-
01 Aug 2024
GS Paper 2
International Relations
Day 22: Evaluate the complexities surrounding Katchatheevu Island as a contentious issue in the diplomatic relations between India and Sri Lanka. (150 words)
Approach
- Briefly introduce Katchatheevu Island and its geographical significance.
- Discuss the complexities surrounding the Katchatheevu Island on India-Sri Lanka relations.
- Propose measures for addressing the Katchatheevu issue.
- Conclude Suitably.
Introduction
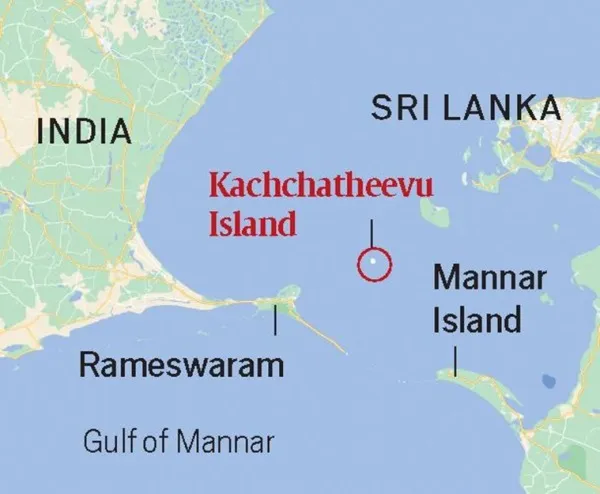
The Katchatheevu Islands are a pair of uninhabited islands located in the Palk Strait, between the southeastern coast of India (Tamil Nadu) and the northern coast of Sri Lanka. These islands have been historically significant due to their strategic location and their importance in the fishing activities of both India and Sri Lanka.
Body
The complexities surrounding the Katchatheevu Island on India-Sri Lanka relations:
- Historical Disagreement:
- The ownership dispute over Katchatheevu between India and Sri Lanka, which had been part of the Madras Presidency during the British Raj, persisted until 1974, with both countries claiming the island as their own.
- Sri Lanka claimed sovereignty over Katchatheevu on the ground that the Portuguese who had occupied the island during 1505-1658 CE had exercised jurisdiction over the islet.
- Fishermen Issues:
- Under the Indo-Sri Lankan Maritime Agreement in 1974 the island’s transfer to Sri Lanka occurred.
- Article 4 of the Agreement stipulated that each State shall have sovereignty and exclusive jurisdiction and control over the waters, the Islands, the Continental Shelf and the subsoil on its side of the Maritime boundary in the Palk Strait and Palk Bay and Katchatheevu Island was determined as falling within Sri Lankan waters.
- The following article added that “Indian fishermen and pilgrims would enjoy access to the island as before and would not be required by Sri Lanka to obtain travel documents or visas for these purposes”.
- Due to differing interpretations of the agreement by both sides, it failed to resolve the fishing rights issue, with Sri Lanka limiting Indian fishermen's access to activities such as resting, drying nets, and visiting the Catholic shrine without visa.
- Human Rights Concerns: Restrictions on fishing activities around Katchatheevu imposed by Sri Lanka have led to humanitarian concerns, including instances of arrests, harassment, and loss of lives among Indian fishermen.
- Security Concerns: Control over Katchatheevu provides India with strategic leverage in monitoring maritime activities in the region, including movements of vessels and potential security threats.
- India has expressed concerns over the use of Katchatheevu for smuggling and other illegal activities that could pose a security threat.
- Environmental Concern: Overfishing by both Indian and Sri Lankan fishermen can lead to environmental degradation, threatening the marine ecosystem
- Diplomatic Challenges: Nationalist sentiments in Tamil Nadu often influence India's foreign policy, with local political pressures urging the government to take a more active stance in defending the rights of Indian fishermen. This domestic pressure can lead to diplomatic tensions between India and Sri Lanka.
Measures for Addressing the Katchatheevu Issue between India and Sri Lanka
- Diplomatic Discussions: Conduct regular diplomatic discussions between India and Sri Lanka to address the Katchatheevu issue, focusing on both fishing rights and sovereignty concerns.
- Engage regional bodies like BIMSTEC or IORA to facilitate discussions on maritime security and cooperation between India and Sri Lanka.
- Reassessment of the 1974 Agreement: Revisit the 1974 agreement that ceded Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka, evaluating its implications on fishing rights and local livelihoods, especially considering the changing socio-economic landscape.
- Bilateral Trade Agreements: Enhance economic ties through trade agreements that benefit both countries, including provisions for joint ventures in fisheries and related industries.
- India has traditionally been among Sri Lanka’s largest trade partners and Sri Lanka remains among the largest trade partners of India in the SAARC
- More than 60% of Sri Lanka’s exports enjoy the benefits of the India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement.
- Joint Conservation Efforts: Collaborate on environmental protection initiatives in the Katchatheevu area to preserve marine biodiversity and promote sustainable fishing.
- Develop tourism initiatives that include Katchatheevu, creating a sense of shared ownership and responsibility for the island and its resources.
- In 2022, India was the largest source of tourists for Sri Lanka with over 100,000 tourists.
- Community Engagement: Engage with fishing communities in Tamil Nadu and Sri Lanka to understand their concerns and aspirations, ensuring their voices are heard in decision-making processes.
- Joint Exercises: Conduct joint military exercises focusing on maritime security to build trust and collaboration between the two nations' naval forces.
- India and Sri Lanka conduct joint military (Mitra Shakti) and Naval exercise (SLINEX).
Conclusion
Addressing the Katchatheevu issue requires a comprehensive approach that combines diplomatic engagement, community involvement, and regional cooperation. By leveraging India’s long-term vision under the SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) initiative, both India and Sri Lanka can resolve the Katchatheevu issue effectively. This collaborative framework not only addresses immediate concerns but also strengthens the overall relationship between the two nations, contributing to lasting peace and prosperity in the region.