-
10 Aug 2023
GS Paper 4
Theoretical Questions
Day 22: What is your understanding of good and ethical governance? What steps/processes would you like to suggest for resolving conflicts of interest in good governance? (150 words).
- Introduce the answer by defining Good Governance and ethical Governance with examples.
- Explain Conflict of Interest and suggest steps or processes for resolving conflicts of interest in good governance.
- Conclude suitably with way forward.
Answer
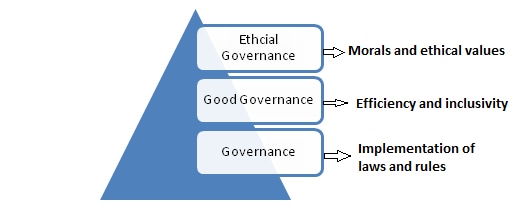
Good governance refers to streamlining the implementation of policies and programes in an efficient and inclusive manner while addressing the grievances of people effectively. For example, use of e-governance applications to remove red-tapism and enhanced transparency and efficiency, simultaneously reducing corruption and nepotism.
Ethical governance is a way of governing which infuses high standards of moral values and behaviour in the governance process. For example, a bureaucrat is bound to serve the people that come to his office, but he couldn't be penalized if he doesn't make provisions for a glass of water for an elderly couple who might be tired after waiting too long in the queue. Those will be the ethics of public service and altruism that will make him do that.
Good governance forms the foundation for ethical governance, which is essential for establishing trust and cooperation between citizens and public servants.
Conflicts of interest are situations where a public official’s private interests may influence or appear to influence the performance of their official duties and responsibilities. Conflicts of interest may undermine public trust and confidence in government and compromise the quality and integrity of public decision-making. Therefore, resolving conflicts of interest is an essential aspect of good and ethical governance.
Some steps or processes that can be suggested for resolving conflicts of interest in good governance are:
- Establishing a legal framework to regulate conflicts of interest for public officials, with sanctions for violations, consistent with constitutional principles, human rights norms, and international standards.
- For example, the UN Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) is a global treaty that obliges its signatories to adopt measures to prevent and combat corruption, including conflicts of interest.
- Implementing an institutional mechanism with independent bodies to oversee, investigate, and enforce compliance. For example, the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) in India is an apex body that exercises superintendence over the vigilance administration of various central government departments and undertakings.
- Developing competent personnel through efficient management policies based on merit and ethics. The 2nd ARC in India recommended various reforms in civil service management to enhance accountability, transparency, and professionalism.
- Adopting policies for delegation, decentralization, and accountability to empower officials. For example, the RTI Act 2005 in India enables citizens to access information held by public authorities and hold them accountable for their functioning.
- Facilitating citizen participation through tools like Citizens' Charters. The Citizens’ Charters in India are documents that specify the standards, quality, quantity, and time frame of service delivery by public authorities to citizens.