-
Q. Discuss key indicators of good governance and suggest strategies for its effective implementation at the grassroots level in India. (150 words)
06 Aug, 2024 GS Paper 2 Polity & GovernanceApproach
- Introduce the answer by defining good governance
- Give Key Indicators of Good Governance
- Suggest strategies for its effective implementation at the grassroots level in India
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction
Good governance refers to the effective, efficient, and responsible management of public affairs and resources.
- It encompasses a set of principles and practices that ensure transparent, accountable, participatory, and responsive governance at all levels.
- It aims to create an environment where government institutions operate in the best interests of all citizens, promoting sustainable development, social justice, and the rule of law.
Body
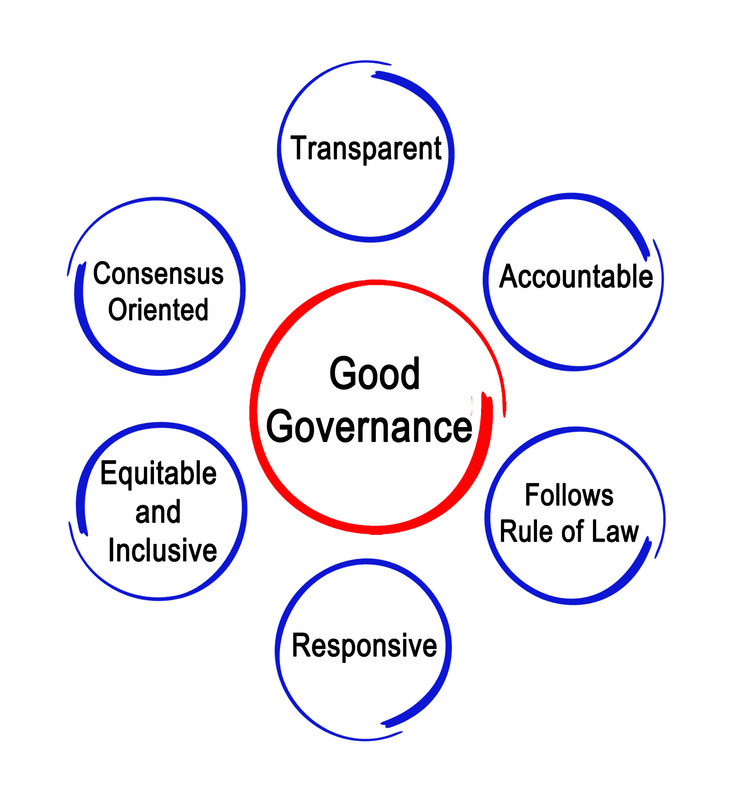
Key Indicators of Good Governance:
- Participation: Citizens actively engage in decision-making, with diverse groups, including marginalized communities, represented effectively. (Example: Gram Sabhas under the Panchayati Raj system).
- Accountability: Government officials are held responsible for their actions through transparent information dissemination about public policies and expenditures. (Example: the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013, which established an anti-corruption ombudsman.).
- Transparency: Government processes and decisions are open and accessible, facilitated by clear and understandable communication with citizens. (Example: Implementation of the Right to Information Act, 2005 in India).
- Responsiveness: Government promptly addresses citizens' needs and concerns through effective grievance redressal mechanisms. (Example: CPGRAMS provides speedy grievance redressal).
- Effectiveness and Efficiency: Desired outcomes are achieved with minimal resources and optimal utilization of public funds. ( Example: The Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) scheme to reduce leakages in subsidy distribution).
- Rule of Law: Laws and regulations are impartially enforced, safeguarding citizens' rights and freedoms. (Example: Independent Judiciary, Separation of Power, Supremacy of written constitution).
Strategies for Implementing Good Governance at the Grassroots Level:
- Strengthening Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs): Enhance capacity building of elected representatives and officials, decentralize financial resources, and empower Gram Sabhas for effective decision-making as recommended by Second Administrative Reforms Commission.
- Technology Adoption: Utilize digital platforms for transparency and accountability, implement e-governance initiatives for service delivery, and leverage Common Service Centers (CSCs) for digital literacy and government services.
- Citizen Participation: Foster community-based organizations and self-help groups, conduct social audits for program monitoring like MGNREGA, and promote government-citizen linkage through Jan Bhagidari initiatives, Mann ki Baat Program and Community radio.
- Capacity Building of Government Officials: Organize training programs on good governance principles and practices, implement performance-based appraisal systems, and effective implementation of programmes like Mission Karmayogi and leverage institutions like the National Institute of Rural Development (NIRD) for capacity building.
- Performance-Based Incentives: Introduce a Local Governance Performance Index in the lines of District Development Governance Index.
- This promotes healthy competition and improved governance but requires developing fair and comprehensive assessment criteria.
Conclusion
Effective governance at the grassroots is imperative for India's progress. By strengthening Panchayati Raj institutions, harnessing technology, and prioritizing citizen participation, we can effectively transition towards 'minimum government, maximum governance'.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF