Science & Technology
Sansad TV Special: India’s AI Readiness
- 03 Oct 2024
- 14 min read
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Machine Learning, National AI Strategy and the National AI Portal, Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Artificial Intelligence Mission, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), India's e-commerce sector.
For Mains: Role of AI in Indian Economy, Challenges and Suggestions.
Why in News?
India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has nearly doubled to USD 3.5 trillion in the past decade, showcasing the nation’s rapid economic growth. To sustain this momentum and drive transformative change, leveraging emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) is crucial.
- By integrating AI into key sectors, India can enhance productivity, foster innovation, and solidify its position as a global economic powerhouse.
What are the Key Highlights of India's AI Market?
- Growing Adoption Across Sectors: AI is increasingly integrated into various sectors in India, driven by initiatives like the National AI Strategy and the National AI Portal.
- Emphasis on Data Analytics: Companies are utilizing analytics to extract insights, enhance operations, and drive innovation, supported by initiatives like NASSCOM's AI for All program.
- Emerging AI Clusters: Major cities, including Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Chennai, Pune, and the National Capital Region (NCR), are developing AI clusters, fueled by supportive policies and academic institutions.
- Bengaluru, often called the "Silicon Valley of India," boasts over 2,000 startups and strong AI research, with over 400 patents filed annually.
- Research and Development: Indian institutions like IITs, ISI, and IISc are actively engaged in AI research, contributing to the global knowledge landscape.
- Investment Opportunities: There are significant prospects in India's AI market, such as using IoT for precision farming, enhancing fraud detection and risk assessment in banking, and employing AI for predictive diagnostics and personalized healthcare.
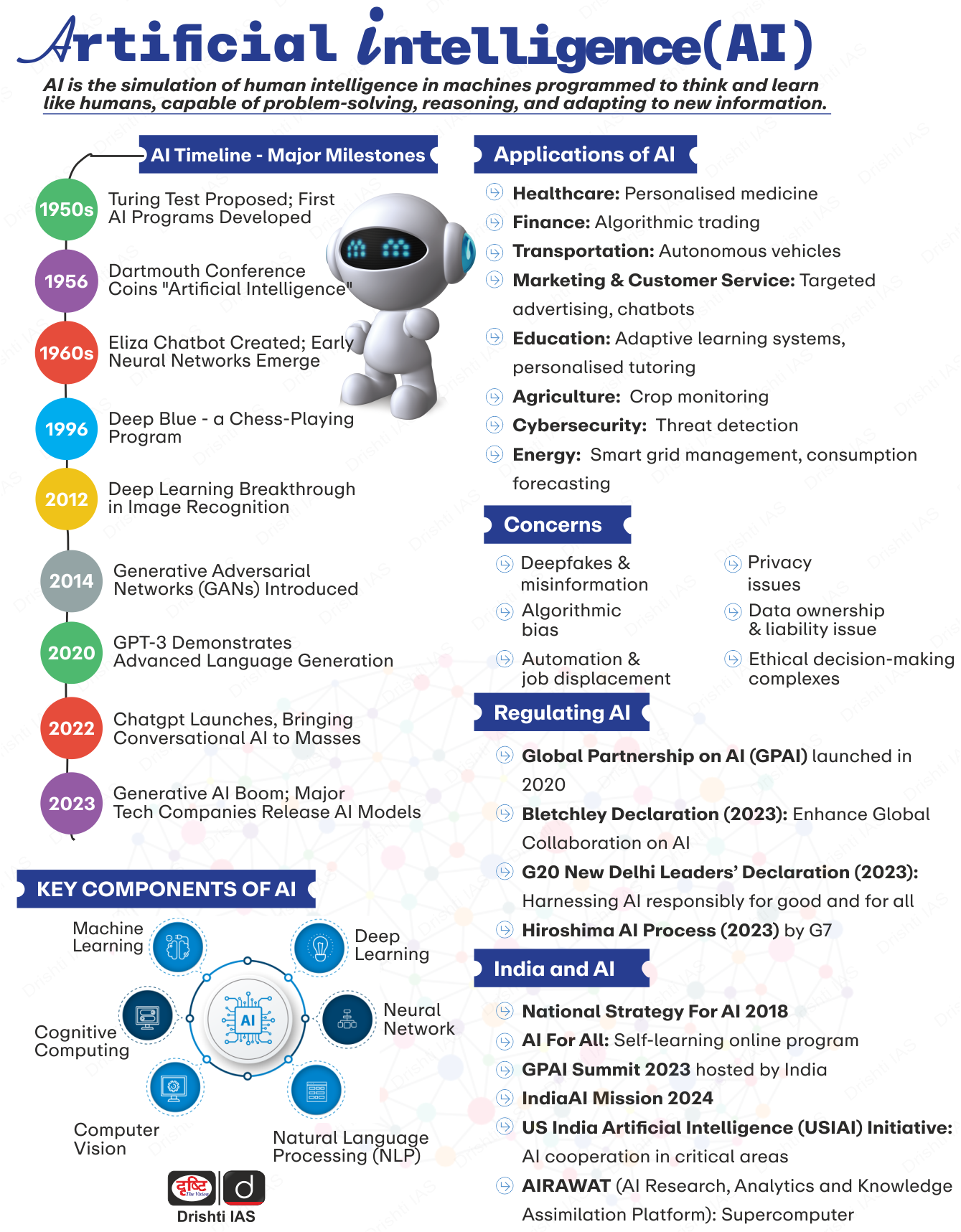
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- About: AI refers to the capability of machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, including learning, decision-making, and language understanding.
- Common applications include virtual assistants, predictive analytics, and robotics, which enhance the efficiency of devices by enabling them to learn from data.
- The phrase "Artificial Intelligence" was introduced by John McCarthy, an American computer scientist and cognitive scientist, who played a foundational role in establishing the field.
- Characteristics and Components:
- A key characteristic of artificial intelligence is its ability to rationalize and act to achieve specific goals effectively.
- Within AI, Machine Learning (ML) is a subset that allows systems to learn from data. Deep Learning (DL) techniques facilitate this process by enabling the analysis of large volumes of unstructured data, including text, images, and video.
- Types of AI:
- Reactive AI: Optimizes outputs based on inputs but does not learn from past experiences, like chess-playing AI.
- Limited Memory AI: Adapts based on past experiences with short-term memory, such as autonomous vehicles that learn from their environment.
- Theory-of-Mind AI: Fully adaptive systems capable of extensive learning and retention, exemplified by advanced chatbots that could pass the Turing Test.
- Self-aware AI: Hypothetical systems that would be sentient and aware of their existence, a concept still largely in science fiction.
- Differences Between AI, ML, and DL:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The simulation of human intelligence by machines.
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI that involves algorithms enabling computers to learn from data without explicit programming.
- Deep Learning (DL): A subset of ML using artificial neural networks to learn from data, mimicking human brain functions.
What is the Current Governance of Global AI?
- India: NITI Aayog has issued guiding documents like the National Strategy for AI and the Responsible AI for All report, focusing on social and economic inclusion, innovation, and trustworthiness.
- United Kingdom: The UK has adopted a light-touch approach, urging regulators to apply existing laws to AI. A white paper outlines five principles for companies: safety, transparency, fairness, accountability, and contestability.
- United States: The US introduced a Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights (AIBoR), highlighting the risks AI poses to economic and civil rights and offering sector-specific governance strategies for areas like health and education.
- China: In 2022, China implemented some of the first nationally binding regulations targeting algorithms, specifically regulating recommendation algorithms to control information dissemination.
What is the Role of AI in India’s Economic Growth?
- Banking and Finance:
- Financial institutions are increasingly using Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to automate repetitive tasks like data entry and compliance checks, potentially reducing operational costs by up to 25% (McKinsey).
- AI algorithms analyze transaction patterns to detect fraudulent activities.
- AI chatbots provide 24/7 customer support, with projections indicating they could save the banking sector USD 7.3 billion annually by 2023 (Juniper Research).
- Healthcare:
- AI is transforming India’s healthcare system by enhancing diagnostics and treatment options. For example, AI algorithms can analyze medical images to detect conditions such as tuberculosis and diabetic retinopathy more accurately and swiftly than traditional methods.
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) released a guiding document titled “The Ethical Guidelines for Application of AI in Biomedical Research and Healthcare,” which delineates 10 essential patient-centric ethical principles for implementing AI in the health sector.
- Personalized treatment plans, driven by AI, analyze patient data to recommend tailored therapies, improving patient outcomes. The Indian government’s initiatives, such as the Ayushman Bharat scheme, are further supported by AI, which enhances the efficiency of healthcare delivery and management.
- Agriculture:
- In agriculture, AI is vital for food security and boosting rural incomes.
- Precision farming uses AI to analyze satellite imagery and IoT data, optimizing crop management and irrigation.
- It also predicts pest outbreaks and enhances crop yield predictions, leading to better planning and reduced waste.
- These innovations are essential for increasing productivity and strengthening rural economic resilience in India.
- E-Commerce:
- India's e-commerce sector is booming, driven by AI. Machine learning enhances personalized shopping through tailored product recommendations, while AI optimizes supply chains by predicting demand and automating logistics.
- AI-driven marketing boosts customer engagement with targeted ads, improving conversion rates and brand loyalty. These innovations are essential for ongoing growth in the sector.
- Driving Innovation:
- AI fosters a culture of innovation across various industries by enabling startups and established businesses to develop new products and services.
- In India, the startup ecosystem has seen a surge in AI-driven ventures, from healthcare apps to fintech solutions.
- The NASSCOM report highlights that the AI sector is expected to contribute significantly to the economy, creating jobs and promoting diversification in economic activities.
- By fostering a supportive environment for innovation, India can leverage its young, tech-savvy population to remain competitive in the global market.
What are India's Initiatives Related to Artificial Intelligence?
What are the Challenges Associated with AI Indian Economy?
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: There is a significant gap in AI talent in India. Despite efforts to enhance education and training in AI, the demand for skilled professionals continues to outpace supply.
- This shortage limits the capacity to innovate and deploy AI solutions across sectors.
- Data Access and Quality: Effective AI models require diverse and high-quality datasets. The current datasets, especially for Indian languages, are often inadequate, hindering the development of robust indigenous AI solutions.
- The lack of comprehensive data hampers machine learning effectiveness and scalability.
- High Implementation Costs: The costs associated with deploying AI technologies, particularly in sectors like manufacturing and healthcare, can be prohibitive.
- These expenses include infrastructure investments and the integration of AI systems, which can deter widespread adoption.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Advanced cloud computing infrastructure is crucial for effective AI deployment. While initiatives like AIRAWAT are steps in the right direction, India still lacks the comprehensive facilities needed to scale AI applications efficiently.
- Geopolitical and Regulatory Challenges: Tensions in global geopolitics and export control regulations can restrict access to essential AI technologies.
- Such limitations impact India’s ability to develop and implement AI solutions effectively, potentially isolating it from key advancements.
Way Forward
- Developing AI Ecosystem: Despite significant digitization, India’s compute penetration remains low. While the nation has excelled in Information Technology (IT) services, these contribute only 1% of the global USD 30 trillion technology industry.
- In contrast, countries like China have rapidly invested hundreds of billions into AI research, infrastructure, and talent.
- India must leverage its strengths in data, computing, and algorithms to establish its own AI stack.
- Data Sovereignty: Data colonization refers to the control and exploitation of data resources by foreign entities, raising issues of data sovereignty and national security.
- Although India generates 20% of the world’s data, a staggering 80% is stored offshore, processed into AI, and then imported back in monetary form.
- Building on successes such as the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), and the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), India can develop the world’s largest open-source AI platform rooted in its ethos.
- Data Quality and Accessibility: High-quality, diverse datasets are vital for effective AI training.
- Efforts should focus on enhancing data collection, cleaning, and labeling processes, along with promoting data sharing to foster collaboration across various fields.
- Continued Education and Workforce Development: Preparing the workforce for an AI-driven future is essential.
- Initiatives aimed at AI education and upskilling can equip individuals with the necessary skills for the evolving job market.
- Encouraging collaboration between academia, industry, and government can further enhance these efforts.
- International Collaboration and Standards: Global collaboration is key to sharing knowledge and best practices in AI.
- Establishing international standards and frameworks can promote interoperability, fairness, and security in AI development and deployment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q1. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)