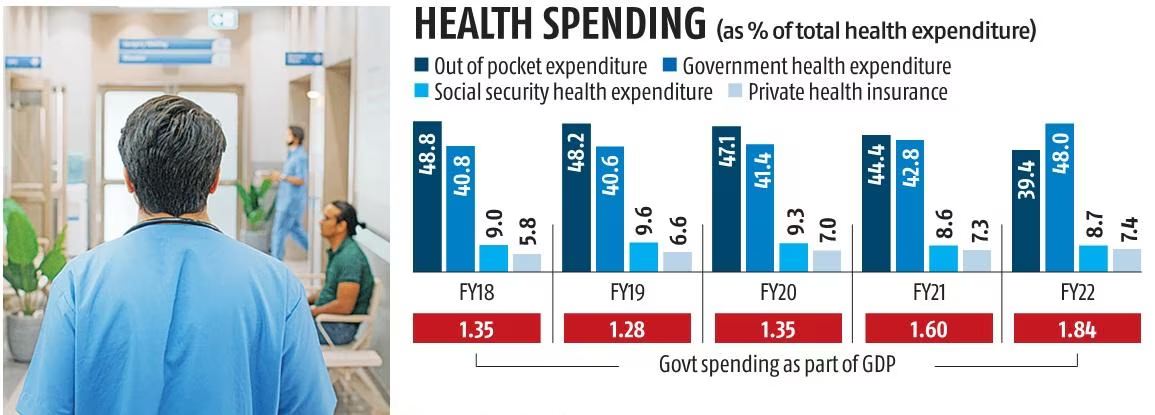
Decline in Out-of-Pocket Health Spending
Recently, the National Health Accounts (NHA) Estimates 2021-22 was released by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare as per which Out-of-pocket expenditure (OOPE) dropped to 39.4% of total health expenditure (THE) in 2021-22, down from 48.8% in 2017-18.
- This aligns with the government's objective to reduce OOPE to 35% of THE by the financial year 2025-26.
- Reasons for Decline in OOPE:
- Increase in the government's share of THE from 40.8% to 48%.
- Initiatives like Ayushman Bharat have facilitated broader access to health coverage.
- Increased private health insurance coverage which grew from 5.8% in 2017-18 to 7.4% in 2021-22.
- Trends in Health Expenditure:
- Social security expenditure for health declined from 9% in 2017-18 to 8.7% in 2021-22.
- Government health expenditure as a percentage of GDP rose from 1.35% in 2017-18 to 1.84% in 2021-22. (Target: 2.5% of GDP by 2025).
- Per capita health expenditure nearly doubled between 2017-18 and 2021-22.
- NHA Estimates is an annual publication that provides estimates of healthcare expenditures in India.
- It explains how money flows in India’s health system, how it’s spent, how healthcare is provided, and the types of services used.
- Based on – ‘A System of Health Accounts (SHA), 2011’ (by WHO).
- Published by – The National Health Systems Resource Centre (NHSRC).