-
30 Jul 2024
GS Paper 2
Polity & Governance
Day 20: By setting clear service standards and making them publicly known, Citizens' Charters help bridge the gap between government promises and citizen expectations. Discuss (150 words)
Approach
- Define Citizens' Charters and their purpose
- Discuss the role of the Citizen Charter in outlining the right
- Mention challenges in implementing and adhering to Citizens' Charters
- Suggest measures to enhance the effectiveness of Citizens' Charters
- Conclude Suitably
Introduction
A Citizens' Charter represents the commitment of the Organisation towards standard, quality and time frame of service delivery, grievance redress mechanism, transparency and accountability. By setting clear service standards and making them publicly known, Citizens' Charters play a crucial role in bridging the gap between government promises and citizen expectations.
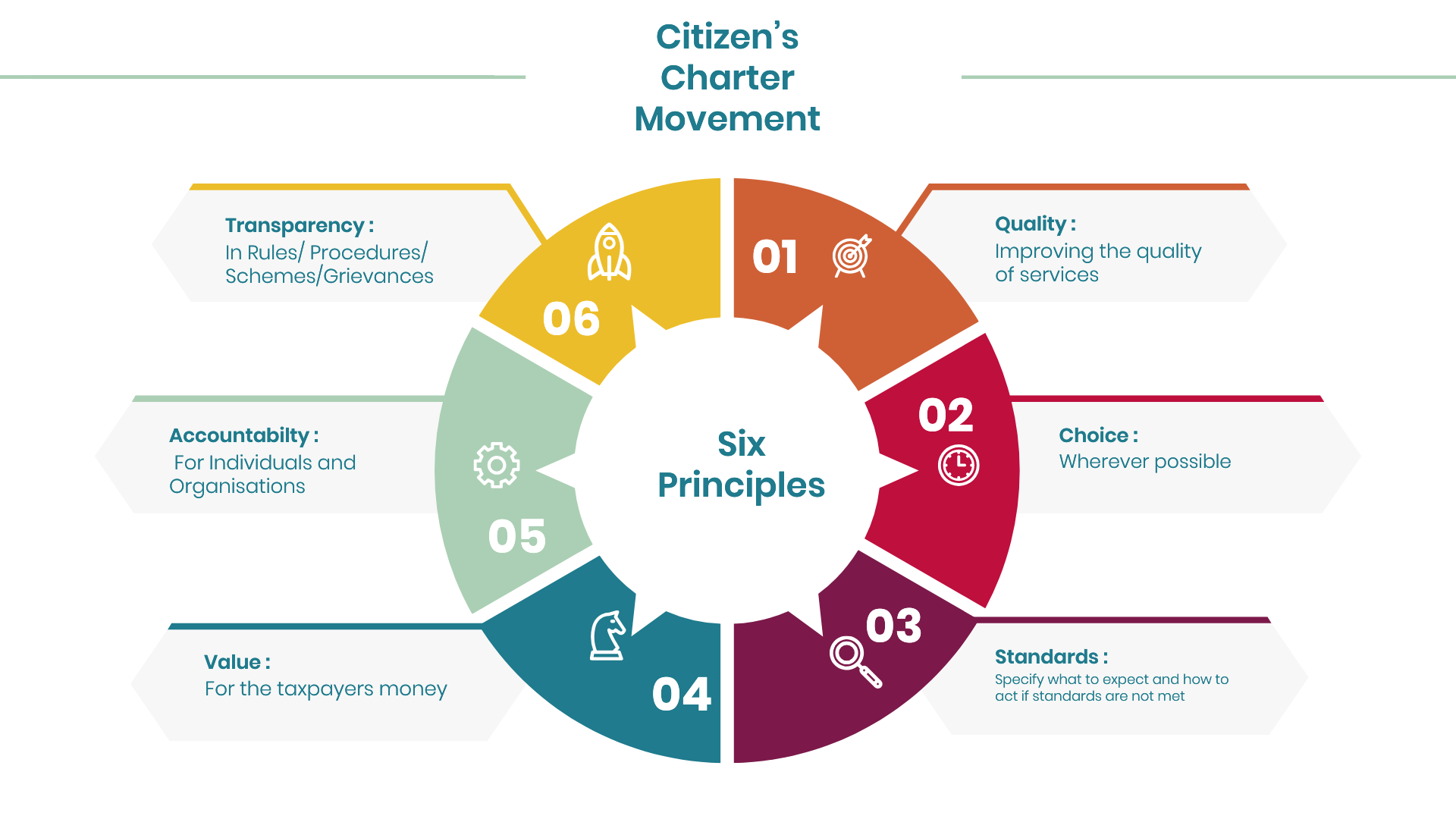
Body
The Charters are expected to incorporate the following elements:
- Vision and Mission Statement
- Details of Business transacted by the Organisation
- Details of clients
- Details of services provided to each client group
- Details of grievance redressal mechanism and how to access it
- Expectations from the clients
Rationale behind formulating a Citizen’s Charter
- Agreement Between Citizens and Service Providers: A Citizen's Charter represents an agreement between citizens and public service providers regarding the quantity and quality of services in exchange for taxes.
- Rights of the Public: Since public services are funded by citizens, they have the right to expect high-quality, efficient, and cost-effective services.
- Written Declaration: The Charter is a voluntary, written declaration by service providers that outlines standards for service quality, choice, accessibility, non-discrimination, transparency, and accountability.
- Promoting Good Governance: It serves as a tool to ensure transparency and accountability, promoting good governance when rigorously implemented by government departments.
- Citizen Centric : The Charter should align with the expectations of citizens and define the nature of service provision and explicit service delivery standards.
- Changing Mindset : It aims to transform the mindset of public officials from wielding power over the public to fulfilling their duty in spending public funds wisely and providing essential services.
- No One-Size-Fits-All Approach : The Charter is not a uniform template but a toolkit of initiatives to enhance service standards and encourage public participation in a suitable manner.
- Potential Benefits: Successful implementation of the Charter can lead to improved service delivery, increased responsiveness of officials to the public, and greater public satisfaction with services.
The implementation of Citizen's Charters in India faces several key challenges:
- Nascent Implementation: The Citizen's Charters initiative in India started in 1997, and most of the Charters were in the early stages of implementation.
- Resistance to Change: Introducing new concepts in government organisations is challenging, particularly due to the traditional bureaucratic setup and rigid attitudes of the workforce.
- Unrealistic Standards: Some Charters contained service standards and time norms that were either too lenient or too strict, creating unrealistic expectations and leaving clients dissatisfied.
- Lack of Genuine Engagement: Many organisations formulated Citizen's Charters primarily because of top-down directives, with minimal or no meaningful consultation. This led to a lack of focus and commitment to the initiative.
- Training and Orientation: Successful Charter implementation requires well-trained and sensitised employees who understand the spirit and content of the Charter. In many cases, the staff lacked proper training and orientation.
- Inadequate Awareness Campaigns: Systematic awareness campaigns to educate clients about the Charter were not consistently conducted, limiting the public's understanding of the initiative.
Conclusion
The 12th Report of the 2nd Administrative Reforms Commission (ARC) in India emphasizes the need for effective Citizens' Charters by recommending clarity in remedies for non-compliance, internal restructuring of processes, and a tailored approach that considers the unique capabilities of different agencies. It advocates for wide consultations in the formulation process, precise and quantifiable commitments regarding service delivery, and robust grievance redressal mechanisms to enhance accountability and service quality.




