-
Q. "Private sector participation is crucial for strengthening India's cybersecurity architecture." Analyze this statement with reference to recent initiatives and challenges. (150 words)
23 Oct, 2024 GS Paper 3 Internal SecurityApproach
- Introduce the answer by highlighting cybersecurity a critical national priority and private role in it.
- Give Importance of Private Sector Participation in Strengthening India's Cybersecurity Architecture
- Highlight Recent Government Initiatives Promoting Private Participation
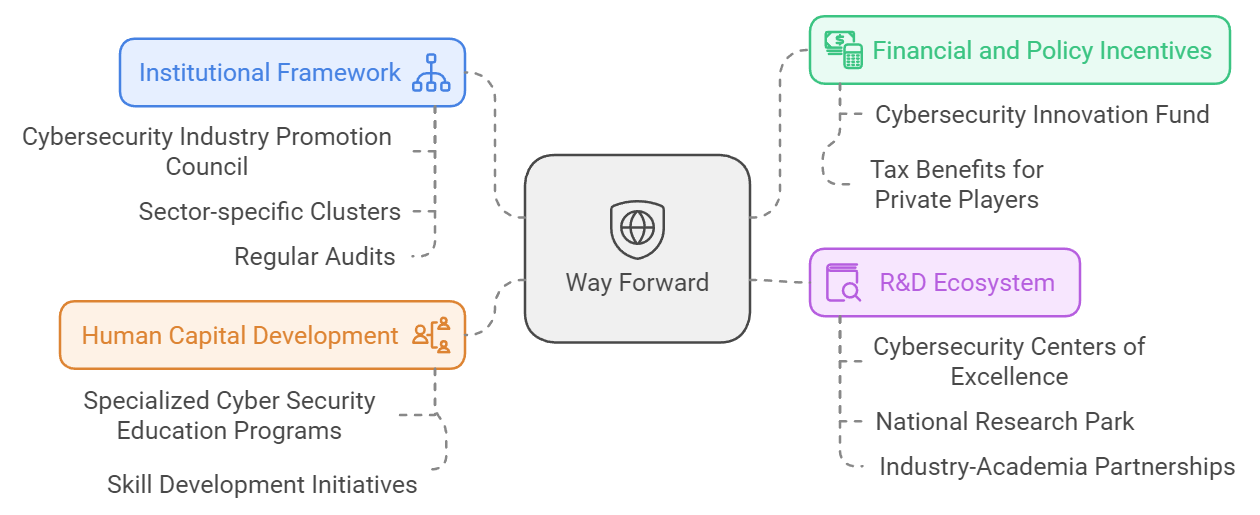
- Suggest a way forward
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction
The rapid digitalization of India's economy has made cybersecurity a critical national priority. While government agencies play a central role, private sector participation has become increasingly vital for building a robust cybersecurity ecosystem.
Body
Importance of Private Sector Participation in Strengthening India's Cybersecurity Architecture:
- Technical Expertise and Innovation: Private companies possess cutting-edge technological capabilities and specialized talent
- Companies like Tech Mahindra have developed advanced threat detection systems and security solutions specifically tailored to Indian contexts
- Private firms can adapt more quickly to emerging threats compared to government agencies
- Investment Capacity: Private sector can provide much-needed capital investment in cybersecurity infrastructure
- Private investments help bridge the funding gap in building sophisticated security systems
- Global Best Practices: Private companies, especially those with international exposure, bring global cybersecurity standards and practices
- IBM's Security Command Center in Bengaluru provides training and simulation exercises based on global cyber threat scenarios
Recent Government Initiatives Promoting Private Participation:
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) works closely with private sector for protecting critical infrastructure
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023 mandates businesses to report all data breaches to the Data Protection Board and affected individuals.
- The Board can also direct remedial measures and impose hefty penalties (up to 250 crore rupees) for inadequate security safeguards.
- Mandatory appointment of Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) in organizations
Challenges:
- Trust and Information Sharing: Reluctance in sharing sensitive security information between public and private sectors
- Regulatory Compliance Burden: Complex regulatory requirements may discourage smaller private players. Cost of compliance affecting competitiveness
- Skills Gap: Shortage of qualified cybersecurity professionals. In May 2023, nearly 40000 cybersecurity professional job vacancies in India were not filled due to talent shortages
- Rapidly Evolving Threat Landscape: The pace of technological advancement and the corresponding evolution of cyber threats can outstrip the capabilities of many organizations.
- For instance, the rise of sophisticated ransomware attacks has caught many businesses unprepared (like the recent Casio Ransomware attack) , resulting in significant financial losses and operational disruptions.
Conclusion
Private sector participation is not just crucial but indispensable for India's cybersecurity architecture. While challenges exist, the combination of government initiatives and private sector capabilities can create a robust cybersecurity ecosystem. The focus should be on creating an enabling environment that promotes collaboration while addressing legitimate concerns about national security and data protection.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF