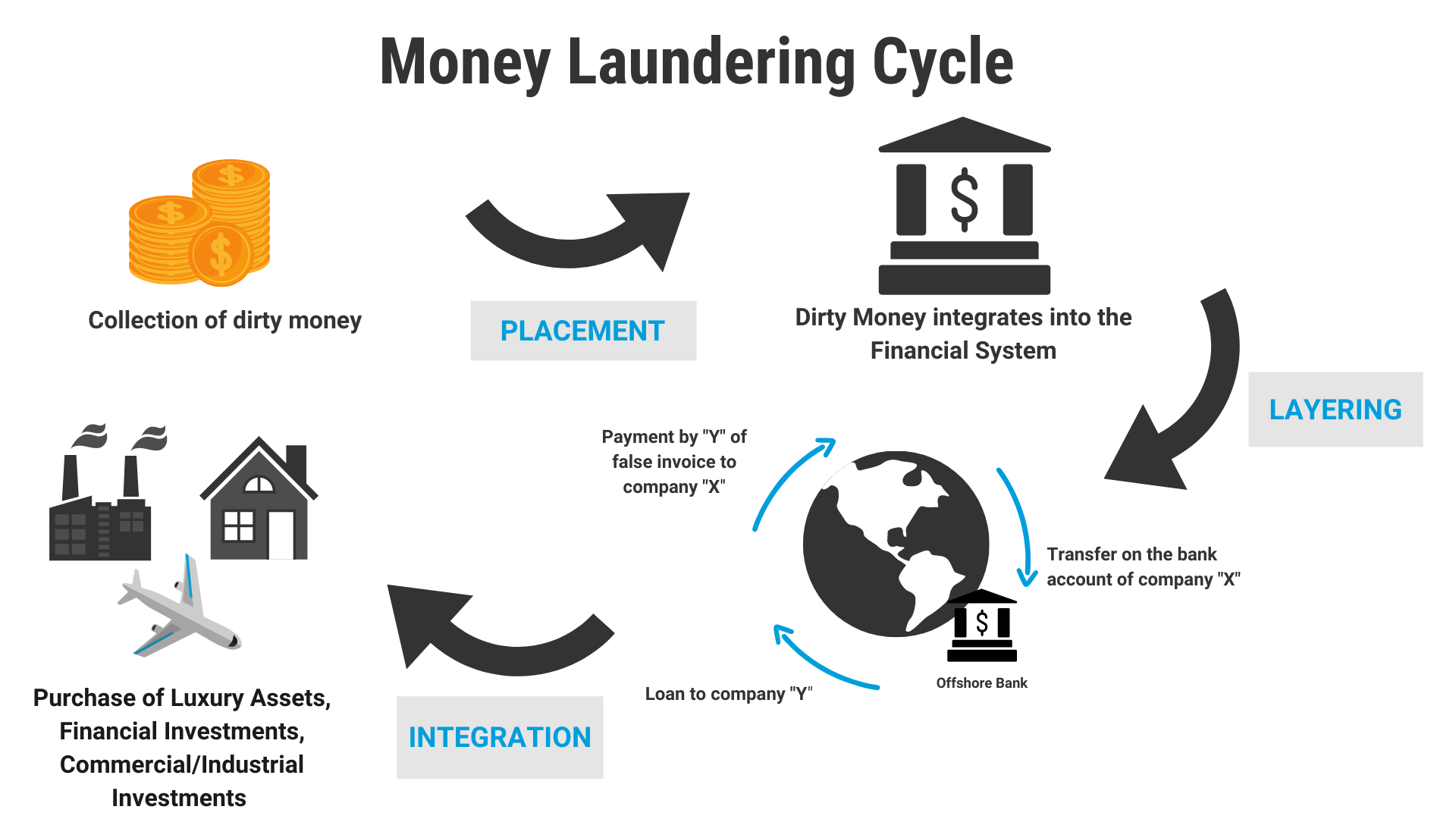
-
Q. The growing influence of money laundering on financing terrorism and organized crime poses a significant threat to India’s internal security. Discuss. (250 words)
17 Jul, 2024 GS Paper 3 Internal SecurityApproach
- Introduce by defining money laundering and link with organized crime and terrorist networks
- Delve into the role Money Laundering in Terrorism Financing and its impacts
- Highlight the role of Money Laundering in Organized Crime and its impacts
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction
Money laundering, the process of disguising the illegal origin of funds, poses a significant threat to India's internal security. It acts as a pernicious lifeblood for organized crime and terrorist networks, enabling them to operate with impunity and destabilize the nation.
Body
- Money Laundering on Terrorism Financing
- Funding Channels:
- Hawala networks: Informal value transfer systems operate outside traditional banking channels, as evidenced by the 2022 National Investigation Agency (NIA) bust of terror funding networks in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Cryptocurrency transactions: The anonymity of digital currencies is exploited, as seen in the Bengaluru Cafe terror attack case where ISIS-linked funding networks operating through crypto platforms.
- Shell companies and front businesses: Legitimate-appearing entities disguise illicit funds, exemplified by the Enforcement Directorate's (ED) 2024 investigations into the Popular Front of India (PFI) for alleged terror financing.
- Impact on Internal Security:
- Sustaining terrorist infrastructure: Providing resources for training camps and logistical support, as revealed in ongoing investigations into Northeast militant groups in Manipur and Nagaland (2021-2023).
- Facilitating recruitment and radicalization: Funding propaganda efforts and offering financial incentives, a tactic observed in PFI's alleged activities across multiple states.
- Enabling procurement of weapons and explosives: Acquiring sophisticated weaponry, as seen in cross-border terrorism cases.
- Funding Channels:
- Money Laundering and Organized Crime:
- Key Areas:
- Drug trafficking: Laundering profits from narcotics trade, particularly from the Golden Crescent and Golden Triangle regions, as evidenced by multiple Narcotics Control Bureau operations.
- Cybercrime: Laundering funds obtained through ransomware attacks and online fraud, exemplified by the ED's 2023 action against Chinese loan apps involved in money laundering.
- Real estate: Using property investments to integrate illicit funds, as seen in numerous cases investigated by the Income Tax Department and ED across major Indian cities.
- Impact on Internal Security:
- Corruption and Political Instability: Organized crime and money laundering fuel corruption, leading to political instability and eroding public trust in governance.
- Example: The 2G spectrum scam involved large-scale money laundering, resulting in political upheaval and loss of public confidence in the political system.
- Undermining Law Enforcement: Criminal organizations involved in money laundering often have significant resources to evade law enforcement, making it difficult to control and prevent organized crime.
- Example: The Dawood Ibrahim crime syndicate successfully laundered money, eluding law enforcement agencies and continuing its criminal activities from abroad.
- Economic Distortion: Money laundering distorts the economy by diverting resources from legitimate to illegitimate activities, affecting economic growth and stability.
- Corruption and Political Instability: Organized crime and money laundering fuel corruption, leading to political instability and eroding public trust in governance.
- Key Areas:
Way Forward
- Strengthening Financial Regulations: Implementing stricter KYC (Know Your Customer) norms and reporting suspicious transactions.
- The PMLA (Prevention of Money Laundering Act) can be further strengthened to address the evolving tactics of money launderers.
- Enhancing Law Enforcement Capacity: Training and equipping law enforcement agencies to investigate and prosecute money laundering effectively using Artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Special units can be established within law enforcement agencies to focus specifically on investigating money laundering activities.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public on money laundering techniques and how to report suspicious activity.
- Public awareness campaigns can help citizens identify and report suspicious financial transactions, hindering money laundering activities.
- International Collaboration: Sharing information and intelligence with other countries to disrupt transnational criminal networks.
- India's enhanced participation in organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is crucial for international cooperation in combating money laundering.
Conclusion
The fight against money laundering is a continuous battle, requiring constant adaptation to evolving criminal tactics. India's future security hinges on its ability to foster closer international cooperation, leverage cutting-edge technologies for financial intelligence, and promote financial inclusion to curb reliance on informal channels.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF