Madhya Pradesh Public Service Commission (MPPCS) GK
Last Updated: May 2024
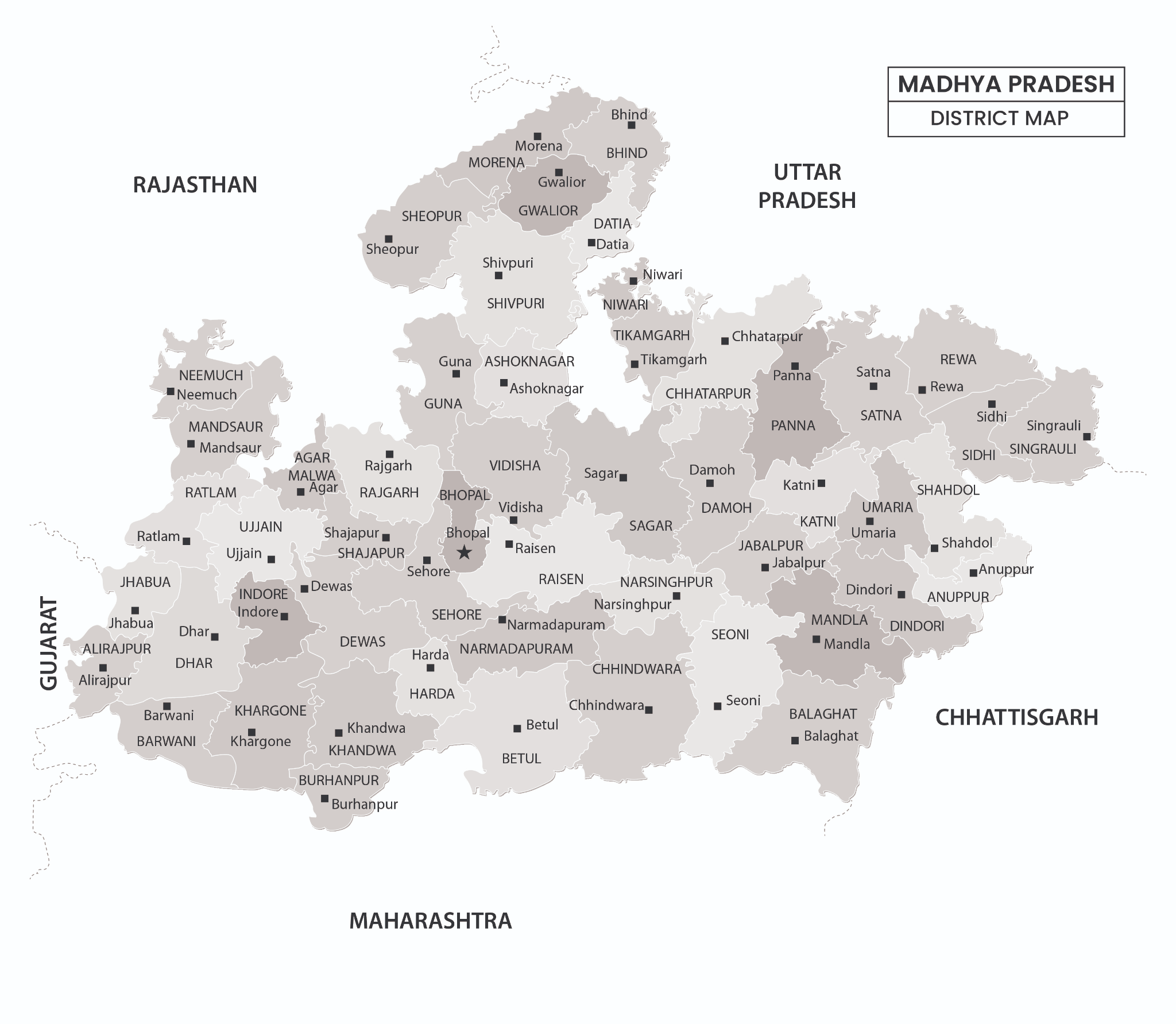
Madhya Pradesh GK
| Formation | 1st november, 1956 |
| Capital | Bhopal |
| Population | 7,26,26,809 |
| Region | 3,08,252 sq. km. |
| Population density in state | 236 persons per sq.km. |
| Total Districts | 55 Districts |
| Other Name of State | Hriday Pradesh, Soya State, Tiger State, Leopard State |
| High Court | Jabalpur (Bench – Indore, Gwalior) |
| State Symbol |
|||
| State Animal: Barahsingha (reindeer) |
 |
State Flower: White Lily |
 |
| State Bird: Dudhraj (Shah Bulbul) |
 |
State Dance: Rai |
 |
| State Tree: Banyan |  |
Official Game: Malkhamb |
 |
Madhya Pradesh : General Information
- State – Madhya Pradesh
- Constitution – 01 November, 1956 (Present Form – 1 November 2000)
- Area – 3,08,252 sq. km.
- Population – 7,26,26,809
- Capital – Bhopal
- Total District – 55
- No. of Divisions – 10
- Block – 313
- Tehsil (March 2024) – 428
- The largest tehsil (area) of the state – Indore
- The smallest tehsil (area) of the state – Ajaygarh (Panna)
- Town/city – 476
- Municipal Corporation (2018-19) – 16
- Municipality – 99
- City Council – 294
- Total Village – 54903
- Zilla Panchayat – 51
- Gram Panchayat – 23066
- Tribal Development Block – 89
- State Symbol – A circle inside the 24 stupa shape, in which there are earrings of wheat and paddy.
- State River – Narmada
- State Theater – Mach
- Official Anthem – Mera Madhya Pradesh Hai (Composer – Mahesh Srivastava)
- State fish – Mahseer (announced in 2013)
- State Crop – Soybean
- Official language – Hindi
- State legislature – Unicameral (assembly)
- Number of Assembly Members – 231 [230 + 1 Anglo-Indian Member]
- Number of seats reserved for Scheduled Castes in the Legislative Assembly – 35
- Number of seats reserved for Scheduled Tribes in the Legislative Assembly – 47
- Number of members in Lok Sabha – 29
- Lok Sabha seats reserved for Scheduled Castes – 4
- Lok Sabha seats reserved for Scheduled Tribes – 6
- Seats for Rajya Sabha – 11
Census
- Male Population – 3,76,12,306
- Female Population – 3,50,14, 03
- Rural Population – 5,25,57,404
- Rural Male – 2,71,49,388
- Rural Female – 2,54,08,016
- Urban population – 200,69,405
- Urban Male – 1,04,62,918
- Urban Women – 96,06,487
- Madhya Pradesh's place in the country in terms of area – Second
- Most malnourished district – Sheopur
- Least malnourished district – Bhopal
- The population density of the state of Madhya Pradesh is – 236 sq. km.
- District with highest population density – Bhopal (855 persons per sq. km.)
- The district with the lowest population density – Dindori (94 persons per sq. km.)
- Largest division in terms of area – Jabalpur
- The smallest division in terms of area – Narmadapuram (Hoshangabad)
- Most densely populated division – Indore
- Most sparsely populated division – Shahdol
- Largest district in terms of area – Chhindwara
- Smallest district in terms of area – Niwari
- Largest district in terms of population – Indore
- Smallest district in terms of population – Harda
- District with highest sex ratio in the state – Balaghat (1021)
- The district with the lowest sex ratio in the state – Bhind (837)
- Literacy rate in Madhya Pradesh – 69.3 percent
- Male Literacy – 78.7 percent
- Female literacy – 59.2 percent
- Most Literate Division – Jabalpur
- Least Literate Division – Indore
- Most literate district of the state – Jabalpur (81.01%)
- Least literate district in the state – Alirajpur (36.1%)
- District with highest male literacy – Indore
- District with highest female literacy – Bhopal
- The largest tribe of the state – Bhil
Geographical and Other Features of the State
- Geographical location of the state – 21° 6' to 26° 30' North Latitude and 74° 9' to 82° 48' East Longitude
- Length from North to South – 605 km.
- Width from East to West – 870 km.
- States bordering the state – 5, [U.P. (North-East), Maharashtra (South-West), Chhattisgarh (South-East), Rajasthan (North-West) and Gujarat (West)]
- State meeting the maximum limit of the state – Uttar Pradesh
- State meeting the minimum limit of the state – Gujarat
- The line passing through the middle of the state – Tropic of Cancer (passes through 14 districts.)
- Percentage of Madhya Pradesh in the total area of India – 9.38%
- Highest point of the state – Dhupgarh hill (located in Mahadev hill)
- Lowest place in the state – Narmada–Son Valley
- Hottest place – Khajuraho
- Coldest place – Shivpuri
- The largest river of the state – Narmada river (1312 km.)
| Districts Bordering Neighbouring States | ||
| Border states | Numbers | Districts |
| Uttar Pradesh | 14 | Bhind, Tikamgarh, Chhatarpur, Panna, Satna, Rewa, Sidhi, Datia, Shivpuri, Sagar, Singrauli, Ashoknagar, Morena, Niwari |
| Chhattisgarh | 6 | Sidhi, Shahdol, Dindori, Balaghat, Singrauli, Anuppur |
| Rajasthan | 10 | Morena, Shivpuri, Guna, Rajgarh, Neemuch, Mandsaur, Ratlam, Jhabua, Sheopur, Agar Malwa |
| Gujarat | 2 | Jhabua, Alirajpur |
| Maharashtra | 9 | Alirajpur, Barwani, Khargone, Khandwa, Burhanpur, Betul, Chhindwara, Seoni, Balaghat |
| States and their districts bordering Madhya Pradesh |
|
| Border states | Border districts |
| Uttar Pradesh (11 Districts) | Agra, Etawah, Jalaun, Jhansi, Lalitpur, Banda, Mirzapur, Allahabad (Prayagraj), Mahoba, Sonbhadra, Chitrakoot |
| Rajasthan (10 Districts) | Pratapgarh, Banswara, Baran, Jhalawar, Sawai– Madhopur, Kota, Dholpur, Chittorgarh, Bhilwara, Karauli |
| Maharashtra (8 Districts) | Dhule, Nagpur, Amravati, Bhandara, Buldhana, Gondia, Nandurbar, Jalgaon |
| Chhattisgarh (7 Districts) | Rajnandgaon, Kabirdham, Bilaspur, Mungeli, Surajpur, Korea, Balrampur |
| Gujarat (2 Districts) | Dahod, Vadodara |
| Major Waterfalls of Madhya Pradesh |
|
| Waterfalls | Location (river) |
| Kapil dhara Waterfall | Amarkantak, Anuppur (Narmada River) |
| Dugdha dhara Waterfall | Amarkantak, Anuppur (Narmada River) |
| Dhuandhar Waterfall | Bhedaghat, Jabalpur (Narmada River) |
| Sahastradhara Waterfall | Maheshwar (Narmada River) |
| Mandhar Waterfall | Khandwa (Narmada River) |
| Dardi Waterfall | Khandwa (Narmada River) |
| Bhalkund Waterfall | Sagar (Bina River) |
| Patalpani Waterfall | Indore (Chambal River) |
| Jhadidaha Waterfall | Indore (Chambal River) |
| Chuliya Waterfall | Mandsaur (Chambal River) |
| Rahatgarh Waterfall | Sagar (Chambal River) |
| keoti Waterfall | Rewa (Mahana River) |
| Chachai Waterfall | Rewa (Beehad River) |
| Bahuti Waterfall | Sailor River (Rewa) |
| Pandava Waterfall | Panna (Ken River) |
| Apsara Waterfall | Pachmarhi |
| Silver Fall | Pachmarhi |
| Duchess Fall | Pachmarhi |
| Bea Fall | Pachmarhi |
| Note: At present the highest waterfall of Madhya Pradesh is Bahuti Falls, which is located in Rewa district. Its height is 198 meters (650 ft). Whereas before this, Chachai Falls was the highest waterfall in Madhya Pradesh, whose height is 130 meters. | |
| Major Cities Situated on the Banks of Rivers |
|
| River | Town |
| Narmada | Omkareshwar, Amarkantak, Hoshangabad, Jabalpur, Maheshwar |
| Chambal | Sheopur, Mhow, Ratlam, Morena |
| Tapti | Multai, Burhanpur |
| Betwa | Orchha, Sanchi, Vidisha, Guna |
| Parvati | Shajapur, Ashta, Rajgarh |
| Sindh | Shivpuri, Datia |
| Kali sindh | Bagli, Dewas, Sonkachh |
| Kshipra | Ujjain |
| Khaan | Indore |
| Mahi | Kukshi, Dhar |
First in State
- First Governor – Dr. B. Pattabhi Sitaramayya
- First Woman Governor – Ms. Sarla Grewal
- First Chief Minister – Pt. Ravi Shankar Shukla
- First Woman Chief Minister – Ms. Uma Bharti
- First Speaker of the Legislative Assembly – Pt. Kunjilal Dubey
- First Deputy Speaker of the Legislative Assembly – Vishnu Vinayak Sarwate
- First Leader of Opposition – Shri Vishnunath Yadavrao Tamaskar
- First Chief Justice of High Court – Mohammad Hidayatullah
- First Lady Judge – Smt. Sarojini Saxena
- First Chief Secretary – Shri H.S. Kamath
- First Election Commissioner – N.B. Lohani
- First Lokayukta – P.V. Dixit
- First State Information Commissioner – T.N. Srivastava
- Chairman of the first Finance Commission – Dr. Sawai Singh Sisodia
- First Woman Leader of Opposition – Jamuna Devi
- The first Nobel Peace Prize recipient – Kailash Satyarthi
- State's first nuclear power station – Chutka village (Mandla)
- State's first I.T. Park – Bhopal
- State's first international airport terminal – Bhopal
- State's first agricultural university – Jabalpur
- State's first university – Dr. Harisingh Gour University, Sagar (1946)
- The first ISO certified SP Office – Dewas
- State's first national park – Kanha Kisli
- State's first dry port – Pithampur
- State's first open jail – Navjeevan Ashram (Hoshangabad)
- State's first Information Technology (IT) University – Gwalior
- State's first DNA laboratory – Sagar
- Herbal bank of the state – Panar water (Pachmarhi)
First in India
- The largest mosque in the country – Taj-ul-Masjid (Bhopal)
- First establishment of optical fiber in the country – Mandideep (Bhopal)
- India's first state to produce diamond in the country – Madhya Pradesh
- Country's first microchip factory – Bhopal
- State to set up India's first Malkhamb Academy – Ujjain
- State to set up country's first cow sanctuary – Agar Malwa
- Country's largest soybean producing state – Madhya Pradesh
- State to establish country's only human museum – Bhopal
- First state on the basis of Scheduled Tribe population in the country – Madhya Pradesh
- The first state in the country to do complete nationalization of forests – Madhya Pradesh
- Asia's first physical education university – Gwalior (Lakshmibai National Institute/University of Physical Education)
- Sanctuary for Babbar lion – Palpur-Kuno Wildlife Sanctuary
- The first marble building in India – Hoshang Shah's Tomb, Dhar
Transport and Communication
- Longest National Highway – NH–46
- Shortest National Highway – NH–135BB
- State's largest railway junction – Itarsi
| Road Transport (August, 2023) | |
| Total district roads | 22,691 kms |
| Total Rural roads | 28,023 kms |
| Historical Forts of Madhya Pradesh |
||
| Name/Place | Construction Period | Constructed By |
| Gwalior Fort (Gwalior) | 8th century | Raja Surajsen |
| Chanderi Fort (Ashoknagar) | 11th century | Pratihara king Kirtipal |
| Ginnorgarh Fort (Raisen) | 13th century | Maharaj Uday Varman |
| Asirgarh Fort (Burhanpur) | 14th century | Asa (Ahir King) |
| Dhar Fort (Dhar) | 1344 A.D century | Mohammed bin Tughlaq |
| Bandhavgarh Fort (Umariya) | 14th century | Kings of Baghelkhand |
| Mandsaur Fort (Mandsaur) | 14th century | Alauddin Khilji |
| Narwar Fort (Shivpuri) | 14th century | King Nal |
| Raisen Fort (Raisen) | 16th century | Raja Rajbasanti |
| Mandala Fort (Mandala) | 16th century | Raja Narendra Shah |
| Garh Kundar Fort (Teekamgarh) | 16th century | Kate Singh |
| Orchha Fort (Niwari) | 17th century | Raja Veer Singh Bundela |
| Ajaygarh Fort (Panna) | 18th century | Raja Ajaypal |
| Major Palaces of Madhya Pradesh |
|
| Palace Name | Location |
| Dayi Palace | Mandu (Dhar) |
| Asharfi Palace | Mandu (Dhar) |
| Rani Roopmati Palace | Mandu (Dhar) |
| Ship palace | Mandu (Dhar) |
| Hindola (carousel) palace | Mandu (Dhar) |
| Kharbuja (cantaloupe) palace | Mandu (Dhar) |
| Chappan Mahal | Mandu (Dhar) |
| Andhra (blind) palace | Mandu (Dhar) |
| Gujari palace | Gwalior |
| Jai Vilas palace | Gwalior |
| Karna palace | Gwalior |
| Vikram palace | Gwalior |
| Chanderi palace | Chanderi (Ashoknagar) |
| Rajmahal | Ashoknagar |
| Badal palace | Gwalior |
| Raja Rohit palace | Raisen |
| Itradar palace | Raisen |
| Kaliyadeh palace | Ujjain |
| Madan palace | Jabalpur |
| Satkhanda palace | Datiya |
| Raja Aman palace | Ajaygarh (panna) |
| Jahangir palace | Orchha (Niwari)/Gwalior |
| Moti palace | Dindori/Burhanpur |
| Shaukat palace | Bhopal |
| Tarabai palace | Shajapur |
| Sheesh palace | Neemuch/Tikamgarh |
| Dhubela palace | Chhatarpur |
| Festivals | Location |
| Kalidasa Ceremony | Ujjain |
| Khajuraho Dance Festival | Khajuraho |
| Tansen Ceremony | Gwalior |
| Malwa Festival | Indore, Ujjain, Mandu |
| Orchha Festival | Tikamgarh |
| Tulsi Ceremony | Chitrakoot (Satna) |
| Muktibodh Ceremony | Bhind |
| Major Irrigation Projects of Madhya Pradesh |
|||
| Project Name | River | Beneficiary Districts | Special Note |
| Chambal Project | Chambal | Neemuch, Mandsaur, Bhind, Morena, Gwalior, Sheopur | This is the first project of the state and joint multipurpose project of Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan. |
| Rani Avantibai Sagar (Bargi Project) | Narmada | Jabalpur, Seoni Mandla | The Bargi Dam constructed under this project is the first dam constructed on the Narmada River. |
| Tawa Project | Narmada | Hoshangabad | Under the Tawa project, a dam has been built in Ranipur village of Hoshangabad district. |
| Indira Sagar Project | Narmada | Khandwa | This is the biggest project in Madhya Pradesh, which has the highest water storage capacity in India. |
| Omkareshwar Project | Narmada | Khandwa, Khargone, Dhar | This project is 40 km from Indira Sagar Project near Mandhata village of Khandwa district. |
| Maheshwar Project | Narmada | Khargone | Maheshwar Project is an important part of Narmada Valley Project located in Khargone. |
| Man Project | Man | Dhar | The tribal dominated tehsils Manawar, Kukshi and Gandhwani of Dhar district will be benefited by this project. |
| Jobat Project | Hathni | Jhabua | It is also called Shaheed Chandrashekhar Azad Sagar Project. |
| Sardar Sarovar Project | Narmada | — | The states of Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Maharashtra are included in this project. |
| Pench Project | Pench | Chhindwara, Balaghat | It is a joint project of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra. |
| Thavar Project | Wainganga | Mandala | The project is situated on Wainganga, a tributary of the Godavari. |
| Urmil Project | Urmil River | Chhatarpur | It is an interstate project of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. |
| Matatila Dam/Rajghat | Betwa | Madhya Pradesh and parts of Uttar Pradesh |
It is an interstate project of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. |
| Bansagar Project | Son | Rewa, Sidhi, Satna, Shahdol | It is a joint project of Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. |
| Ken-Betwa Project | Ken-Betwa | Chhatarpur, Panna, Tikamgarh and other major districts of Bundelkhand (Total 9 districts). | It is a joint project of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. |
| Choral Project | Choral | Indore | This is an inter valley project. |
| Halali Project | Halali River | Vidisha, Raisen | This project is also known as Samrat Ashok Sagar Project. |
Forest/Wildlife/National Park
| Recorded forest area of Madhya Pradesh according to State Forest Report, 2019 | |
| Recorded Forest Area | Area (sq.km.) |
| Reserved area | 61,886 (65.36%) |
| Protected area | 31,098 (32.84%) |
| Unclassified area | 1,705 (1.80%) |
| Total | 94,689 |
| District wise Forest Cover of Madhya Pradesh (ISFR-2019) |
||
| On the basis of percentage of geographical area | Highest | Balaghat (53.44%), Sheopur (52.38%), Umaria (49.62%), Mandla (44.44%) |
| Lowest | Ujjain (0.59%), Shajapur (1.02%), Ratlam (1.23%), Bhind (2.39%) | |
| Area-wise (in sq. km) | Highest | Balaghat (4932.06), Chhindwara (4588.01), Betul (3663.70), Sheopur (3460) |
| Lowest | Ujjain (36.22), Ratlam (59.85), Shajapur (63.35), Bhind (106.75) | |
| Protected Area for Specific Animals/Birds |
||
| Animals/Birds | Area | Location |
| Alligator/Crocodile | Chambal National Sanctuary | Morena |
| Son River Sanctuary | Sidhi | |
| Ken River Sanctuary | Chhatarpur | |
| Asian paradise flycatcher (State Bird) | Sailana Sanctuary | Ratlam |
| Lesser florican Bird | Sailana Sanctuary | Ratlam |
| Sardarpur Sanctuary | Dhar | |
| Great Indian Bustard | Ghatigaon Sanctuary | Gwalior |
| Karera Sanctuary | Shivpuri | |
| Asiatic Lion | Kuno Palpur Sanctuary (Kuno National Park) | Sheopur |
| National Parks and Sanctuaries included in Project Tiger |
||
| National Park / Sanctuary | District | Year |
| Kanha kisli | Mandala–Balaghat | 1973–74 |
| Pench | Seoni–chhindwara | 1992–93 |
| Bandhavgarh | Umariya | 1993–94 |
| Panna | Panna–Chhatarpur | 1993–94 |
| Satpura | Narmadapuram | 1999–2000 |
| Sanjay Dubari | Sidhi | 2008–09 |
| Ratapani | Raisen–Sehore | 2013 (in some sources 2012) |
| Biosphere Reserve area of Madhya Pradesh | |
| Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve | Pachmarhi, Narmadapuram (March 1999) |
| Achanakmar – Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve | Amarkantak, Anuppur (March 2005) |
| Panna Biosphere Reserve | Panna (August 2011) |
| National Park of Madhya Pradesh |
|||
| Name | Districts | Area (Square Kms.) | Established |
| Kanha–Kisli | Mandala–Balaghat | 940 | 1955 |
| Madhav | Shivpuri | 354.61 | 1958 |
| Bandhavgarh | Umariya | 448.842 | 1968 |
| Panna | Panna and Chhatarpur | 576 | 1975 |
| Sanjay | Sidhi | 467 | 1975 |
| Satpura | Hoshangabad | 524 | 1981 |
| Pench | Seoni–chhindwara | 293 | 1983 |
| Ghughua/ Ghughua fossil (fossil) | Dindori | 0.270 | 1983 |
| Van Vihar | Bhopal | 4.43 | 1983 |
| Dinosaur fossil | Dhar | 0.8974 | 2010 |
| Kuno | Sheopur | 404 | 2018 |
| Major Sanctuaries of Madhya Pradesh |
||
| Name | District | Major Wild Animal |
| Narsinghgarh | Rajgarh | Peacock, Leopard, Sambar, Chital, Wild Boar |
| Gandhisagar | Mandsaur/Neemuch | Nilgai, Leopard, Chital, Chinkara, Waterfowl |
| Bori | Narmadapuram | Lion, Leopard, Sambar, Chital, Gaur, Deer, Wild Boar |
| Pachmarhi | Narmadapuram | Lion, Leopard, Chital, Sambar, Gaur, Nilgai, Deer, Chinkara |
| Dubari (Sanjay) | Sidhi | Lion, Leopard, Chital, Nilgai, Sambar, Chinkara |
| Ratapani | Raisen/Sehore | Lion, Sambar, Leopard, Chital, Nilgai, Langur |
| Singhori | Raisen | Leopard, Lion, Sambar, Chital, Nilgai |
| Nauradehi (Largest) | Sagar | Lion, Leopard, Chital, Sambar, Gaur, Nilgai, Wild Dog |
| Pench (Mogali) | Seoni | Lion, Black antelope, Leopard, Sambar, Chital, Gaur |
| Chambal | Muraina | Alligator, Crocodile, Turtle, Beaver, Dolphin |
| Ken (Ghadiyal) | Chhatarpur/Panna | Alligator, Crocodile |
| Son (Ghadiyal) | Sidhi | Alligator, Crocodile, Tortoise, Migratory Birds |
| Karaira | Shivpuri | Sambar, Chital, Nilgai, Golden bird |
| Ghatigaon | Gwalior | Chinkara, Sambar, Nilgai, Golden bird |
| Bagdara | Sidhi | Leopard, Chital, Sambar, Nilgai |
| Pen | Mandala | Lion, Leopard, Chital, Sambar |
| Panpatha | Umaria / Shahdol | Lion, Leopard, Chital, Sambar, Nilgai, Chausinga, Deer |
| Sardarpur | Dhar | Kharmor Bird |
| Sailana | Ratlam | Kharmor Bird, Dudhraj |
| Gangau | Panna/Chhatarpur | Leopard, Wild Boar, Sambar, Chital, Nilgai, Chinkara |
| Ralamandal (Smallest) | Indore | Tiger, Leopard, Chital, Sambar, Gaur, Bear |
| Veerangana Durgavati | Damoh | Sambar, Nilgai, Krishna Deer, Chital |
| Orchha | Niwari/Tikamgarh | Chital, Nilgai, Peacock |
| Khivni | Dewas/Sehore | Chital, Sambar, Chausinga |
Industry/Minerals/Energy
- Detroit of Madhya Pradesh – Pithampur (Dhar)
- India's first optical fiber factory – Mandideep (Raisen)
- Asia's largest soybean plant – Ujjain
- India's first National Soybean Research Center – Indore
- India's first Gemstone Refining Center – Jabalpur
- State's first special economic zone – Bhopal
- Industrially developed districts of the state – Bhopal, Indore, Jabalpur, Gwalior
- State Mega Food Parks – Khargone and Dewas
- Largest center of automobile industry in the state – Pithampur (Dhar)
- The only watch factory in the state – Betul
- The only umbrella industry in the state – Mhow (Indore)
- Auto Cluster in the State – Pithampur (Dhar)
- State's largest coal deposit area – Sohagpur
- State's first nuclear power station – Chutka village (Mandla)
- World's largest floating solar plant – Omkareshwar
- Bio Energy Park – Rewa
- Copper mines in the state – Malanjkhand
- National Power Training Institute – Shivpuri
- State Mining Corporation Headquarters – Bhopal
- Energy Development Corporation Headquarters – Bhopal
- Uranium reserves in the state – Shahdol
- Energy Capital of Madhya Pradesh– Singrauli