-
16 Aug 2024
GS Paper 3
Internal Security
Day 35: Discuss the challenges and the strategies required for effective border management in India. (150 words)
Approach
- Briefly introduce the importance of border management in India
- Discuss the diverse challenges posed by India’s extensive land and maritime boundaries.
- Explain the strategies required for effective border management in India.
- Conclude Suitably.
Introduction
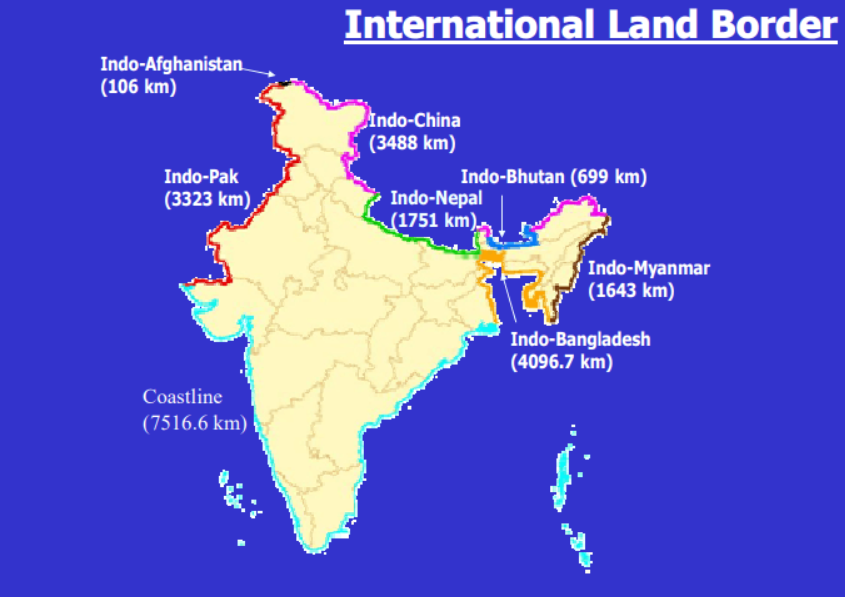
Border management is a security function that aims to secure our frontiers and safeguard our nation from the risks involved in the movement of goods and people from India to other countries and vice versa. India has 15,106.7 Km of land border and a coastline of 7,516.6 Km including island territories.
Body :
The Diverse Challenges in Managing Indian Borders:
- Indo-Pak Border Challenges:
- Cross-Border Terrorism: It stands out as one of the major reasons for disaccord between India and Pakistan.
- Infiltration: Political instability and crisis in Pakistan also lead to an upsurge in cross-border infiltration and threats due to terrorism.
- Indo-China Border Challenges:
- Not Clearly Demarcated: The border between India and China is not clearly demarcated throughout and there is no mutually agreed Line of Actual Control (LAC) along certain stretches.
- Border Confrontations: Border confrontations have occurred in different instances, including Demchok in 2014, Depsang in 2015, Doklam in 2017, and the Galwan incident in 2020.
- Indo-Bangladesh Border Challenges:
- Illegal immigration: Due to the porosity of the border, the primary challenge has been the influx of illegal immigrants in India.
- Smuggling: A Major challenge with this part of the Indian border is the smuggling of arms, ammunition and drugs.
- Indo-Nepal Border Challenges:
- Open Borders: Open borders lead to illegal activities such as smuggling of drugs, stolen vehicles and arms and ammunition into India.
- Indo-Myanmar Border Challenges:
- Drug Trafficking: Insurgents are extensively involved in drug trafficking, especially in areas such as Moreh in Manipur and Golden Triangle covering Northern Thailand, Laos and Myanmar.
- Insurgency: The open border and cross-ethnic ties among the tribal community help insurgents escape from the hands of the border security forces.
- Long Coastline: India has a long coastline of over 7,000 km, which makes it vulnerable to various threats such as piracy, terrorism, smuggling, illegal fishing, and environmental degradation.
- India needs to protect its coastal and offshore assets, such as oil and gas installations, fishing grounds, and ports, from these threats.
- Zero-Sum Competition in the Indo-Pacific:
- The perceived zero-sum competition among powerful nations in the Indo-Pacific is identified as a threat, particularly for Indian interests.
The Strategies Required for Effective Border Management in India :
- Infrastructure Development: To enhance border security, there is a need for robust infrastructure, including all-weather roads, border fencing, and integrated check posts (ICPs). Improved infrastructure will facilitate better patrolling, quicker mobilization of forces, and more efficient management of border areas.
- For instance, the length of roads constructed in the China border areas in the period from 2014 to 2022 (6,806 km) is almost double the length constructed from 2008-2014 (3,610 km).
- Use of Technology: Adopting advanced surveillance technologies such as drones, satellite imagery, thermal sensors, and radars is crucial for effective border monitoring. These technologies can help in real-time detection of infiltrations and illegal activities, allowing for prompt action.
- Two pilot projects covering about 71 Kms on Indo-Pakistan Border (10 Kms) and Indo-Bangladesh Border (61 Kms) of Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS) have been completed.
- Strengthening Border Forces:
Border security forces should be provided with modern equipment, better training, and improved welfare measures. This will enhance their operational capabilities and morale, enabling them to handle the challenges of border management more effectively. - Cross-Border Cooperation (CBC): It includes information sharing and collaborative approach between neighboring countries for border security for issues such as human trafficking, arms or drugs smuggling, terrorist threats, etc.
- Development of Border Areas: The government initiated the Border Area Development Program (BADP) in 1987 to facilitate the provision of the required socio-economic infrastructure and adequate security.
- Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP) was launched for comprehensive development of the select villages in 19 districts of abutting the northern border in the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand and UT of Ladakh.
Conclusion
Effective border management is vital for India's national security and regional stability. The challenges are significant, but with a holistic approach that includes infrastructure development, technological advancements, community engagement, and diplomatic efforts, these challenges can be overcome. A coordinated and comprehensive strategy is essential to ensure the safety and security of India's borders.