-
15 Aug 2024
GS Paper 3
Internal Security
Day 34: India is situated between the Golden Crescent and the Golden Triangle, making it vulnerable to drug trafficking. Discuss the challenges in addressing this issue and evaluate the government initiatives implemented to combat drug trafficking in India. (250 words)
Approach
- Give a brief introduction about Golden Crescent and Golden Triangle
- Mention the challenges in addressing the issue of drug trafficking
- State the initiatives taken by government to combat drug trafficking
- Give suggestions to combat drug trafficking
- Conclude suitably
Introduction
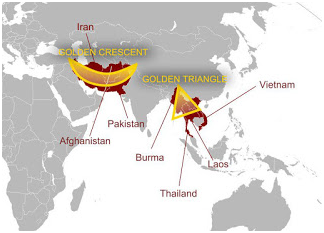
India's geographical location between two major drug-producing regions, the Golden Crescent and the Golden Triangle, significantly exacerbates its vulnerability to drug trafficking and abuse. The Golden Crescent, comprising Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan, is a key global hub for opium production, directly impacting Indian states like Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Gujarat due to their proximity to the Indo-Pakistan border.
Similarly, the Golden Triangle, which includes parts of Laos, Myanmar, and Thailand, is notorious for the production and trafficking of heroin, with Myanmar alone accounting for 80% of the world's heroin supply. These regions not only serve as the source of illicit drugs but also use India as a transit route, posing serious challenges to the nation's internal security and public health.
Body
Challenges in addressing the issue of drug trafficking in India
- Inadequate Infrastructure and Resources: Shortage of trained personnel, specialized equipment, and facilities impedes effective drug control.
- This includes insufficient resources for addressing emerging psychoactive substances not covered by existing laws.
- High Demand and Social Stigmatization: The large population creates high demand for drugs, while social stigma discourages individuals from seeking treatment, complicating prevention and rehabilitation efforts.
- Narcoterrorism and Cross-Border Smuggling: Complex interactions between terrorist organizations and drug trafficking networks, particularly along porous borders with Myanmar and Pakistan.
- For example, 15% of narcotics trade revenue was used to finance terrorism in Kashmir, with drugs and weapons smuggling routes frequently used by both terrorists and smugglers.
- Increased Production and Trafficking Routes: Surge in drug production in neighboring countries like Myanmar, which produced 1,080 metric tonnes of opium in 2023, and Afghanistan, which saw increased opium production despite a Taliban ban.
- Drugs are trafficked through maritime routes and porous borders, with significant seizures reported, including 2,826 kg of drugs seized in 2023 and a major intersection of 3,132 kg of drugs in February 2024.
- Emerging Smuggling Techniques: Use of advanced smuggling techniques such as drones and underwater drones, with incidents of drones carrying drugs being reported along the India-Pakistan border and other maritime routes.
- Dark Net and Cryptocurrency: Rising use of the dark net and cryptocurrencies for drug trafficking.
- In 2020, 2021, and 2022, the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) investigated 59 cases involving these technologies.
Government initiatives to Combat Drug Trafficking
- Legislative Measures:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985: Prohibits production, possession, sale, purchase, transport, storage, and consumption of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (2018-2025):
- Preventive education and awareness generation.
- Identification, counseling, treatment, and rehabilitation of drug-dependent individuals.
- Training and capacity building for service providers through government and NGO collaboration.
- National Fund for Control of Drug Abuse:
- Created under the NDPS Act to fund:
- Combating illicit trafficking.
- Controlling drug abuse.
- Identifying, treating, and rehabilitating addicts.
- Preventing drug abuse.
- Public education against drug abuse.
- Created under the NDPS Act to fund:
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Campaign (2020):
- Aims to make India drug-free through:
- Supply reduction efforts by the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB).
- Outreach, awareness, and demand reduction by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- Treatment and rehabilitation through the Health Department.
- Aims to make India drug-free through:
- Initiatives of Indian Coast Guard:
- Collaboration with security agencies and coast guards of neighboring countries (Sri Lanka, Maldives, Bangladesh) for drug seizures.
- Recent seizures include 2,160 kg of methamphetamine near Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- International Treaties and Conventions:
- India is a signatory to:
- UN Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961).
- UN Convention on Psychotropic Substances (1971).
- UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (1988).
- UN Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (2000).
- India is a signatory to:
Way Forward
- Enhanced Enforcement and Legal Measures:
- Strengthen cross-border trafficking controls and improve drug enforcement.
- Consider imposing stricter punishments under the NDPS Act, 1985, to deter drug-related offenses.
- Demand Reduction and Public Awareness:
- Increase public awareness through campaigns and NGOs, and work to reduce the stigma associated with drug addiction.
- Recognize drug addicts as victims needing support rather than criminals.
- Increase public awareness through campaigns and NGOs, and work to reduce the stigma associated with drug addiction.
- Integrated Approach and Socioeconomic Solutions:
- Incorporate drug education into school curricula and provide proper counseling. Coordinate efforts among all agencies, and create more employment opportunities to address the root causes of drug abuse.
Conclusion
In conclusion, India’s efforts to combat narcoterrorism must evolve with the changing tactics of drug traffickers and terrorist organizations. Strengthening legal frameworks, enhancing forensic capabilities, and improving international cooperation are crucial for disrupting narcotic supply chains and financial networks. A comprehensive risk-mitigation approach, including targeted legislation and regional coordination, is essential to safeguarding national security and effectively addressing the complex challenge of drug trafficking.