-
15 Aug 2022
GS Paper 1
Indian Society
Day 36: Slums in urban areas are a reality of mega cities. Do you agree that India’s urban development is yet to be inclusive? (250 Words)
- Define slums and give the data for Indian Slums.
- Discuss why India’s urban development is yet to be inclusive by stating the issues faced by slums.
- Mention schemes launched by Government of India to promote inclusive growth in urban areas.
- Write way forward.
Answer:
The UN operationally defines a slum as “one or a group of individuals living under the same roof in an urban area, lacking in one or more of the following five amenities”:
- Durable housing
- Sufficient living area
- Access to improved water
- Access to improved sanitation facilities; and
- Secure tenure
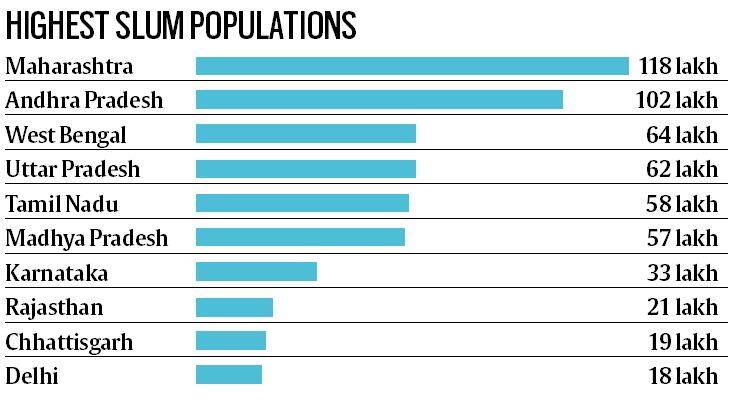
According to 2011 census, the slum population in India is roughly 65 million which is 17% of urban India and 5.4% of the total population of India. Maharashtra had a population of 1.18 crore living in slums in 2011, followed by Andhra Pradesh at nearly 1.02 crore. These two states accounted for more than one-third of India’s 6.55 crore slum population (2011 Census).
India’s urban development is yet to be inclusive as there are several challenges faced by Slums:
- Lack of Basic amenities: More than 90% of the housing shortage in urban India is faced by economically weaker sections and low-income groups. Only about 18% of slum areas have precarious access to piped water. Non-notified slums (which amounts to 60% of all slums) are completely deprived of water supply.
- Vulnerable to Diseases: People living in slum areas are also prone to suffer from waterborne diseases such as Typhoid and cholera, as well as from more fatal ones like Cancer and HIV/AIDS.
- Victims of Social Evils: Also, women and children living in slums are prone to become victims of social evils like prostitution, beggary and Child trafficking. Slum dwellers in general and regardless of gender, often become victims of such social evils.
- Incidence of Crime: Slum areas are also commonly believed to be places that generate a high incidence of crime. This is due to official neglect towards education, law and order, and government services in slum areas.
- Poverty: Then, the majority of slum dwellers in a developing country earn their living from the informal sector which neither provides them with financial security nor with enough earnings for a decent living, keeping them firmly within the vicious cycle of poverty.
Causes for the slum in Urban areas:
- Rural-urban migration: Many rural-urban migrant workers cannot afford housing in cities and eventually settle down in only affordable slums.
- Urbanization: Governments are unable to manage urbanization, and migrant workers, without an affordable place to live in, dwell in slums.
- Poor housing and planning: Lack of affordable low-cost housing and poor planning encourages the supply side of slums.
- Poverty: Urban poverty encourages the formation and demand for slums.
- Politics: Removal and replacement of slums created a conflict of interest, and politics prevented efforts to remove, relocate or upgrade the slums into housing projects that are better than the slums.
Schemes for Inclusive Urban Planning:
- Under the Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana-Urban, the government is targeting to complete 11.2 million houses in urban areas by 2022.
- AMRUT 2.0: It aims to provide 100% coverage of water supply to all households in around 4,700 ULBs (Urban Local Bodies). It is the continuation of the AMRUT mission launched in June 2015 to ensure that every household has access to a tap with the assured supply of water and a sewerage connection.
- Smart Cities Mission: It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, launched in June 2015 to transform 100 cities to provide the necessary core infrastructure and clean and sustainable environment to enable a decent quality of life to their citizens through the application of "Smart Solutions". The mission aims to meet the aspirations of India’s population living in cities through various urban development projects.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: SBM-U first phase was launched on 2nd October 2014 aiming at making urban India Open Defecation Free (ODF) and achieving 100% scientific management of municipal solid waste. It lasted till October 2019.
Way forward
- Segregated data are needed to make the slums inclusive in the context of urban poor.
- Further categorization of urban poor on the basis of basic survival needs, the security issue, and standards of living, such as core poor, intermediate poor and transitional poor, declining poor, coping poor, and improving poor, can be done only through reliably segregated data. Otherwise, creating such categories can further lead to the exclusion of the real target during prioritization.
- Thoughtful planning be done to rehabilitate the economic opportunities for these people.
Thus, Urban Development is to be inclusive as the issues of slums are a big problem in mega cities. If their challenges are not addressed properly, then development can't be called inclusive development.