-
Q. How can India leverage its demographic dividend while simultaneously addressing the challenges of skill development and employment generation? Discuss with reference to recent government initiatives. (250 words)
19 Nov, 2024 GS Paper 2 Social JusticeApproach
- Introduce the answer by giving a data on demographic dividend
- Give Opportunities of India's Demographic Dividend
- Delve into Challenges in Skill Development and Employment Generation
- Highlight Government Initiatives to Address These Challenges
- Suggest Measures to HarnessDemographic Dividend Along with Skill Development and Employment Generation
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction
India entered its demographic dividend window in 2005-06, which will last until 2055-56. It offers a window of opportunity to accelerate economic growth. However, harnessing this potential requires addressing challenges in skill development and employment generation.
Body
Opportunities of India's Demographic Dividend:
- Young Workforce: India has more than 50% of its population below the age of 25 and more than 65% below the age of 35.
- Economic Impact: According to the World Bank, increasing the average years of schooling by one year can increase a country's GDP growth by 0.37%
- It may also lead to Increased domestic consumption, savings, and productivity in manufacturing and services.
- Global Competitiveness: Availability of cost-effective, skilled labor positions India as a global hub for industries.
Challenges in Skill Development and Employment Generation
- Skill Development Challenges
- Low Formal Training Penetration: Only 4.7% of the workforce receives vocational training (2022).
- Employability Gap: India Skills Report 2024 states that 48.7% of youth lack job-ready skills.
- Only 45% of engineering graduates meet industry standards.
- Access Inequalities:
- Gender Gap: Women’s participation in vocational training remains low (18.6% of women aged 18-59).
- Rural-Urban Divide: Rural areas lack adequate training infrastructure.
- Economic Barriers: High costs of quality training limit access for economically weaker sections.
- Employment Generation Challenges
- Unemployment Statistics: Overall unemployment rate: 8.1% (CMIE, April 2024). Youth unemployment: 23.2%. (World Bank)
- Women’s labor force participation remains underutilized.
- Structural Issues: 90% of the workforce in the informal sector, with low wages and job security.
- Manufacturing sector job creation (contributing mere 14% of GDP)) lags behind workforce growth.
- Quality job creation does not match demographic dividend requirements.
- Regional Disparities: Employment opportunities remain concentrated in urban and industrialized regions.
- Unemployment Statistics: Overall unemployment rate: 8.1% (CMIE, April 2024). Youth unemployment: 23.2%. (World Bank)
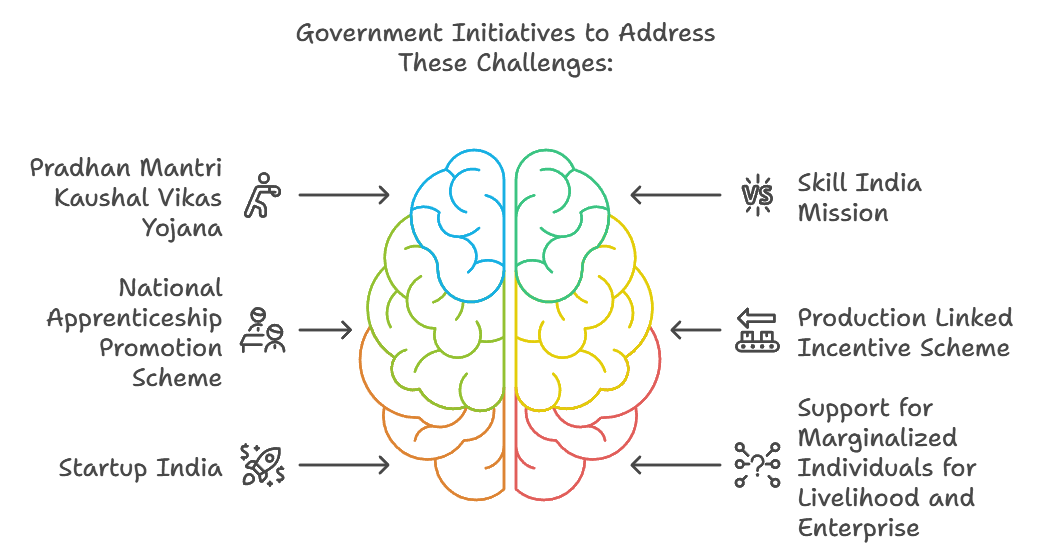
Government Initiatives to Address These Challenges:
Harnessing Demographic Dividend Along with Skill Development and Employment Generation:
- Skilling and Education Reforms: Align Education with Industry Needs:
- Enhance vocational training in schools and higher education.
- Update curricula to include emerging technologies such as AI and robotics.
- Example: NEP 2020's focus on experiential learning and internships.
- Expand Digital and Green Skills Training: Integrate digital literacy and green economy skills to prepare the workforce for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
- Leverage initiatives like the Skill India Digital Platform and NASSCOM FutureSkills.
- Boost Formal Sector Opportunities: Promote formalization of the workforce through ease of doing business reforms and tax incentives for formal job creation.
- Encourage employers to integrate more apprentices under the National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS).
- Enhance MSME Growth: Strengthen financial and logistical support for MSMEs, which employ 62% of the workforce.
- Expand credit guarantee schemes and provide skill-based subsidies.
- Promote Sector-Specific Growth: Focus on high-growth sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, renewable energy, and digital services.
- PLI Schemes should include more labor-intensive sectors to boost job creation.
- Rural Entrepreneurship: Promote agro-based and handicraft enterprises in rural areas through cluster-based development.
- Establish rural entrepreneurship hubs with mentorship and funding support.
- Target Aspirational Districts: Expand the Aspirational Districts Program to build skill centers and industrial clusters in underdeveloped areas.
- Address regional disparities by providing employment-linked incentives in backward states.
Conclusion
India's demographic dividend offers a window of opportunity to accelerate economic growth. By implementing targeted skill development programs, fostering employment generation, and integrating education with vocational training, India can harness the potential of its young population.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF