Q."The evolution of Lok Adalats represents a successful adaptation of alternative dispute resolution in India's justice system." Discuss. (150 words)
12 Nov, 2024 GS Paper 2 Polity & Governance
Approach:
|
Introduction:
The Lok Adalat, or "People’s Court," is an innovative form of alternative dispute resolution in India, designed to deliver quick, cost-effective, and amicable justice. The experiment of ‘Lok Adalat’ as an alternate mode of dispute settlement has come to be accepted in India, as a viable, economic, efficient and informal one.
Body:
Evolution of Lok Adalats:
- Pre-Independence Roots: Inspired by Nyaya Panchayats, village-based tribunals resolved disputes informally, relying on community elders.
- These systems emphasised reconciliation and harmony, aligned with Indian traditions and cultural values.
- Post-Independence Decline and Revival:
- Post-independence, Nyaya Panchayats were formalised but failed due to procedural complexities and limited powers.
- The need for informal justice resurfaced, especially with Chief Justice N.H. Bhagwati's 1976 report emphasised free legal aid and public-interest litigation as mechanisms for social justice.
- Modern Era of Lok Adalats:
- The Gujarat experiment in the late 1970s marked the first formal Lok Adalats. Encouraged by their success, other states adopted the model.
- The Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987, provided statutory recognition to Lok Adalats, enabling them to hear pending and pre-litigation cases and issue binding, non-appealable awards.
- The 1999 amendment to the Civil Procedure Code introduced Section 89, enabling courts to refer cases for ADR, including Lok Adalats.
- The 2002 amendment established Permanent Lok Adalats for public utility disputes, granting them the power to decide cases even without a mutual settlement.
Lok Adalats as Successful Adaptation of ADR Mechanism
- Accessibility and Cost Effectiveness: Lok Adalats ensure access to justice to economically weaker sections and marginalised ones.
- Informal proceedings reduce costs and time compared to formal courts.
- Reduction of Case Backlog: By settling disputes expeditiously, Lok Adalats have helped alleviate the burden on formal courts. (Over 1.14 crore cases were resolved during the 3rd National Lok Adalat 2024)
- Emphasis on Reconciliation: Resolutions are achieved through compromise, fostering social harmony and avoiding prolonged adversarial litigation.
- Wide Jurisdiction: Lok Adalats handle a wide range of disputes, including civil matters, family issues, financial disputes, and compoundable criminal offenses, making them versatile.
- Binding Nature of Awards: Awards issued are legally binding and enforceable, preventing appeals and ensuring finality.
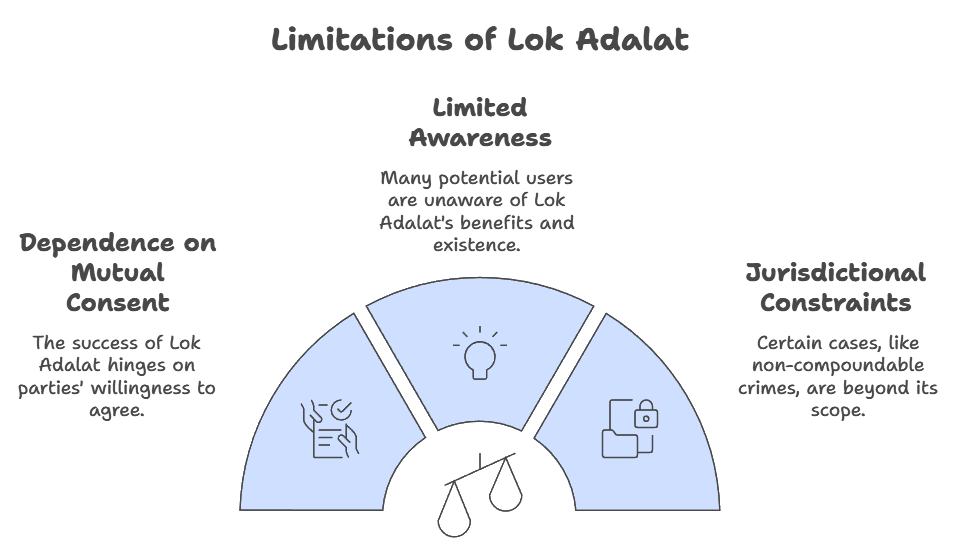
Challenges and Limitations:
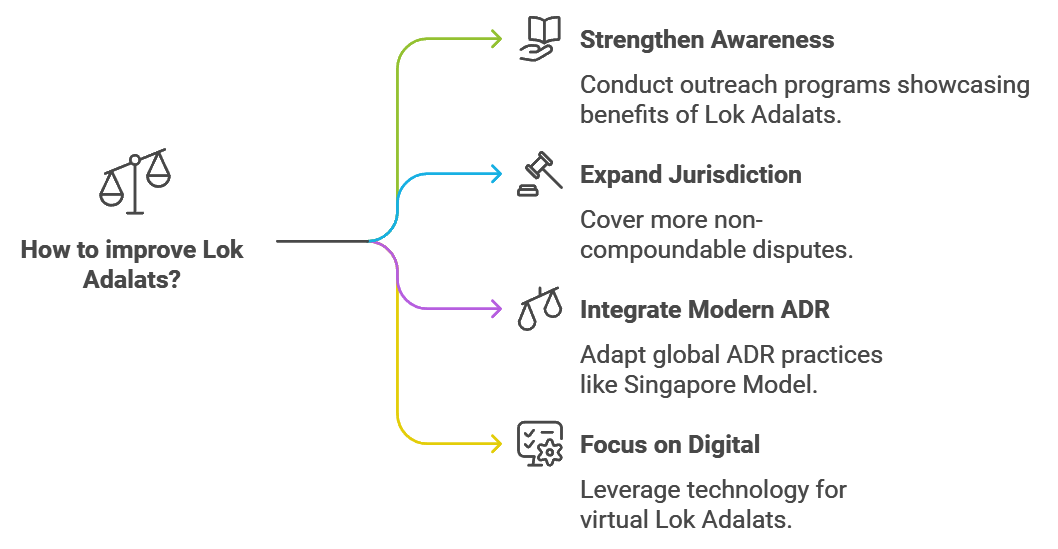
Way Forward:
Conclusion:
The Lok Adalat system symbolises a successful adaptation of ADR within India's justice system, bridging the gap between formal judicial processes and the socio-economic realities of the people. By blending traditional methods with statutory backing, Lok Adalats provide a harmonious and cost-effective platform for dispute resolution, promoting the constitutional mandate of equal access to justice.