-
Q. Discuss the principles and potential benefits of Zero Budget Natural Farming for sustainable agriculture in India, considering both ecological and economic aspects. (150 words)
22 May, 2024 GS Paper 3 Bio-diversity & EnvironmentApproach:
- Introduce with Zero Budget Natural Farming
- Mention key principles of ZBNF
- Delve into its potential benefits in ecological as well as economical context.
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction:
Zero Budget Natural Farming is an agricultural practice that promotes sustainable farming methods with minimal external inputs and costs.
- The toolkit of ZBNF was developed by Subhash Palekar in the 1990's.
- It has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential benefits for both ecological and economic sustainability.
Body:
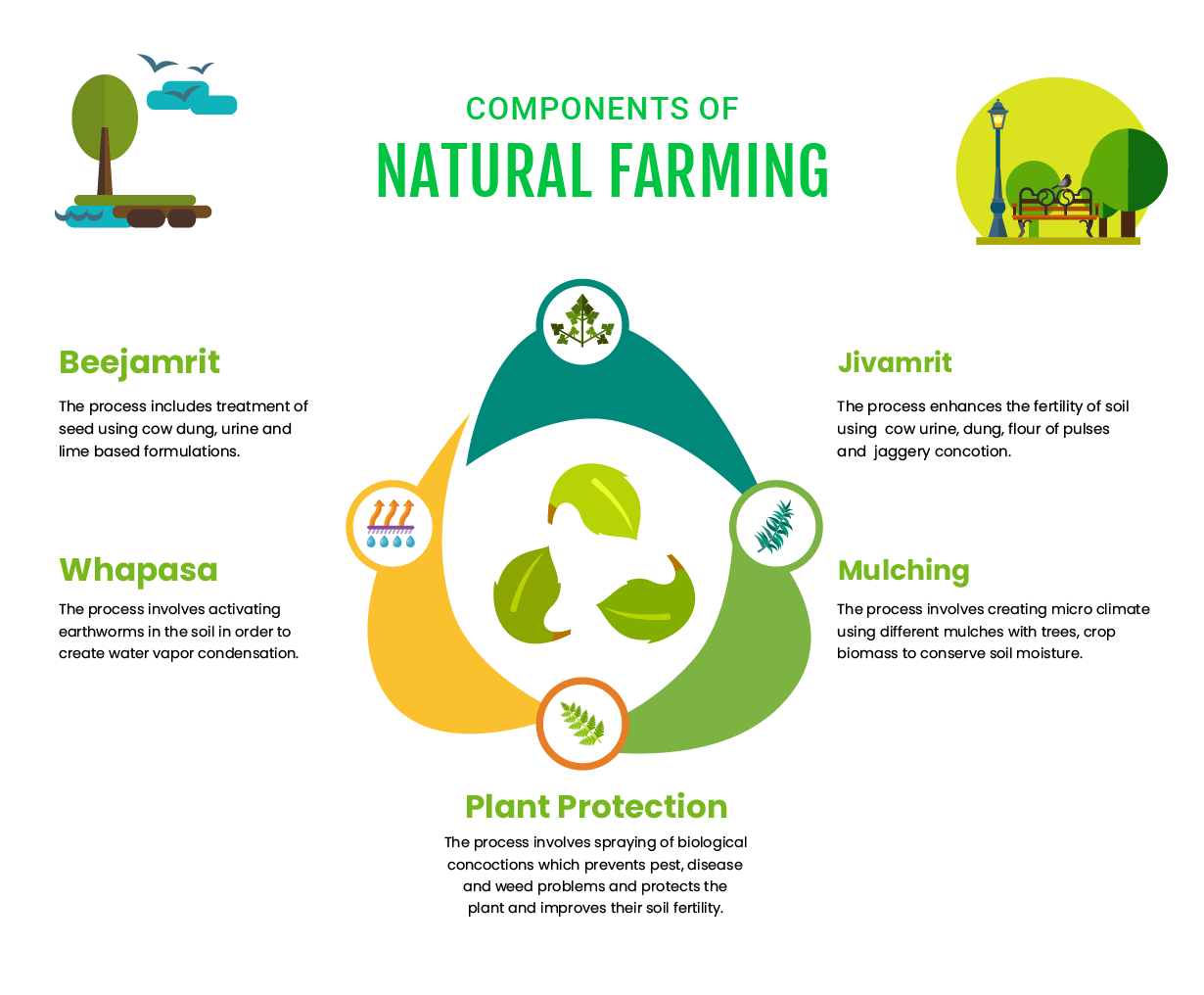
Principles of Zero Budget Natural Farming:
- No Chemicals: Avoidance of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides to maintain soil and environmental health.
- Natural Inputs:
- Jeevamrit: Utilization of microbial culture to enrich the soil with beneficial microorganisms.
- Beejamrit: Seed treatment with natural solutions to enhance seed germination and resistance to pests.
- Acchadana(Mulching): Application of organic matter to cover soil, retain moisture, suppress weeds, and enhance fertility.
- Whapasa: This condition refers to the presence of both air and water molecules in the soil, which in turn helps decrease the need for irrigation.
- Promoting Biodiversity:
- Intercropping: Growing multiple crops together to create a diverse ecosystem, promoting natural pest control, and improving soil health.
- Focus on Soil Health:
- Composting: Recycling organic waste into nutrient-rich compost to improve soil structure and fertility.
- Crop Residue Management: Incorporating crop residues into the soil to enhance organic matter content and soil health.
Potential Benefits of Zero Budget Natural Farming:
- Ecological Benefits:
- Improved Soil Health: ZBNF's focus on organic inputs and microbial activity can improve soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient availability, leading to healthier and more productive soils.
- Reduced Environmental Pollution: By eliminating the use of synthetic chemicals, ZBNF can reduce water, air, and soil pollution, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable environment.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The promotion of diverse crop varieties and the integration of livestock in ZBNF systems can help preserve biodiversity and support ecosystem services, such as pollination and pest control.
- Climate Resilience: ZBNF practices, such as mulching and water conservation, can enhance the resilience of agricultural systems to the impacts of climate change, such as droughts and extreme weather events.
- Economic Benefits:
- Reduced Input Costs: By relying on locally available materials and eliminating the need for expensive chemical inputs, ZBNF can significantly reduce the production costs for farmers, increasing their net income.
- Reduced Dependency on External Inputs: ZBNF's emphasis on self-reliance and the use of on-farm resources reduces the dependence on external inputs, which can be subject to price fluctuations and supply disruptions.
- Market Opportunities: The growing demand for organic and sustainable agricultural products can provide ZBNF farmers with access to premium markets and higher prices for their produce.
- Long-term Sustainability: ZBNF's focus on maintaining soil fertility and promoting biodiversity can contribute to the long-term sustainability of agricultural systems, ensuring food security and economic stability for farmers.
Conclusion:
ZBNF has shown promising results in some regions like Himachal Pradesh (Prakritik Kheti Khushhal Kisan Yojana). By embracing ZBNF as a sustainable agricultural approach, India can pave the way for a more environmentally friendly, economically viable, and socially equitable food production system, ensuring the well-being of both people and the planet.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF