-
20 Aug 2024
GS Paper 4
Theoretical Questions
Day 38: Sexual violence against women persists despite existing legal frameworks. Identify the factors contributing to this social attitude and suggest measures to address the issue. (250 words)
Approach
- Briefly mention the persistence of sexual violence against women in India.
- Identify the factors contributing to this social attitude.
- Suggest measures to address the issue.
- Conclude suitably.
Introduction
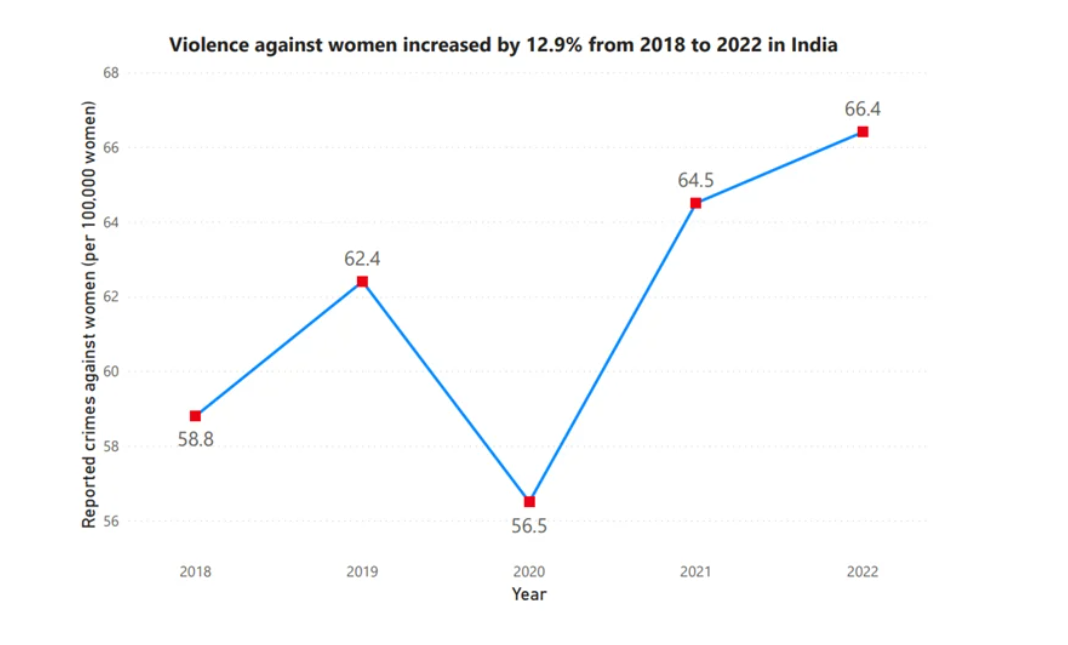
Sexual violence against women continues to be a pervasive issue in India, despite the existence of robust legal frameworks designed to protect women.The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) reported 445,256 cases of crime against women in 2022.The National Family Health Survey-5 found that nearly one-third of women aged 15-49 in India have experienced some form of violence.
Body
The Key Factors Contributing to this Social Attitude :
- Patriarchal Norms:
- India's patriarchal society promotes the idea of male dominance and female subordination.
- These norms perpetuate a sense of entitlement among men, leading to behaviors that devalue women and justify violence against them.
- This ingrained belief system often manifests in the control over women’s bodies and choices, fueling sexual violence.
- Victim-Blaming Attitudes:
- Society often questions the behavior, attire, or actions of the victim rather than holding the perpetrator accountable.
- This attitude discourages victims from reporting crimes and perpetuates a culture of silence and impunity.
- Economic Dependence:
- Women who are financially dependent on their abusers may find it difficult to leave abusive relationships, even if legal protections are in place.
- Inadequate Implementation of Laws:
- Strict laws enacted after the 2012 Nirbhaya case, like the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2013, enforcement remains inconsistent across different regions and police jurisdictions.
- Implementation of regulations, like establishing Internal Complaints Committees (ICC) in organizations, remains inadequate.
- Delays in Judicial Process :
- Delays in the judicial process, lack of sensitivity among law enforcement officers, and inadequate support systems for victims undermine the effectiveness of these legal frameworks, allowing perpetrators to evade justice.
- Lack of Education and Awareness:
- The lack of proper education and awareness about gender equality and women’s rights contributes to the persistence of regressive attitudes.
- Without education that challenges traditional gender roles, individuals continue to internalize harmful stereotypes that perpetuate violence against women.
Measures to Address the Issue:
- Education and Awareness Programs:
- Implementing comprehensive sex education and gender sensitization programs in schools and communities is essential.
- These programs should focus on challenging patriarchal norms, promoting respect for women, and educating both men and women about gender equality and consent.
- Strengthening Law Enforcement:
- Enhancing the training of police officers and judicial personnel to handle cases of sexual violence with sensitivity and urgency is crucial.
- Establish fast-track courts and enhance punishment for grave cases like rape, as recommended by Justice Verma Committee. Increase women's representation in the judiciary.
- Monitoring Mechanisms :
- Strengthen the monitoring mechanisms to ensure compliance with existing laws such as the PoSH Act, 2013. Regular audits and reports should be mandated to track effectiveness and compliance.
- Safe City Designs:
- Integrating safety features into urban planning, such as improved street lighting and secure public spaces.
- Support Systems:
- Strengthen support systems for victims, including counseling services and legal aid. Ensure victims have access to resources without additional barriers.
- Media and Public Campaigns:
- National campaigns that promote positive portrayals of women, challenge harmful stereotypes, and raise awareness about the consequences of sexual violence can help shift societal norms and reduce the prevalence of such violence.
Conclusion
Addressing sexual violence against women in India requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond legal solutions to tackle the underlying social attitudes that perpetuate such violence. By changing societal attitudes through education, effective law enforcement, community support, and media engagement, we can create an environment where women are respected, valued, and safe. The collective effort of society is essential in ensuring that sexual violence becomes a relic of the past, rather than a persistent reality.