World’s Population Touches 8 Billion
For Prelims: United Nations Population Fund (UNPFA), Mortality Rate, Fertility Rate, Population Growth Rate, Global Population, Replacement-level Fertility
For Mains: Population Distribution, Estimates, Projections and Way Forward
Why in News?
According to the United Nations Population Fund (UNPFA), the human population across the globe touched 8 billion.
- As of 2022, more than half the world’s population lives in Asia, China and India being the two most populous countries with more than 1.4 billion people each.
What are the Trends of Population Growth?
- Overall Decrease in Population Growth Rate:
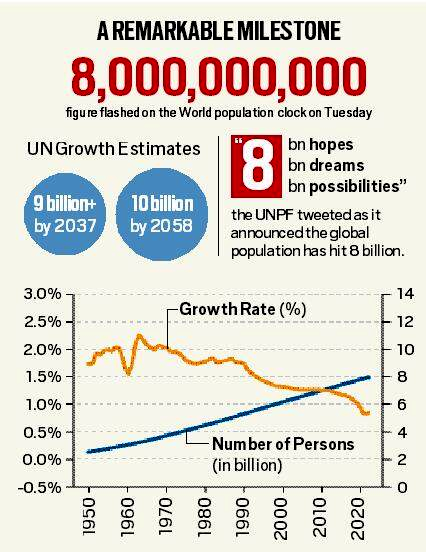
- According to UN, it took the global population 12 years to grow from 7 billion to 8 billion, it will take approximately 15 years until 2037, for it to reach 9 billion.
- This indicates that overall growth rate of global population is slowing.
- The UN population report said the global population is growing at its slowest rate since 1950, having fallen under 1% in 2020.
- The world’s population could grow to around 8.5 billion in 2030 and 9.7 billion in 2050.
- It is projected to reach a peak of around 10.4 billion people during the 2080s and to remain at that level until 2100.
- According to the UN, 60% of the global population lives in a region where the fertility rate is below replacement level.
- In 1990, 40% lived in a region where fertility rate was below replacement level.
- According to UN, it took the global population 12 years to grow from 7 billion to 8 billion, it will take approximately 15 years until 2037, for it to reach 9 billion.
- High-Fertility Levels in Poor Countries:
- Countries with the highest fertility levels tend to be those with the lowest income per capita.
- More than half of the projected increase in the global population up to 2050 will be concentrated in eight countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines and the United Republic of Tanzania.
- Countries of sub-Saharan Africa are expected to contribute more than half of the increase anticipated through 2050.
- International Migration:
- International migration is now the driver of growth in many countries, with 281 million people living outside their country of birth in 2020.
- All South Asian nations including India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka have seen high levels of emigration in recent years.
What are the Findings about India’s Population?
- Stabilising Population Growth:
- According to UN, India’s fertility rate has hit 2.1 births per woman i.e., replacement-level fertility and is further declining.
- While India’s population growth is stabilising, it is “still growing at 0.7% per year” and is set to surpass China in 2023 as the world’s most populous country.
- According to UN, China's population is no longer growing and may start declining as early as 2023.
- The World Population Prospects 2022, put India’s population estimate at 1.412 billion in 2022, compared with China’s 1.426 billion.
- India is likely to peak at 1.7 billion population in 2048 and then start declining to 1.1 billion at the end of century.
- World’s Largest Adolescent Population:
- According to UNFPA estimates, 68% of India’s population is between 15-64 years old in 2022, while people aged 65 and above comprise 7% of the population.
- Over 27% of the country’s population is between the age of 15-29.
- At 253 million, India is also home to the world’s largest adolescent population (10-19 years).
- India has its largest ever adolescent and youth population.
- India will continue to have one of the youngest populations in the world till 2030 and is currently experiencing a demographic window of opportunity, a “youth bulge” that will last till 2025.
- According to UNFPA estimates, 68% of India’s population is between 15-64 years old in 2022, while people aged 65 and above comprise 7% of the population.
What is the United Nations Population Fund?
- About:
- It is a subsidiary organ of the UN General Assembly and works as a sexual and reproductive health agency.
- The UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) establishes its mandate.
- Establishment:
- It was established as a trust fund in 1967 and began operations in 1969.
- In 1987, it was officially renamed the United Nations Population Fund but the original abbreviation, ‘UNFPA’ for the United Nations Fund for Population Activities was retained.
- Objective:
- UNFPA works directly to tackle Sustainable Development Goals on health (SDG3), education (SDG4) and gender equality (SDG5).
- Funding:
- UNFPA is not supported by the UN budget, instead, it is entirely supported by voluntary contributions of donor governments, intergovernmental organizations, the private sector, foundations and individuals.
Way Forward
- To maximize the potential benefits of a favourable age distribution, countries need to invest in the further development of their human capital by ensuring access to health care and quality education at all ages and by promoting opportunities for productive employment and decent work.
- India is at a stage of demographic transition where mortality rates are declining and fertility rates would decline in the next two to three decades or so. India can now focus on eliminating the need for contraception.
- Women can decide if they want to have children, and if yes, when, how many, and at what intervals.
- For young and adolescent populations, there is a need for skilling, which is the only way to ensure they are more productive and have better incomes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which two countries follow China and India in the decreasing order of their populations? (2008)
(a) Brazil and USA
(b) USA and Indonesia
(c) Canada and Malaysia
(d) Russia and Nigeria
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The 5 most populous countries in descending order are China, India, USA, Indonesia and Brazil.
- Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Mains
Q1. Discuss the main objectives of Population Education and point out the measures to achieve them in India in detail. (2021)
Q2. ‘’Empowering women is the key to control the population growth.’’ Discuss. (2019)