-
02 Sep 2023
GS Paper 1
Geography
Day 42: Examine the role of plate tectonics in the occurrence of earthquakes and the formation of various types of seismic zones across the world. (250 words)
- Start with a brief introduction to the plate tectonics. Mention that it is a fundamental concept in geology and that it explains the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates.
- Discuss how plate tectonics influence earthquakes and seismic zones.
- Conclude by emphasizing the significance of plate tectonics.
Answer:
Plate tectonics play a crucial role in the occurrence of earthquakes and the formation of various types of seismic zones across the world. The plate tectonics theory explains how the Earth's lithosphere is divided into several large and small plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them. These plates are in constant motion, and their interactions at plate boundaries are responsible for the majority of earthquakes and seismic activity on our planet.
How do plate tectonics influence earthquakes and seismic zones?
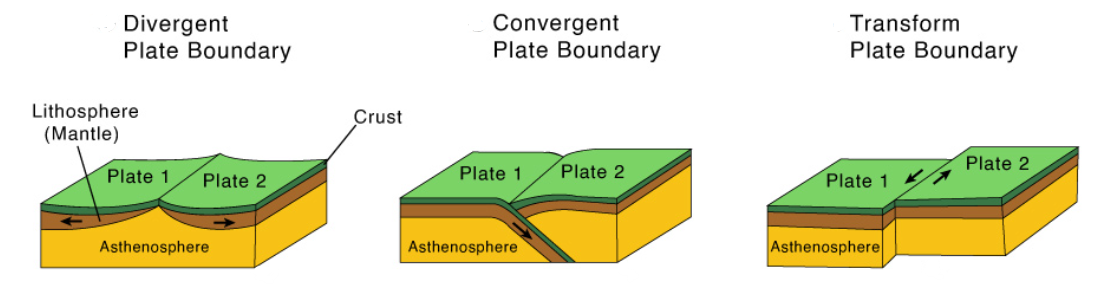
1. Plate Boundaries and Earthquake Generation:
- Convergent Boundaries: At convergent plate boundaries, two plates are moving toward each other. This collision can result in subduction, where one plate sinks beneath the other, leading to intense pressure and the release of energy in the form of earthquakes. Subduction zones are some of the most seismically active areas on Earth, with deep-focus and shallow-focus earthquakes occurring.
- Divergent Boundaries: At divergent plate boundaries, two plates are moving away from each other. As they separate, the Earth's crust can crack and create fractures. Magma from the mantle can then rise to fill these gaps, leading to volcanic activity and associated seismic events.
- Transform Boundaries: At transform plate boundaries, two plates slide past each other horizontally. The friction between these plates prevents them from smoothly sliding, and when the stress overcomes the friction, it can result in earthquakes along transform faults. The San Andreas Fault in California is a well-known example.
2. Intraplate Earthquakes: While most earthquakes occur at plate boundaries, some also happen within the interior of a tectonic plate, known as intraplate earthquakes. These are often associated with ancient fault lines or regions of high stress within a plate. They are less common but can still be quite destructive.
3. Formation of Seismic Zones:
- Ring of Fire: The Pacific Ring of Fire is a horseshoe-shaped seismic belt that surrounds the Pacific Ocean. It is also known as the Circum-Pacific Belt. It is a convergent plate boundary, where the Pacific Plate and other smaller plates are subducting under the continental plates along the margins of Asia, Australia, North America, and South America. It is the most seismically and volcanically active zone in the world, with about 81% of our planet’s largest earthquakes and 75% of its active volcanoes.
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge: It is a purely oceanic seismic belt that lies along the boundary between the North American and Eurasian Plates, and the South American and African Plates. It is a divergent plate boundary, where the plates are moving away from each other, and new oceanic crust is being formed by volcanic eruptions. It is part of a global mid-ocean ridge system that encircles the Earth.
- Himalayan Seismic Zone: It is a belt of intense seismic activity that extends from Java and Sumatra, through the Indochinese Peninsula, the Himalayas and Trans Himalayas, the mountains of Iran, Caucasus, Anatolia, the Mediterranean, and out into the Atlantic. It is also known as the Alpine-Himalayan Orogenic Belt. It is the result of the collision between the northward-moving African, Arabian, and Indian Plates with the Eurasian Plate. It accounts for about 17% of the world’s largest earthquakes.
Plate tectonics are the fundamental drivers of earthquake activity and the formation of seismic zones across the world. Understanding these tectonic processes is crucial for predicting and mitigating the impact of earthquakes on human populations and infrastructure.