-
Q. To what extent have poverty alleviation programs in India been effective in addressing the challenges of poverty? Examine the role of political will in the successful implementation of these programs. (250 words)
20 Aug, 2024 GS Paper 2 International RelationsApproach
- Give a brief introduction about the status of Poverty in India
- State the challenge of Poverty in India
- Mention the poverty alleviation programs and highlight the effectiveness of these programs.
- Examine the role of political will in the successful implementation of these programs.
- Suggest a way forward to strengthen these programs and alleviate poverty
- Conclude suitably
Introduction
India has made notable progress in poverty alleviation, with the poverty rate declining to 4.5–5% in 2022–2023 and significant reductions in rural and urban poverty compared to a decade ago. This improvement is attributed to various government initiatives and schemes.
Despite these gains, India still faces challenges, as evidenced by its 111th position in the 2023 Global Hunger Index and varying poverty lines across states. Examining the effectiveness of these programs and the role of political will in their implementation is crucial for understanding their impact on addressing poverty.
Body
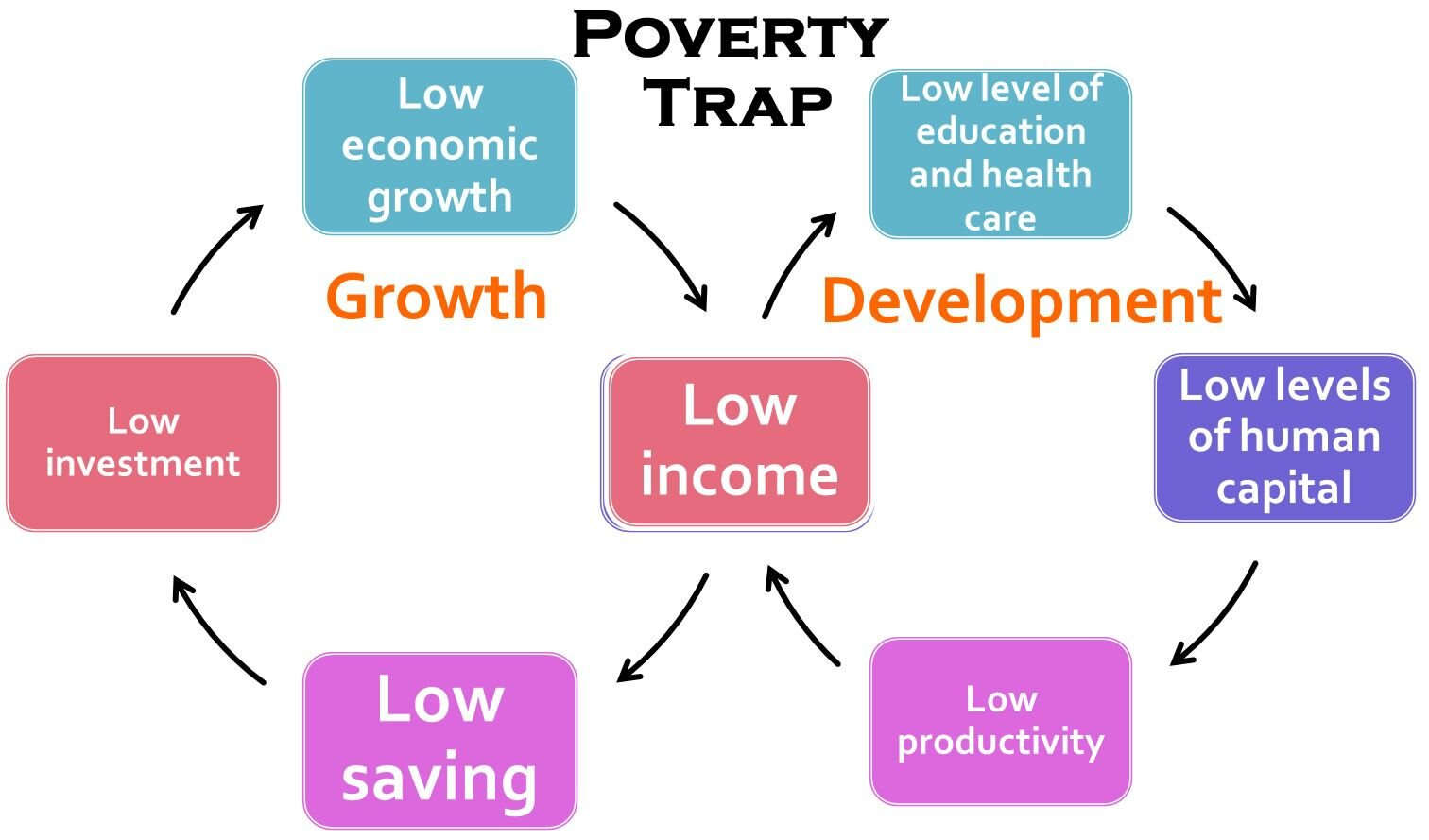
Causes of Poverty in India
- Population Growth and Unemployment: Rapid population increase, averaging 17 million annually, amplifies demand for resources and jobs, leading to higher unemployment and strain on economic systems.
- Low Agricultural Productivity and Climatic Factors: Fragmented land holdings, outdated farming methods, and frequent natural disasters like floods and cyclones reduce agricultural output and exacerbate poverty in vulnerable states.
- Economic and Resource Inefficiencies: Slow economic development before 1991, coupled with underemployment, disguised unemployment, and inefficient use of resources, limits economic opportunities and growth.
- Price Rise and Lack of Capital: Persistent inflation increases the cost of living, disproportionately affecting low-income groups, while insufficient capital and entrepreneurial activity restrict investment and job creation.
- Social and Historical Factors: Social issues such as caste-based discrimination and inheritance laws, along with the legacy of colonial exploitation, perpetuate inequalities and hinder poverty alleviation efforts.
Poverty Alleviation Programs in India
- Integrated Rural Development Programme (IRDP) and other programs:
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana: This program has provided free foodgrains to over 80 crore households monthly, ensuring food security and addressing immediate needs.
- PM Awas Yojana (Rural & Urban): Over 4 crore pucca houses built under this scheme have improved housing conditions for the poor, targeting both rural and urban areas.
- Employment and Income Generation:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA): Guarantees 100 days of employment annually, significantly contributing to income stability in rural areas.
- Health and Sanitation:
- Ayushman Bharat – PM Jan Aarogya Yojana: Provides insurance coverage of ₹5 lakh per family to 55 crore beneficiaries for secondary and tertiary care, addressing healthcare access.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Around 12 crore toilets built have improved sanitation and hygiene, crucial for health and dignity.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: 14.5 crore rural households now have tap water connections, enhancing access to clean water and reducing health risks.
- Saubhagya Yojana: With 2.8 crore households electrified, this scheme has enhanced quality of life and productivity in rural areas.
- Financial Inclusion and Empowerment:
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana: Enabled 52 crore people to access formal banking services, promoting financial inclusion.
- PM SVANidhi Scheme: Provided collateral-free loans to over 62 lakh urban street vendors, supporting their businesses and economic stability.
- Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM): Mobilized 10.04 crore women into 90.76 lakh Self-Help Groups, enhancing income opportunities and social empowerment.
- Results and Impact:
- Multidimensional Poverty Reduction: Approximately 25 crore people have escaped multidimensional poverty in the last nine years, demonstrating the effectiveness of these programs.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDG): The government's efforts are on track to achieve the SDG target of halving multidimensional poverty well before 2030, reflecting the success of these interventions.
Role of Political Will in Program Implementation
- Policy Formulation and Prioritization:
- Political will is crucial in prioritizing poverty alleviation within the national agenda.
- Strong political leadership drives the formulation of targeted policies and allocates sufficient resources to tackle poverty effectively.
- Ensuring Accountability and Transparency:
- Political commitment is essential for enforcing accountability and transparency in the implementation of programs.
- For instance, reforms in DBT and digitization of processes were driven by political decisions to curb corruption and improve service delivery.
- Addressing Regional Disparities:
- Political will is required to address regional inequalities in the implementation of poverty programs.
- States with strong governance, such as Tamil Nadu and Kerala, have seen more effective implementation of welfare schemes compared to states with weaker political commitment.
- Overcoming Political Populism and Short-Termism:
- The success of poverty programs is often hampered by political populism and short-term measures aimed at electoral gains rather than long-term poverty reduction.
- A committed political leadership that prioritizes sustainable development over vote-bank politics is crucial.
Way Forward for Poverty Alleviation in India
- Sustained Economic Growth and Investment Efficiency
- Aim for a continuous annual growth rate of 6-7% over the next 25 years to raise per capita income.
- Increase Gross Fixed Capital Formation to 30-32% of GDP and improve the Incremental Capital-Output Ratio (ICOR) by focusing on technological advancements and efficiency improvements.
- Boosting Domestic and Foreign Investments
- Encourage substantial domestic investments, especially in technology and infrastructure, while attracting Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in emerging technological sectors.
- Ensure that investments complement domestic efforts and drive growth and employment.
- Adaptation to Technological and Environmental Challenges
- Embrace and integrate technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) while addressing potential impacts on employment through skill development.
- Implement sustainable practices to manage pollution and reduce carbon emissions, adjusting growth targets to accommodate environmental goals.
- Development of Social Safety Nets and Inclusive Growth
- Explore the implementation of a basic income scheme to provide financial security and streamline subsidies to focus on essentials like food.
- Invest in social infrastructure, including healthcare and education, to improve overall quality of life and support poverty alleviation.
- Strengthening Policy Framework and Investment Climate
- Develop policies that foster a conducive investment climate, encouraging both domestic and international investments.
- Continuously monitor economic performance and adjust strategies to effectively meet growth and poverty reduction goals.
Conclusion
Looking ahead, India's path to eradicating poverty hinges on sustaining robust economic growth and optimizing investment efficiency. By embracing technology, addressing environmental challenges, and strengthening social safety nets, India can foster inclusive development. With a forward-thinking approach and strategic policies, the nation is poised to significantly elevate living standards and achieve comprehensive poverty alleviation
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF