-
Q. The development of regional kingdoms in early medieval India led to the flourishing of distinct architectural and artistic traditions. Elaborate with suitable examples. (250 words)
16 Sep, 2024 GS Paper 1 Indian Heritage & CultureApproach
- Introduce the answer by highlighting the emergence of distinct architectural and artistic traditions in early medieval India
- Delve into Key Architectural Traditions
- Highlight the Regional Artistic Traditions
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction
The development of regional kingdoms in early medieval India, marked by the decline of the Gupta Empire and the rise of various dynasties, fostered a climate of cultural diversity and experimentation.
- This period witnessed the emergence of distinct architectural and artistic traditions, each reflecting the unique cultural, religious, and political influences of its respective region.
Body
Architectural Traditions:
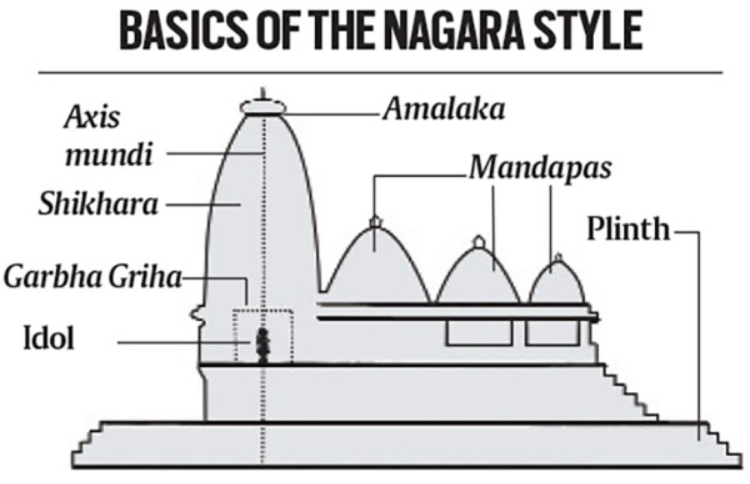
- Nagara Style:
- Characteristics:
- Curved roofs: Often featuring shikharas (spires) that rise gracefully from the base.
- Ornate carvings: Intricate sculptures and decorative motifs adorn the exterior walls.
- Mandapas: Assembly halls with square or circular plans.
- Characteristics:
- Examples:
- Khajuraho Temples: Most of them were constructed by the Chandela dynasty.
- Konark Sun Temple: Built by King Narasimha Deva I, the ruler of the Ganga Dynasty.
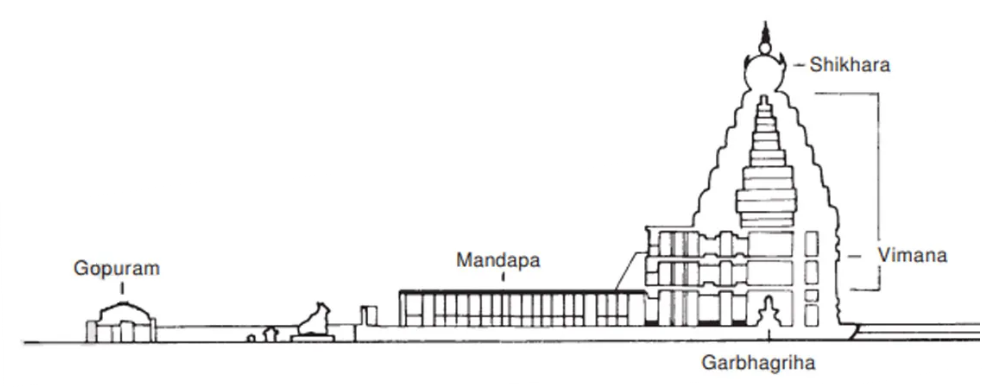
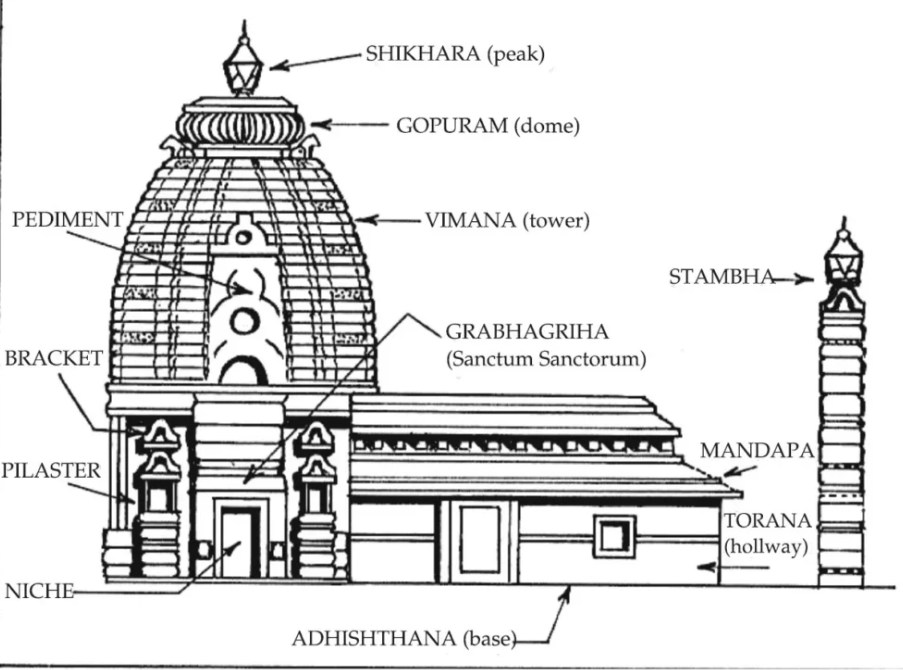
- Dravidian Style:
- Characteristics:
- Pyramidal structures: Known as gopurams that tower over the temple complex.
- Characteristics:
- Massive halls: Spacious mandapas with intricate carvings and sculptures.
- Linear plan: Temples typically follow a linear or rectangular layout.
-
- Examples:
- Brihadeeswarar Temple, Thanjavur: Built in the year 1010 CE by Chola emperor Rajaraja I.
- Meenakshi Amman Temple, Madurai: Built by Pandyan Emperor Sadayavarman Kulasekaran I.
- Examples:
- Vesara Style:
- Characteristics:
- Hybrid style: Combines elements of both Nagara and Dravidian styles.
- Curved roofs: Similar to Nagara style, but often with more elaborate curvatures
- Characteristics:
-
-
- Ornate carvings: Intricate sculptures and decorative motifs, often depicting mythological scenes.
- Examples:
- Kailasa Temple, Ellora: Built by Krishna I of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty
-
Regional Artistic Traditions
- Pala School (Eastern India)
- Buddhist and Hindu stone and bronze sculptures
- Intricate miniature paintings on palm leaves (Pala manuscript paintings)
- Example: Bronze Buddha statues from Kurkihar, Bihar
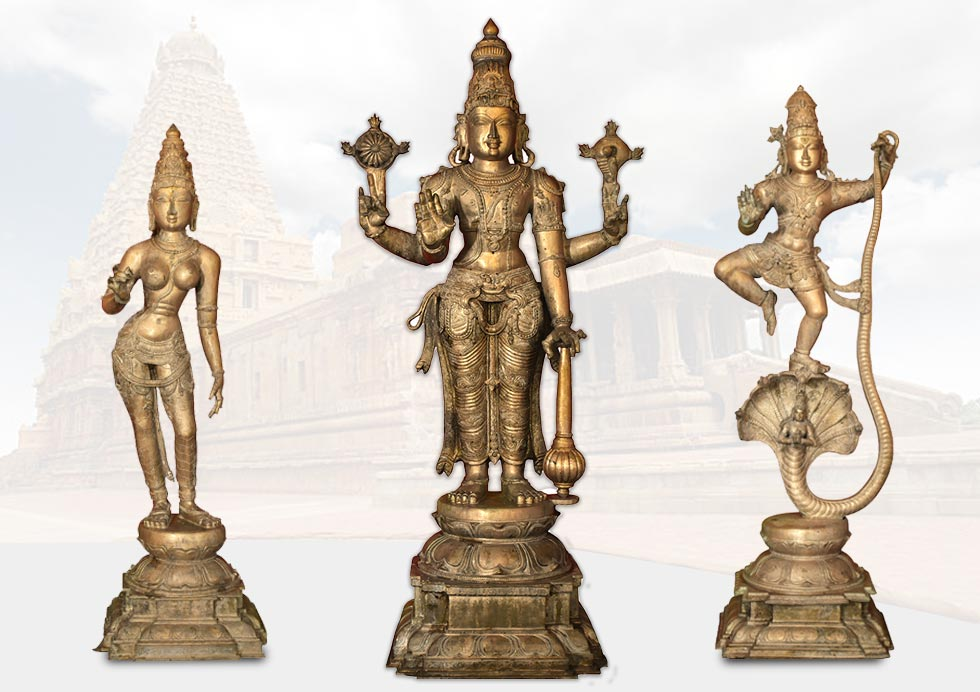
- Chola Bronzes (South India)
- Lost-wax casting technique for bronze sculptures
- Dynamic poses and exquisite detailing
- Example: Nataraja (Dancing Shiva) bronze statues
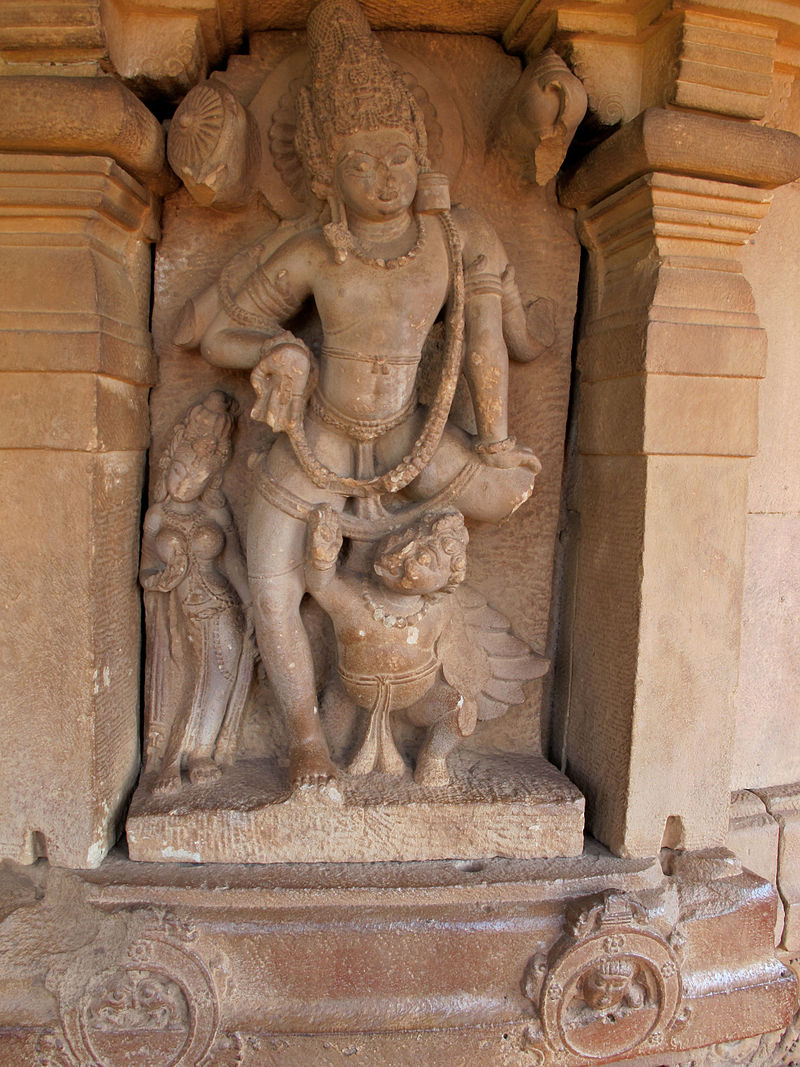
- Chalukya Art (Deccan)
- Ornate stone temple architecture
- Distinctive style of sculpture with elongated figures
- Example: Sculptures at Badami Cave Temples, Karnataka

Conclusion
The flourishing of regional kingdoms in early medieval India led to a rich diversity in architectural and artistic expressions. This period laid the foundation for the continued evolution of Indian art and architecture in subsequent centuries, creating a lasting legacy that continues to inspire and awe to this day.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF