-
Q. "India's decision to stay out of RCEP while pursuing other trade agreements reflects a strategic balance between economic interests and security concerns." Discuss. (250 words)
12 Nov, 2024 GS Paper 2 International RelationsApproach:
- Introduce the answer by mentioning about signing of RCEP and India’s decision to opt out
- Give Reasons for Opting Out of RCEP
- Highlight India’s Strategy of Pursuing Bilateral and Regional Agreements
- Delve into Benefits and Challenges of India’s Strategic Approach
- Conclude in a balanced manner.
Introduction:
In November 2019, India chose to stay out of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), a trade agreement that includes 15 countries accounting for 30% of global GDP.
- This decision reflects India’s strategic approach to balancing economic ambitions with security concerns, especially in light of its trade deficits, the rise of China, and the need for stronger domestic industries.
Body:
Reasons for Opting Out of RCEP
- Trade Deficit Concerns: India's trade deficit with RCEP nations, particularly China, has been substantial.
- Joining RCEP could have exacerbated this imbalance, potentially harming domestic industries.
- In the first half of 2024, India's trade deficit with China reached a staggering $41.9 billion, highlighting the economic risks involved.
- Protection of Domestic Industries: There were apprehensions that RCEP would lead to an influx of cheaper goods, adversely affecting sectors like agriculture and manufacturing.
- The dairy industry, for instance, feared competition from countries like New Zealand, which could have impacted local farmers.
- Non-Tariff Barriers and Market Access: India sought assurances on non-tariff barriers and greater market access for its services sector, which were not adequately addressed in the RCEP negotiations.
- The lack of a favourable framework for India's service exports was a significant concern.
- India-EFTA Free Trade Agreement: In March 2024, India signed a landmark free trade deal with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA).
- This agreement includes a commitment by EFTA members to invest $100 billion and create one million jobs in India over the next 15 years. .
India’s Strategy of Pursuing Bilateral and Regional Agreements
- Diversification of Trade Agreements: India has since focused on strengthening trade relations through smaller, more manageable agreements with countries like Japan, Australia, and the European Union.
- Example: In March 2024, India signed a landmark free trade deal with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA).
- India’s exports to UAE grew by 11.8% to reach $31.3 billion in FY23 after the CAPE implementation.
- Example: In March 2024, India signed a landmark free trade deal with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA).
- Emphasis on Indo-Pacific and Security Partnerships: India’s participation in the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) with the U.S., Japan, and Australia showcases its preference for partnerships balancing economic cooperation with security collaboration in the Indo-Pacific region.
- The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), which India joined, represents an economic alignment with countries outside China’s influence, reinforcing India’s desire for security-conscious trade policies.
- Strengthening Domestic Capabilities: The government has initiated several programs like Atmanirbhar Bharat (Self-Reliant India) to make Indian industries more competitive globally, reducing dependence on imports and building resilient supply chains domestically and regionally.
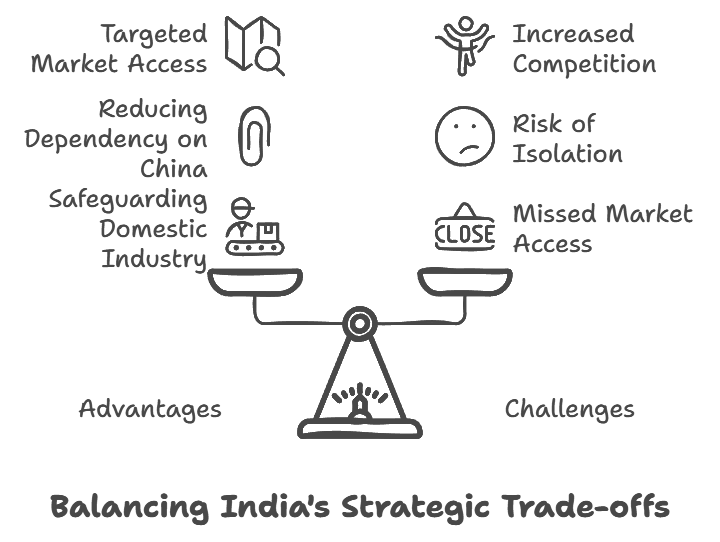
Benefits and Challenges of India’s Strategic Approach
Conclusion:
India’s decision to stay out of RCEP demonstrates a nuanced strategy that prioritises domestic economic resilience and national security. By pursuing selective trade partnerships and building self-reliant capabilities, India aims to harness the benefits of globalisation while maintaining control over its economic sovereignty.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF