-
Q Discuss the impact of India's changing relations with its neighbors on regional stability and India's foreign policy objectives. (250 Words)
23 Apr, 2024 GS Paper 2 International RelationsApproach
- Start the answer by introducing the India’s neighbourhood.
- Illustrate the impact of India's changing relations with its neighbors on regional stability.
- Evaluate the impact of India's changing relations with its neighbors on foreign policy objectives.
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction
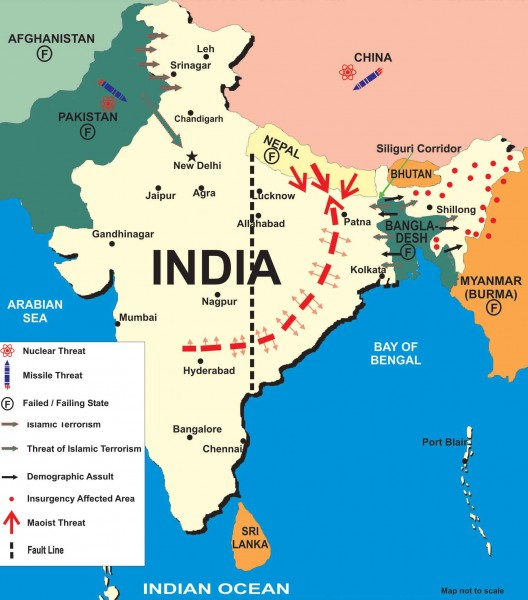
India's neighborhood, often referred to as South Asia or the Indian subcontinent, comprises countries that share geographical proximity and historical, cultural, and economic ties with India. The region is of strategic importance to India due to its impact on regional stability, security, and economic growth.
Body
Historical Context:
- India's relations with neighbors have been shaped by historical, cultural, and geopolitical factors.
- Post-independence, India aimed for regional leadership, emphasizing non-alignment and regional cooperation.
- However, challenges such as border disputes and security concerns have strained relations at times.
Current Scenario:
- China Factor: China's growing influence in South Asia, highlighted by initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), has led to strategic concerns for India, impacting regional dynamics.
- India-Pakistan Relations: India-Pakistan relations, marred by conflicts and terrorism, have a significant impact on regional stability. Despite efforts, issues like Kashmir remain unresolved.
- Bangladesh: Improved relations with Bangladesh have led to cooperation in areas like trade and security, positively influencing regional stability.
- Sri Lanka: India-Sri Lanka relations have been complex, with issues like the Tamil minority rights impacting ties. However, recent cooperation in areas like maritime security signals positive developments.
- Nepal: Historically close ties with Nepal have faced challenges such as Kalapani border dispute etc. India's focus on people-centric projects aims to strengthen relations.
- Bhutan: Strong historical ties with Bhutan have been reinforced through development cooperation, contributing to regional stability such as development of Gelephu Millennium City.
Impact on Regional Stability:
- Security Concerns: Tensions with Pakistan have implications for regional stability, especially regarding nuclear proliferation and terrorism.
- China Factor: China's growing influence in the region, particularly through initiatives like the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, adds complexity to India's relations with its neighbors.
- Economic Cooperation: Enhanced economic ties with neighbors promote stability by fostering interdependence and shared prosperity such as Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Bhutan etc.
- Transnational Challenges: Issues like cross-border terrorism, illicit trade, and environmental degradation require regional cooperation for effective management.
- Soft Power Diplomacy: India's cultural diplomacy, through initiatives like the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) and Bollywood, helps foster goodwill and stability in the region.
India's Foreign Policy Objectives:
- Neighborhood First Policy: Prioritizing relations with neighbors reflects India's commitment to regional stability and prosperity.
- Act East Policy: Strengthening ties with Southeast Asian countries enhances India's strategic presence in the Indo-Pacific region, countering China's influence.
- Strategic Autonomy: India seeks to balance its relations with major powers like the US, Russia, and China while safeguarding its national interests.
- Economic Integration: Initiatives like the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) and the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) aim to promote economic integration and development in the region.
- Global Leadership: Aspiring for a greater role in international affairs such as permanent UNSC Seat, India's engagements with neighbors contribute to its image as a responsible global actor.
Way Forward:
- Security Dilemmas: Balancing security concerns with the imperative for dialogue and cooperation remains a challenge, particularly in conflict-prone regions like Kashmir.
- China's Influence: Addressing China's expanding footprint in the region requires nuanced diplomacy and strategic partnerships with like-minded countries.
- Domestic Politics: Domestic political dynamics in neighboring countries such as Nepal can impact bilateral relations, necessitating flexibility and pragmatism in India's approach.
- Economic Disparities: Addressing economic disparities among neighbors is crucial for sustainable development and regional stability, requiring investments in infrastructure and capacity-building like India’s assistance to Sri Lanka in seeking IMF’s bailout.
- Track II Diplomacy: Strengthening people-to-people contacts and Track II diplomatic initiatives can complement official channels, fostering mutual understanding and trust.
Conclusion
India's evolving relations with its neighbors have far-reaching implications for regional stability and its foreign policy objectives. While challenges persist, proactive engagement, dialogue, and cooperation offer avenues for advancing mutual interests and fostering a conducive environment for peace and prosperity in the region.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF