-
25 Jul 2024
GS Paper 2
Polity & Governance
Day 16: The Parliamentary Committee system is an indispensable part of the legislative process in India.Comment. (150 words)
Approach
- Provide a brief introduction to the Parliamentary Committee system in India.
- State the importance of the committee system in enhancing the effectiveness of the legislative process.
- Mention the challenges faced by the Committee System.
- Conclude Suitably.
Introduction
The Parliamentary Committee system in India is a vital component of the legislative framework that facilitates the effective functioning of Parliament. It consists of various committees composed of Members of Parliament (MPs) from both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha. These committees are tasked with specific responsibilities, including scrutinizing legislation, examining government policies, and overseeing the implementation of programs and budgets.
Body
Parliamentary Committees in India are categorized into several types:
- Standing Committees: These committees operate continuously and are responsible for specific areas. Based on the nature of functions performed by them, standing committees can be classified into the following six categories:
- Financial Committees
- Departmental Standing Committees
- Committees to Inquire
- Committees to Scrutinise and Control
- Committee on Government Assurances
- Committees Relating to the Day-to-Day Business of the House
- House-Keeping Committees or Service Committees
- Select Committees: Temporary committees formed to examine particular bills or issues in depth.
- Joint Committees: Comprising members from both the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, these committees focus on specific matters requiring a comprehensive approach.
- Ad hoc Committees: Formed for a specific task and dissolved once their objective is achieved.
The committee system is indispensable for several reasons:
- Scrutinizing Legislation: Committees analyze bills and propose amendments, ensuring that legislation is comprehensive and practical.
- For instance, the Committee on Human Resource Development reviews education bills, such as the National Education Policy, and suggests amendments to improve educational standards and access.
- Examining Government Policies: Committees review the implementation of government programs and policies, assessing their effectiveness and impact on citizens.
- The Committee on Health and Family Welfare examines health initiatives like the Ayushman Bharat scheme, analyzing its implementation and outreach to ensure that it effectively addresses healthcare needs.
- Conducting Inquiries: Committees investigate issues of public concern, such as corruption, maladministration, and violations of rights, holding the government accountable for its actions.
- The Public Accounts Committee (PAC) plays a significant role in examining the financial accounts of the government, investigating instances of financial irregularities, and ensuring transparency in the use of public funds.
- Budget Review: Committees scrutinize budget proposals, ensuring transparency and accountability in financial matters.
- The Committee on Finance reviews the annual budget presented by the Ministry of Finance, assessing revenue and expenditure proposals, and providing recommendations to improve fiscal management and accountability.
- Enhanced Efficiency: By allowing detailed examination of issues, committees can manage complex matters that would be time-consuming in a full House setting.
- For example, the Committee on External Affairs can hold hearings on international treaties and agreements, enabling in-depth discussions that are not feasible in the larger parliamentary setting.
- Expertise and Specialization: Members can focus on specific areas, contributing informed perspectives and enhancing the quality of legislative scrutiny.
- The Committee on Agriculture, consisting of members with expertise in farming and rural issues, reviews policies related to agricultural production and farmer welfare, ensuring that legislative decisions are well-informed.
- Public Accountability: Committees play a critical role in holding the government accountable, ensuring that public resources are utilized effectively.
- The Committee on Social Justice and Empowerment monitors programs aimed at uplifting marginalized communities, ensuring that funds are used appropriately and that beneficiaries receive the intended support.
- Facilitating Dialogue: Committees provide a platform for discussion between members of different parties and stakeholders, fostering collaboration and consensus-building.
- The Committee on Transport, Tourism and Culture conducts consultations with various stakeholders, including state governments and industry representatives, to develop comprehensive policies that benefit multiple sectors.
Despite its importance, the committee system faces several challenges:
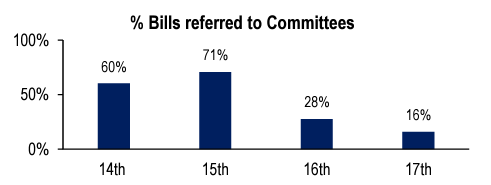
- Less than 20% of Bills were Referred to Committees in the 17th Lok Sabha: 16% of Bills were referred to Committees for detailed scrutiny. This is lower than the corresponding figures for the previous three Lok Sabhas.
- Recommendatory Nature: The committees do not have adequate powers to enforce their recommendations. The government is not bound to accept or implement them. The committees also do not have any follow-up mechanism to track the status of their recommendations.
- Shortage of Time and Resources: The committees have to deal with a large number of bills and issues within a limited time frame. They often lack sufficient staff, research support, data, and information to undertake comprehensive studies.
- Low attendance of MPs: The attendance of MPs at the committee meetings is often low due to various reasons such as conflicting schedules, political pressures, lack of interest, or incentives.
Conclusion
To enhance their efficiency, it is crucial to increase budgetary support, strengthen research capabilities, encourage public participation, and provide regular training for committee members. Ensuring that committees work collaboratively on cross-cutting issues can enhance their effectiveness and impact.