Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana
For Prelims: Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY), Blue Revolution , Kisan Credit Card
For Mains: Fisheries sector in India, Steps Taken to Improve the Fisheries Sector in India
Why in News?
As Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) enters its 4th year of implementation, the Department of Fisheries plans to expedite the pace of implementation of the scheme.
- As part of this plan, the Department has scheduled a series of review meetings with states and Union Territories (UTs). The first review meeting recently took place in the Northeastern Region (NER) of India.
What is PMSSY?
- About:
- It aims to bring about the Blue Revolution through sustainable and responsible development of the fisheries sector in India.
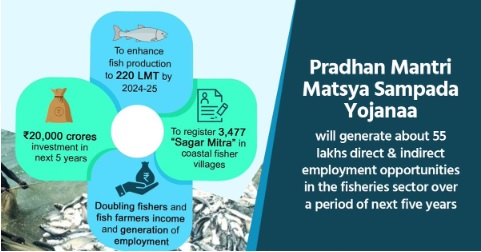
- PMMSY was introduced as part of the ‘Atma Nirbhar Bharat’ package with an investment of Rs. 20,050 crores, the highest-ever investment in this sector.
- The scheme is being implemented in all States and UTs for a period of 5 years from FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25.
- In order to facilitate access to institutional credit, fishermen are provided with insurance coverage, financial assistance and a facility of Kisan Credit Card (KCC) as well.
- Implementation:
- It is implemented as an umbrella scheme with two separate components namely:
- Central Sector Scheme: The project cost will be borne by the Central government.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: All the sub-components/activities will be implemented by the States/UTs, and the cost will be shared between the Centre and State.
- It is implemented as an umbrella scheme with two separate components namely:
- Objectives:
- Harness the potential of the fisheries sector in a sustainable, responsible, inclusive and equitable manner
- Enhance fish production and productivity through expansion, intensification, diversification and productive utilisation of land and water
- Modernise and strengthen the value chain including post-harvest management and quality improvement
- Double fishers' and fish farmers’ incomes and generate meaningful employment
- Enhance the contribution of the fisheries sector to agricultural Gross Value Added (GVA) and exports
- Ensure social, physical and economic security for fishers and fish farmers
- Build a robust fisheries management and regulatory framework
- Significance:
- The fisheries sector plays an important role in the Indian economy. It contributes to national income, exports, food and nutritional security as well as employment generation.
- The sector provides a livelihood for more than 2.8 crore fishers and fish farmers at the primary level and several more along the fisheries value chain.
- It is a major source of income for a large proportion of the country's economically disadvantaged population.
- To improve fish production, it is important to conduct integrated fish farming and diversify fish production.
- Further, the fisheries sector has been a major contributor to foreign exchange earnings, with India being one of the world's leading seafood exporters.
- In FY20, aquaculture products accounted for 70–75% of the country's total fishery exports.
- The fisheries sector plays an important role in the Indian economy. It contributes to national income, exports, food and nutritional security as well as employment generation.
- Achievements:
- As of 2023, under PMMSY, projects worth Rs 14,654.67 crore have been approved from 2020-21 to 2022-23.
- As the 3rd largest fish producer and the 2nd largest aquaculture producer globally, India recognizes the significance of the fisheries and aquaculture industry.
- The fish production reached an all-time high of 16.25 MMT during FY 2021-22 with marine exports touching Rs. 57,586 Crores.
Note:
- Aquaculture refers to the breeding, rearing, and harvesting of fish, shellfish, algae, and other organisms living in all types of water environments whereas Pisciculture refers to the breeding, rearing, and transplantation of fish by artificial means.
What are the Challenges in Implementation of the Scheme?
- Infrastructural and Technological Gap:
- The fisheries sector faces a lack of adequate infrastructure and technology for fish production, processing, storage, transportation and marketing.
- Lack of Human Resource Development:
- Lack of skilled and trained manpower and extension services for fish farmers and fishermen affects the adoption of best practices, innovations and standards in the sector.
- Financial Inclusion and Social Protection:
- Inadequate access to timely credit and insurance for fish farmers and fishermen exposes them to various risks and vulnerabilities such as natural disasters, diseases, market fluctuations, etc.
- Regulatory and Legal Compliance:
- The fisheries sector faces a lack of awareness and compliance with the regulatory and legal framework for fisheries management such as fishing rights, licenses, quotas, conservation measures, quality control, traceability, etc. This affects the sustainability and competitiveness of the sector.
What are the Other Initiatives Related to Fisheries Sector?
What is the Blue Revolution?
- About:
- The Blue Revolution, with its multi-dimensional activities, focuses mainly on increasing fisheries production and productivity from aquaculture and fisheries resources, both inland and marine.
- Objectives:
- To increase overall fish production in a responsible and sustainable manner for economic prosperity
- To modernise the fisheries with a special focus on new technologies
- To ensure food and nutritional security
- To generate employment and export earnings
- To ensure inclusive development and empower fishers and aquaculture farmers
What is the Kisan Credit Card Scheme?
- About:
- The scheme was introduced in 1998 for providing adequate and timely credit support from the banking system, under a single window with flexible and simplified procedures to farmers for their cultivation and other needs like the purchase of agriculture inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides etc. and draw cash for their production needs.
- The scheme was further extended for the investment credit requirement of farmers viz. allied and non-farm activities in the year 2004.
- In the Budget-2018-19, the government announced the extension of the facility of KCC to fisheries and animal husbandry farmers to help them to meet their working capital needs.
- The scheme was introduced in 1998 for providing adequate and timely credit support from the banking system, under a single window with flexible and simplified procedures to farmers for their cultivation and other needs like the purchase of agriculture inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides etc. and draw cash for their production needs.
- Implementing Agencies:
- Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Small Finance Banks
- Cooperatives
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for which of the following purposes? (2020)
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets
- Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini trucks
- Consumption requirements of farm households
- Post-harvest expenses
- Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Explain various types of revolutions, took place in Agriculture after Independence in India. How have these revolutions helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India? (2017)
Q. Defining blue revolution, explain the problems and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (2018)