- Filter By :
- Geography
- History
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Indian Society
-
Q. Explain the reasons for the decline of mangroves forest and discuss their significance in the preservation of coastal ecology. (250 words)
07 Nov, 2022 GS Paper 1 GeographyApproach
- Explain briefly about mangroves.
- Discuss the reasons for the decline of mangroves.
- Explain their role in preservation of costal ecology.
- Conclude accordingly.
Introduction
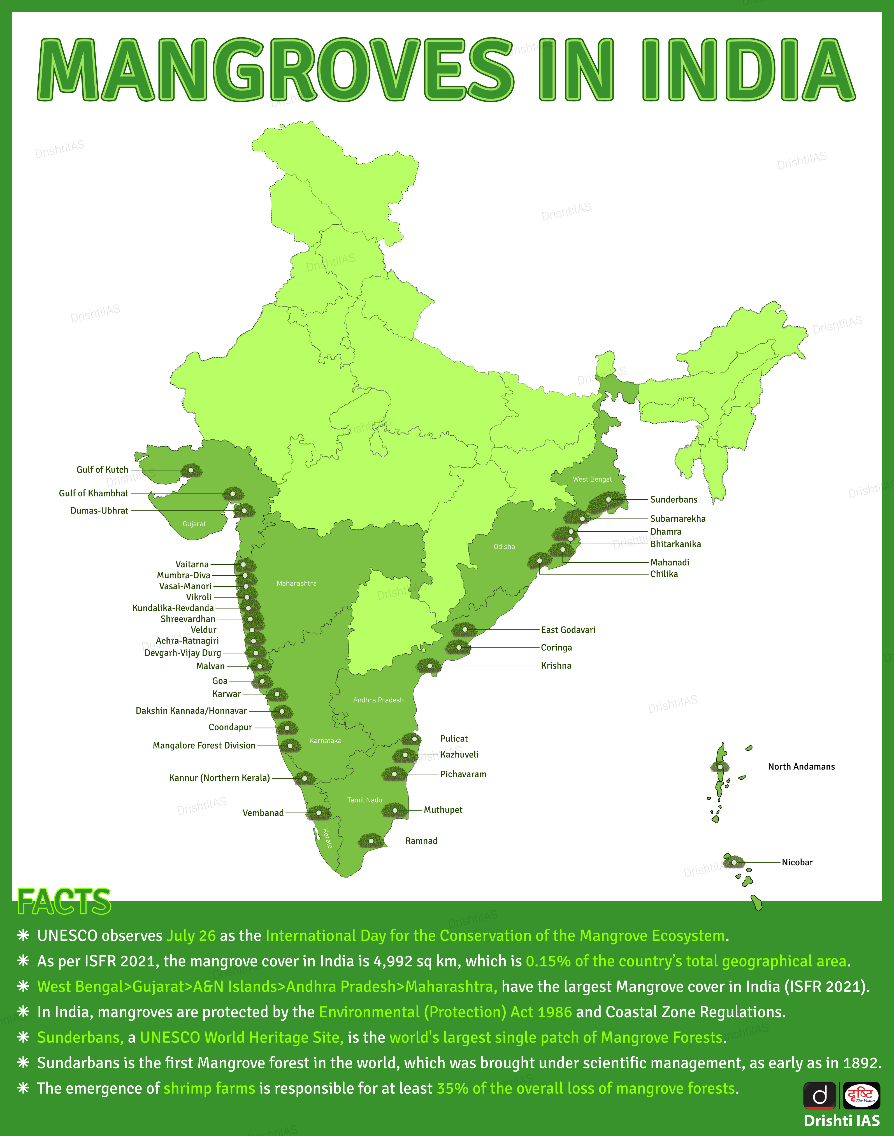
- A Mangrove is a small tree or shrub that grows along coastlines, taking root in salty sediments, often underwater.
- The word ‘mangrove’ may refer to the habitat as a whole or to the trees and shrubs in the mangrove swamp.
- Mangroves are flowering trees, belonging to the families Rhizophoraceae, Acanthaceae, Lythraceae, Combretaceae, and Arecaceae.
- According to a study by UNEP, more than 35% of the world’s mangroves are already depleted and about 100% of mangrove species and 92% of mangrove associates are under threat.
Body
- Reasons for the decline in mangroves:
- Commercialization of Coastal Areas: Aquaculture, coastal development, rice and palm oil farming and industrial activities are rapidly replacing mangroves and the ecosystems they support.
- According to UNESCO, mangroves are disappearing at three to five times faster rate than overall losses of global forest cover in the face of infrastructure development, urbanisation and agricultural land conversion.
- Shrimp Farms: The emergence of shrimp farms has caused at least 35% of the overall loss of mangrove forests.
- The rise of shrimp farming is a response to the increasing appetite for shrimp in the United States, Europe, Japan and China in recent decades.
- Temperature Related Issues: A fluctuation of ten degrees in a short period of time is enough stress to damage the plant and freezing temperatures for even a few hours can kill some mangrove species.
- Soil Related Issues: The soil where mangroves are rooted poses a challenge for plants as it is severely lacking in oxygen.
- Most plants can easily take oxygen from gases trapped within the surrounding soil, but for mangrove roots this is not an option as not only their roots underground, they are also flooded with water up to two times a day.
- Excessive Human Intervention: During past changes in sea level, mangroves were able to move further inland, but in many places human development is now a barrier that limits how far a mangrove forest can migrate.
- Mangroves also frequently suffer from oil spills.
- Commercialization of Coastal Areas: Aquaculture, coastal development, rice and palm oil farming and industrial activities are rapidly replacing mangroves and the ecosystems they support.
- Significance of mangroves:
- Ecological Stabilisation: Ecologically mangroves are important in maintaining and building the soil, as a reservoir in the tertiary assimilation of waste.
- They provide protection against cyclones.
- They play a significant role in promoting land accretion, fixation of mud banks, dissipation of winds, tidal and wave energy.
- Mangroves and Tides: The dense tangle of roots allows the trees to handle the daily rise and fall of tides.
- Most mangroves get flooded at least twice per day.
- Coastal Stabilisation: Mangrove forests stabilize the coastline, reducing erosion from storm surges, currents, waves, and tides.
- Ecological Stabilisation: Ecologically mangroves are important in maintaining and building the soil, as a reservoir in the tertiary assimilation of waste.
Conclusion
As Mangroves play an important role in maintaining and preserving the coastal ecosystem. There are many threats from human activities which could upset the natural balance of the ecology and lead to its depletion. Further, there is a need for strict enforcement of coastal regulatory measures, scientific management practices and the involvement of local communities in conservation and management that are essential for the conservation and sustainable management of valuable mangrove forests.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF