Sansad TV Vishesh: Digital Payment Revolution | 02 May 2024
For prelims: Unified Payments Interface (UPI), digital transaction, Inclusive growth, Digital payments, Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM), UPI 123PAY, Jan Dhan bank accounts National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) Goods and Services Tax (GST), Digital wallet, Paytm, Direct benefit transfer (DBT) schemes, Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Internet of Things (IoT), Payment and Settlement Systems (PSS) Act 2007, Infrastructure, fiscal deficit, Foreign reserves, UPI (Unified Payments Interface)
For mains: Significance and challenges of Digital payment for Indian economy.
Why in News?
- Recently, India has witnessed a staggering surge in digital transactions with the phenomenal success of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
- During the fiscal year of 2023, India witnessed over 100 billion digital transactions occurring nationwide.
What are the Key Highlights?
- India accounts for 46% of all Digital payments in the world and UPI transactions now account for 80% of all digital payments in India.
- In 2012-13, there were 162 crore digital payments, this number has grown to 14,726 crore in 2023-24 till February.
- In 2022, the value of instant digital transactions was four times higher than the combined transactions in the United States, Britain, Germany, and France combined.
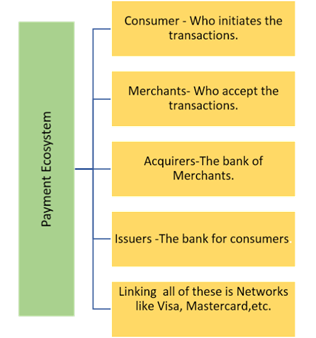
What is Digital Payment?
A digital payment system, also known as electronic payment, refers to the transfer of funds from one account to another through digital devices like mobile phones, POS terminals, or computers.
- Varieties of Digital Payment Modes include:
What are the Components of Digital Payments?
- JAM Trinity:
- Jan Dhan Accounts: Over 46 crore Jan Dhan bank accounts have been opened, with significant representation from women and rural areas.
- Aadhar: Nearly all adults possess a biometric identification number with over 1.3 billion IDs issued.
- Mobile: The accessibility of mobile phones has increased due to a significant drop in data costs since 2016.
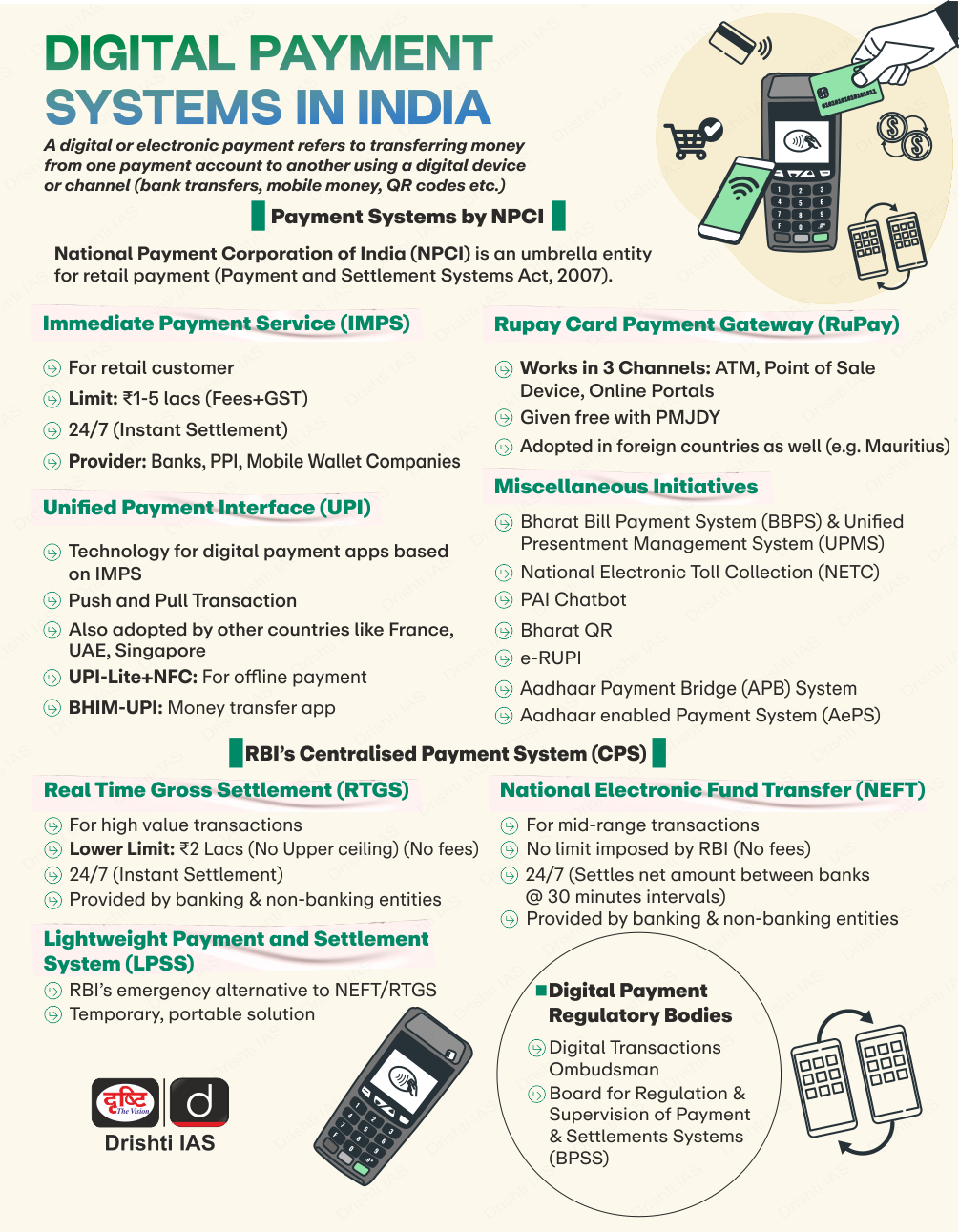
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI):
- Launched in 2016 by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), with 21 member banks, UPI is a public-private partnership that provides an interoperable platform for direct payments linked to bank accounts.
- An advanced version of Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), UPI manages multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application (of any participating bank), merging several banking features, seamless fund routing & merchant payments into one hood.
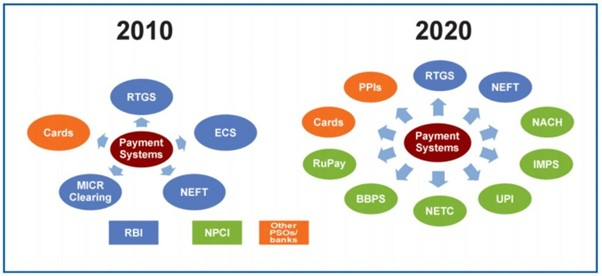
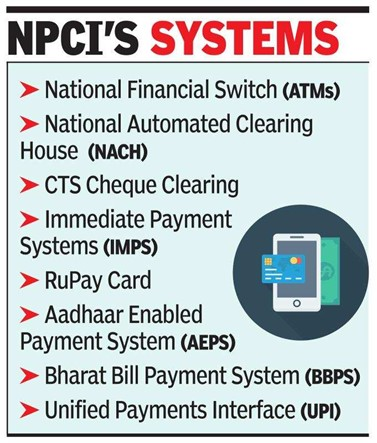
About NPCI
- The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) a not-for-profit company) is an initiative taken by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Indian Bank’s Association (IBA) to operate retail payments and settlement systems in India.
- This organisation was founded in the year 2008 under the Payment and Settlement Systems (PSS) Act 2007
- NPCI International Private Ltd (NIPL): NIPL is the subsidiary of NPCI to popularise domestic payment technologies such as UPI and RuPay abroad and co-create payment technologies with other countries.
What is the Significance of Digital Payment?
- Enhanced Convenience: Digital payments have made daily life more convenient for individuals.
- Financial Inclusion: It has expanded access to banking services, including credit and savings, to millions of previously unbanked Indians.
- Last Mile Access: Digital payments have extended the reach of government programs and tax collection, ensuring broader participation.
- Encouragement of Entrepreneurship: The digital infrastructure serves as a foundation for innovation, allowing entrepreneurs to innovate at a low cost.
- Behavioural Shift: There has been a significant change in behavior, with more people transitioning from a cash-driven economy to digital transactions.
- Decreased reliance on cash: Embracing a cashless economy promotes transparency and curtails the circulation of illicit funds.
- Augmented tax earnings: The uptick in digital transactions facilitates more efficient income tracking and bolsters tax collection efforts.
What are the Initiatives Taken for Digital Payments in India?
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI): The introduction of UPI revolutionised digital payments in India by enabling instant and seamless fund transfers between bank accounts using smartphones.
- RuPay Cards: It is an indigenous card payment network launched by NPCI, which provides a domestic alternative to international card schemes.
- It aims to promote digital payments and financial inclusion by offering affordable payment solutions.
- GST Network (GSTN): It facilitates digital payments by providing a unified platform for taxpayers to file their Goods and Services Tax (GST) returns and make tax payments online.
- Rise of Digital Wallets: Digital wallet services like Paytm, PhonePe, and Google Pay have gained immense popularity in India, offering users a convenient way to store money digitally and make payments for a wide range of goods and services.
- Government Subsidies and Benefits: Direct benefit transfer (DBT) schemes, where government subsidies and welfare payments are transferred directly to beneficiaries' bank accounts, have encouraged people to open bank accounts and adopt digital payment methods.
- Supportive Regulatory Environment: Regulatory reforms and incentives by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and other regulatory bodies have created a conducive environment for the growth of digital payments, ensuring security, interoperability, and consumer protection
What are the Challenges for Digital Payment in India?
- Digital Infrastructure: Despite significant improvements, access to reliable internet connectivity and electricity remains uneven, especially in rural areas, hampering the adoption of digital technologies.
- Digital Literacy: A large portion of the population lacks basic digital literacy skills, limiting their ability to use digital tools effectively and securely.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: With the increase in digital transactions, cybersecurity threats such as data breaches, identity theft, and financial fraud have become more prevalent, posing risks to individuals and businesses.
- Privacy Issues: There are concerns about the privacy and protection of personal data in the digital realm, particularly with the proliferation of social media platforms and digital services collecting vast amounts of user information.
- Digital Divide: Disparities in access to digital infrastructure, education, and economic opportunities exacerbate the digital divide between urban and rural areas, as well as among different socio-economic groups.
Way Forward
- RBI's Payments Vision 2025: Emphasizing the 5Is for Digital Payment Landscape- integrity, inclusion, innovation, institutionalization, and internationalization - essential for shaping the digital payment ecosystem.
- Enhancing Digital Literacy for Fraud Awareness: Digital education aims to equip citizens with knowledge about potential fraudulent practices encountered during digital transactions.
- Harnessing Technology: Develop a framework for Internet of Things (IoT) based payment systems, enabling customers to conduct transactions through connected devices beyond traditional smartphones and tablets.
- Reviewing Legal and Institutional Infrastructure for Payments: The RBI is initiating a comprehensive review of the Payment and Settlement Systems (PSS) Act 2007 to align it with India's evolving digital payment landscape.
- Driving Innovation and Regulatory Strength: Impact of Legislative Initiatives such as the new Digital Personal Data Protection Bill,2022 and Digital India Actl, 2023 are poised to stimulate growth and foster cutting-edge innovation in digital payments, both domestically and globally.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q Regarding ‘DigiLocker’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- It is a digital locker system offered by the Government under Digital India Programme.
- It allows you to access your e-documents irrespective of your physical location.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: C
Mains
Q. The emergence ofthe Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) hasinitiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)