- Filter By :
- Geography
- History
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Indian Society
-
Q. How do geomorphological processes influence the formation and evolution of river systems in India? Illustrate with examples from different river basins. (150 words)
24 Mar, 2025 GS Paper 1 GeographyApproach
- Introduce the answer by briefing about geomorphological processes and their influence on river systems
- Highlight the Role of Geomorphological Processes in River System Formation
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction
Geomorphological processes—such as weathering, erosion, transportation, and deposition—play a fundamental role in shaping river systems. In India, diverse physiographic features (Himalayas, Peninsular Plateau, Coastal Plains) have led to the formation of distinct river basins.
Body
Role of Geomorphological Processes in River System Formation
- Tectonic Activity and River Origin
- Himalayan rivers like the Ganga and Brahmaputra originated due to tectonic uplift and folding of the Himalayas during the Tertiary period.
- Example: The Ganga River flows through a synclinal trough (Ganga Basin), formed due to Himalayan uplift and subsequent subsidence of the foreland basin.
- Himalayan rivers like the Ganga and Brahmaputra originated due to tectonic uplift and folding of the Himalayas during the Tertiary period.
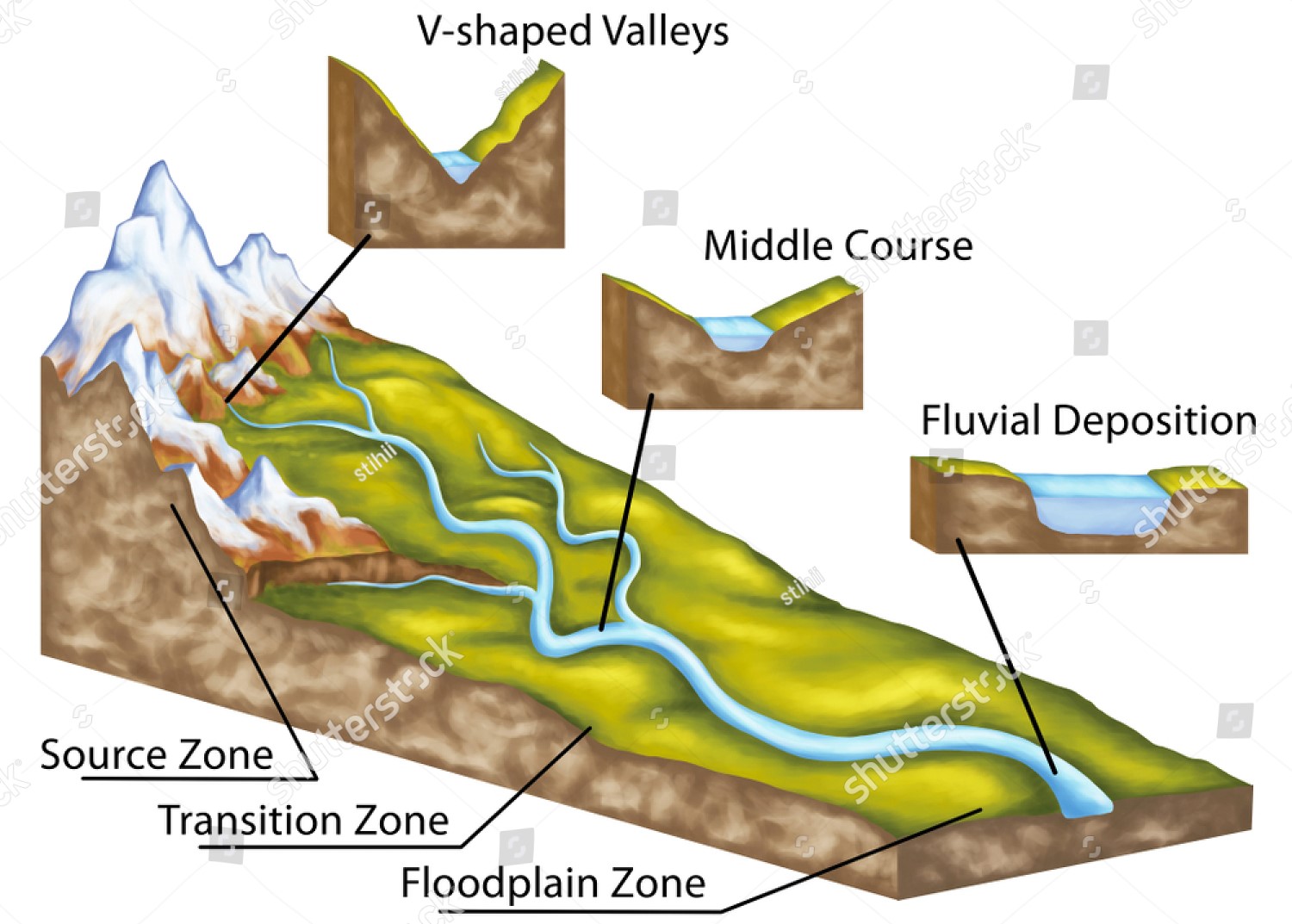
- Erosion and Valley Formation
- Vertical and lateral erosion shapes valleys and floodplains. In the Yamuna Basin, upper reaches in the Himalayas show V-shaped valleys due to active downcutting.
- In contrast, the Godavari and Krishna rivers in Peninsular India form broad U-shaped valleys, shaped over time by denudational processes on stable landmasses.
- Vertical and lateral erosion shapes valleys and floodplains. In the Yamuna Basin, upper reaches in the Himalayas show V-shaped valleys due to active downcutting.
- Sediment Deposition and Delta Formation
- Rivers carry eroded materials and deposit them in plains and deltas.
- Example: The Ganga-Brahmaputra Delta, the largest delta in the world, formed by extensive alluvial deposition.
- The Mahanadi Delta shows classic arcuate delta features due to sediment deposition by slower river flow near the coast.
- Rivers carry eroded materials and deposit them in plains and deltas.
- Climate and Fluvial Activity
- Monsoonal rainfall leads to high discharge and sediment load.
- Example: Chambal River Basin in semi-arid regions shows badland topography due to rain wash and gully erosion.
- Monsoonal rainfall leads to high discharge and sediment load.
- Sea-Level Changes and Coastal Processes
- Changes in sea level influence estuary formation.
- Example: Narmada and Tapi rivers, which flow westward into the Arabian Sea, show estuarine mouths due to subsidence near the coast.
- Changes in sea level influence estuary formation.
Conclusion
Geomorphological processes act as dynamic forces shaping the origin, course, and characteristics of river systems across India. From tectonic birth to fluvial deposition, these processes create the physical templates that influence drainage patterns, water availability, soil fertility, and land use planning.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF