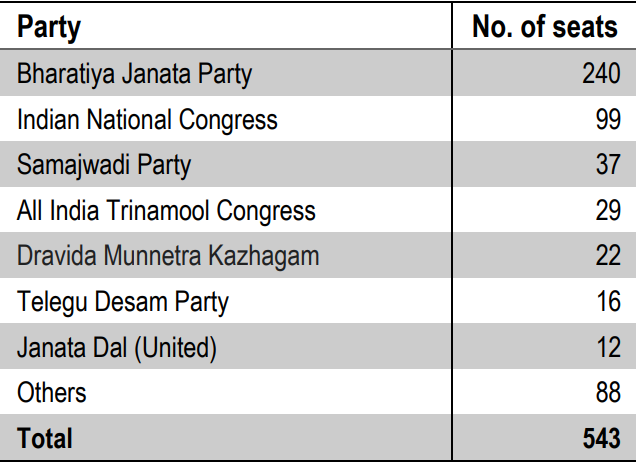
New Union Government Formed after General Elections to Lok Sabha
- Results to the elections to the 18th Lok Sabha were declared on June 4, 2024, and members from 41 parties were elected from 543 constituencies.
- The National Democratic Alliance (NDA) formed the government with Mr. Narendra Modi as the Prime Minister.
President’s Address Highlights Achievements of the Government
- The President of India addressed a joint sitting of both Houses of Parliament on June 27, 2024.
- Key Highlights of the Address Include:
- Economy: In 10 years, India has risen from being the 11th largest to being the fifth largest economy in the world. The government is striving to make India the third largest economy in the world.
- Industry: Sunrise sectors ranging from semiconductors to fighter jets and aircraft carriers are being promoted in mission mode. The north-eastern region will be a hub of Made-in-India chips.
- Defense: In the last year, about 70% of defense procurement was sourced from Indian manufacturers. Defense corridors are being developed in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- Infrastructure and Transport: Feasibility studies will be conducted for bullet train corridors in the northern, southern and eastern regions. Government is making continuous efforts to reduce the cost of logistics.
- Urban and Rural Development: Construction of three crore houses has been approved under PM Awas Yojana.
- Home Affairs: Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, 1958 is being withdrawn from disturbed areas of the north-east in a phased manner.
Cinematograph (Adjudication of Penalty) Rules, 2024 Notified
- The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting notified the Cinematograph (Adjudication of Penalty) Rules, 2024.
- Key Features of the Rules Include:
-
Appointment of Authorized Officers:
- The central and state governments may appoint authorized officers for adjudicating penalties.
- In case of the central government, the authorized officer must not be below the rank of Under Secretary.
- In case of state governments, the officers must not be below the rank of:
- Additional District Magistrates
- Additional Collectors
- Additional Deputy Commissioners of a district
- Under Secretary to the state government
- Levy of Penalty:
- The quantum of penalty will be decided after considering specified factors including:
- Nature of the violation
- Amount of disproportionate gain or advantage
- Repetition of the violation.
- The order deciding the penalty must be passed within 90 days of issuing the notice.
- The quantum of penalty will be decided after considering specified factors including:
- Powers of the Authorized Officer:
- The authorized officer may exercise certain powers to investigate violations. These include:
- Entering (or authorizing another officer to enter) a place of exhibition
- Summoning individuals (in writing)
- Order for evidence considered relevant, such as surveillance footage and ticket scans.
- The authorized officer may exercise certain powers to investigate violations. These include:
- Appellate Process:
- The appellate authority must be an officer not below the rank of
- Deputy Secretary or Director where the authorized officer is of the rank Under Secretary
- The District Magistrate, where the authorized officer is of the rank Additional District Magistrate.
- Appeals must be filed within 30 days of the order by the authorized officer.
- The appellate authority must decide appeals within six months, wherever possible.
- The appellate authority must be an officer not below the rank of
-
Cabinet Approves Scheme to Enhance Forensic Infrastructure in India
- The Union Cabinet approved the National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement Scheme with an outlay of Rs 2,254 crore.
- It will be implemented between 2024-25 to 2028-29.
- The Scheme will:
- Establish campuses of the National Forensic Sciences University (NFSU) in the country
- Establish Central Forensic Science Laboratories
- Enhance existing infrastructure of the Delhi campus of NFSU.
- The scheme seeks to address the shortage of trained forensic manpower in the country and help achieve a conviction rate of over 90%.
Economy
Rules to Identify Offshore Mineral Areas for Granting Concessions Notified
- The Ministry of Mines has notified the Offshore Areas (Existence of Mineral Resources) Rules, 2024.
- These have been issued under the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002.
- Key Features of the Rules Include:
- Identification of Areas for Production Lease:
- A production lease may be granted for an area for which:
- At least general exploration has been completed
- A geological study report has been prepared.
- A production lease may be granted for an area for which:
- Identification of Areas for Composite License:
- A composite license may be granted for an area for which:
- At least the reconnaissance survey has been completed, or mineral potential of the mineral block has been identified based on existing geoscience data but resources are yet to established.
- A geological study report has been prepared.
- A composite license may be granted for an area for which:
- Application to Notify an Area for Composite License:
- Based on the criteria outlined above, the central government will notify areas for granting composite licenses.
- Any interested person may also submit a proposal to the government to notify an area for granting a composite license.
- Identification of Areas for Production Lease:
CERC Notifies New Regulations for Grant of Inter-State Transmission Licenses
- The Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) has notified the CERC (Procedure, Terms and Conditions for Grant of Transmission Licence and Other Related Matters) Regulations, 2024.
- It provides a framework for grant and administration of licenses for inter-state transmission of electricity.
- Key Changes under the 2024 Regulations Include:
-
Exemption for Certain Purposes:
- Distribution licensees and bulk consumers will not need a license to develop and operate transmission lines that connect their systems to the inter-state transmission system.
- Bulk consumers refer to consumers who avail supply at the voltage of 33 KV or above.
- Authorisation for Additional Works under Existing Licenses:
- It provides for the inclusion of such additional works under an existing license.
- A licensee may apply to CERC to amend the existing license for this purpose.
-
Education
UGC Releases Curriculum and Credit Framework for Postgraduate Programmes
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) released the “Curriculum and Credit Framework for Post Graduate Programmes”.
- The Framework Seeks to Provide Flexibility to:
- Pursue subjects different from those studied in undergraduate programmes (UG)
- Pursue PG education in different modes of learning
- Pursue simultaneous academic or industry engagements and obtain credits for the same
- Exit a PG programme after one year with a PG diploma.
- Key Features of the Framework Include:
-
Credit Requirement and Eligibility for PG Programme:
- It prescribes criteria for undergraduate students to be eligible for various types of PG programmes.
- For instance, to be eligible for a one-year MA, MCom or MSc degree, a candidate must have a Bachelor’s degree with Honors with minimum 160 credits.
- However, to be eligible for a two-year MA, MCom, or MSc degree, they need a three year/ six semester Bachelor’s degree with 120 credits.
- Credit Distribution:
- In line with National Education Policy 2020, the framework requires PG programmes to span one or two years.
- One-year PG programmes will contain 40 credits. This can be obtained by doing either course work, research (20 credits each), or both.
- A two-year PG Diploma contains 40 credits, which must be obtained through coursework only.
- Other two-year PG programmes also contain 40 credits. These can be obtained through either coursework, research, or both (20 credits each).
- Flexibility in Switching Subjects in PG:
- The Framework permits graduate students to:
- Pursue a different subject in post-graduation, if they qualify in the entrance examination,
- Apply for a PG programme that was a major or minor in graduate studies.
- Under the Framework, certain students will be eligible for admission in Master in Engineering or a Master of Technology.
- The Framework permits graduate students to:
- Assessment:
- The framework suggests assessments to be continuous as opposed to summative (this includes unit tests and semester-wise exams).
- It also suggests for assessments to be driven by learning outcomes.
- The National Higher Education Qualification Framework (NHEQF) delineates learning outcomes for UG and PG programmes.
- It prescribes criteria for undergraduate students to be eligible for various types of PG programmes.
-
High-Level Committee Constituted to Suggest Reforms in Examination Process
- The Department of Higher Education, under the Ministry of Education, has constituted a high-level Committee to ensure transparent, smooth and fair conduct of examinations.
- The committee will be chaired by Dr. K. Radhakrishnan, Chairman of the Board of Governors, IIT Kanpur, and the former Chairman of ISRO.
- The committee will make recommendations on:
- Reforming the mechanism of the examination process
- Improvements in data security protocols
- Structure and functioning of the National Testing Agency.
Environment
Cabinet Approves Viability Gap Funding for Offshore Wind Energy Projects
- The Union Cabinet has approved a scheme to provide for viability gap funding to offshore wind energy projects.
- Offshore wind energy refers to generation of electricity through wind turbines installed in the water bodies, usually at sea.
- Viability gap funding refers to financial support for projects that may be economically justified but fall short of financial viability.
- The scheme will support installation of a total of one gigawatt capacity, comprising 500 MW each off the coast of Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
- These two projects are estimated to generate 3.7 billion units of electricity annually.