-
13 Aug 2024
GS Paper 3
Bio-diversity & Environment
Day 32: Desertification is a silent crisis in India that requires sound action. Comment.(150 words)
Approach
- Define desertification and highlight the current status of desertification in India.
- Discuss the factors that are leading to desertification in India.
- Suggest measures to tackle desertification.
- Conclude Suitably.
Introduction
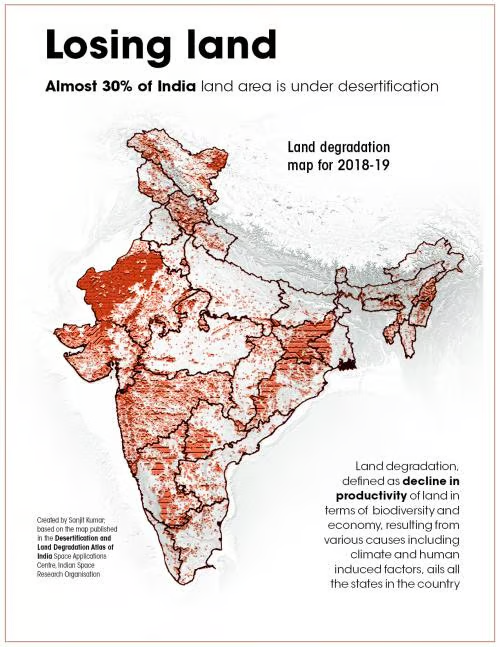
Desertification refers to the process by which fertile land becomes increasingly arid and unproductive due to various factors, including climate change, deforestation, overgrazing, and unsustainable agricultural practices. Desertification is a silent crisis gripping India with a staggering 25% of its landmass undergoing this process. Currently, 97.85 million hectares (mha) of land — an area 2.5 times the size of India’s largest state Rajasthan— has already been degraded.
Body
The Factors that are Leading to Desertification in India :
- Deforestation and Forest Degradation: India's insatiable appetite for timber and land for agriculture and settlement has led to rampant deforestation.
- According to a recent report by the IISc.’s Energy and Wetlands Research Group, Western Ghats lost 5% evergreen forest cover.
- Overexploitation of Groundwater: Excessive extraction of groundwater for irrigation and industrial purposes depletes water tables, leading to land subsidence and reduced soil moisture.
- India is the largest groundwater user in the world, with an estimated usage of around 251 bcm per year, more than a quarter of the global total.
- Salinity Ingress in Coastal Areas: In coastal regions like Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, the intrusion of seawater into groundwater aquifers and agricultural lands has led to soil salinization and reduced productivity.
- As per an estimate 627 villages of Saurashtra and Kutch region are highly affected by salinity ingress.
- Mining and Industrial activities: Unregulated mining and industrial operations have resulted in soil contamination, air pollution, and the degradation of surrounding lands, contributing to desertification.
- The mining activities in the Jharia coalfields of Jharkhand have led to land subsidence, soil contamination, and desertification in the surrounding areas.
- Urbanization and Infrastructure Development: Rapid urbanization and the construction of large-scale infrastructure projects, such as highways, airports, and industrial corridors, have led to the loss of productive agricultural lands and the disruption of natural ecosystems, exacerbating desertification.
- The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor project, spanning across several states, has resulted in the acquisition of vast tracts of fertile land, contributing to land degradation and desertification in the surrounding areas..
Measures to Tackle Desertification in India :
- Promote Agroforestry and Reforestation with Native Species: Implementing large-scale agroforestry initiatives, integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural systems, to restore soil fertility, reduce erosion, and create microclimate conditions that combat desertification.
- Successful agroforestry initiatives in Niger, Mali, Burkina Faso, Senegal, Ethiopia, and Malawi can be a prominent model.
- Seed Biopriming and Seed Encapsulation: Developing and promoting the use of seed biopriming techniques, which involve treating seeds with beneficial microorganisms to improve seed viability and water-use efficiency in desertified areas.
- Fog Harvesting Nets: Installing specialized mesh nets in arid regions to capture moisture from fog. The collected water can then be used for irrigation purposes or to support native vegetation, promoting plant growth and reversing desertification trends.
- Biosaline Agriculture and Halophyte Cultivation: Investing in research and development of biosaline agriculture, which involves cultivating salt-tolerant crops (halophytes) in saline or degraded soils.
- Halophytes like Salicornia and Atriplex can be grown for food, fodder, and biofuel production, providing economic opportunities in desertified regions.
- Establishing Desertification Adaptation Zones: Identifying and designating specific areas as "Desertification Adaptation Zones," where targeted interventions, such as sustainable agriculture practices, soil conservation measures, and ecosystem restoration, are strictly implemented.
- Providing incentives and support to local communities within these zones to encourage their active participation in desertification control efforts.
- Establish Desertification Early Warning Systems: Develop advanced monitoring and early warning systems that integrate remote sensing, ground-based sensors, and environmental data to detect and predict desertification trends in various regions.
- Using this information to guide decision-making and implement timely interventions can mitigate the impacts of desertification.
- Desert Tourism with a Conservation Focus: Designing responsible desert tourism programs that raise awareness about desertification and generate revenue for local communities.
- These programs can incentivize conservation efforts and promote sustainable practices within the tourism industry.
Conclusion
At the 14th Conference of Parties (COP-14) to the UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), participating countries including agreed to set achieving land degradation neutrality by 2030 as a national target.By implementing sustainable practices and policies, India can combat desertification, safeguard its natural resources, and ensure a more secure future for its population.