Geography
Chapter - 21 Transport
- 08 Nov 2024
- 11 min read
The present transport system of the country comprises several modes of transport including rail, road, coastal shipping, air transport etc. The Ministry of Shipping and the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways are responsible for the formation and implementation of policies and programmes for the development of various modes of transport.
Railways
- Indian Railways is a crucial mode of transportation in India.
- From a very modest beginning in 1853, when the first train steamed off from Mumbai to Thane, it has grown to encompass 7,325 stations and 67,956 km of routes, with extensive locomotive and rolling stock fleets.
- Modernisation efforts include fuel-efficient locomotives, improved freight bogies, and advanced signalling systems.
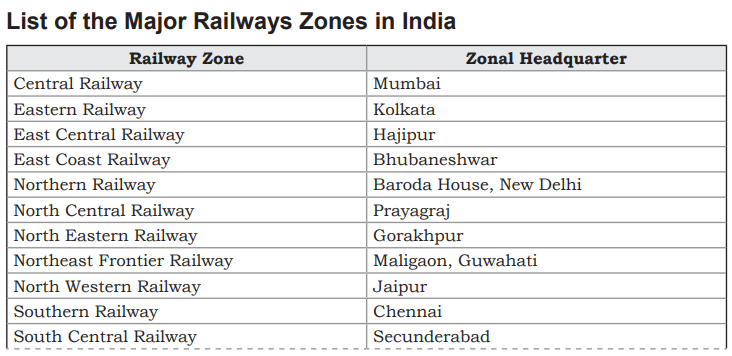
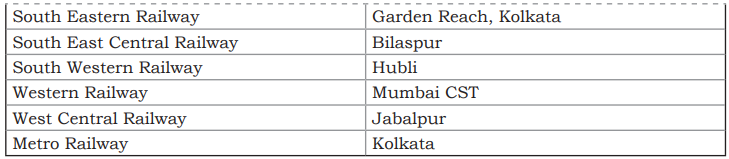
- The railway network is divided into 17 zones, with a focus on system modernization since the planned era of 1950-51.
- Electrification efforts aim to reduce dependence on imported petroleum-based energy, with 80.20% of the broad gauge network electrified by March 2022.
- The Vande Bharat Express, formerly Train 18, is a domestically manufactured semi-high-speed train launched in 2019.
- Indian Railways has played a pivotal role in promoting tourism, operating luxury tourist trains such as the Palace on Wheels and Deccan Odyssey since 1982.
Roads
Bharatmala Pariyojana:
- Aimed at developing road connectivity to border areas, coastal roads, and economic corridors.
- Targets development of 26,000 km of economic corridors, along with inter corridors and feeder routes.
- Includes construction of ring roads/bypasses and elevated corridors to alleviate urban traffic congestion.
- Network optimization conducted through stakeholder consultations to improve connectivity across economic centres.
Green National Highways Corridor Project (GNHCP):
- Launched in 2016 to upgrade 781 km of national highways passing through Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Part of the Green Highways Policy to develop eco-friendly highways.
- Aims to create employment, reduce air and noise pollution, and prevent soil erosion.
- Implemented with aid from the World Bank.
Char Dham Mahamarg Vikas Pariyojana:
- Envisions improved access to the four prominent Dhams in Uttarakhand: Gangotri, Yamunotri, Kedarnath, and Badrinath.
PM Gati Shakti Plan:
- A digital platform bringing together 16 ministries, including Railways and Roadways, for integrated planning and coordinated implementation of infrastructure connectivity projects.
- Launched in 2021
- Aims to provide seamless multi-modal connectivity for movement of people, goods, and services.
- Key features include:
- Comprehensiveness: Centralised portal for all existing and planned initiatives of various ministries.
- Optimization: Assists ministries in identifying critical gaps and selecting optimum routes for transportation.
- Analytical: Provides GIS-based spatial planning and analytical tools with over 200 layers for better visibility.
- Dynamic: Allows visualisation, review, and monitoring of cross-sectoral projects through satellite imagery and regular updates on progress.
Parvatmala Pariyojana:
- National Ropeways Development Programme aimed at improving accessibility, convenience, and promoting tourism.
- Developing ropeways in hilly areas and congested urban areas like Varanasi and Ujjain as alternative transportation modes.
National Highways Authority of India
|
Shipping
The Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW), created from the Ministry of Shipping, Road Transport and Highways in 2020, encompasses within its fold, shipping and port sectors which also include shipbuilding and ship repair, major ports and inland water transport.
- India has a long coastline of about 7,517 km, spread on the western and eastern shelves of the mainland and also along the Islands.
- Approximately 95% of India’s trade by volume and 68% by value is moved through maritime transport.
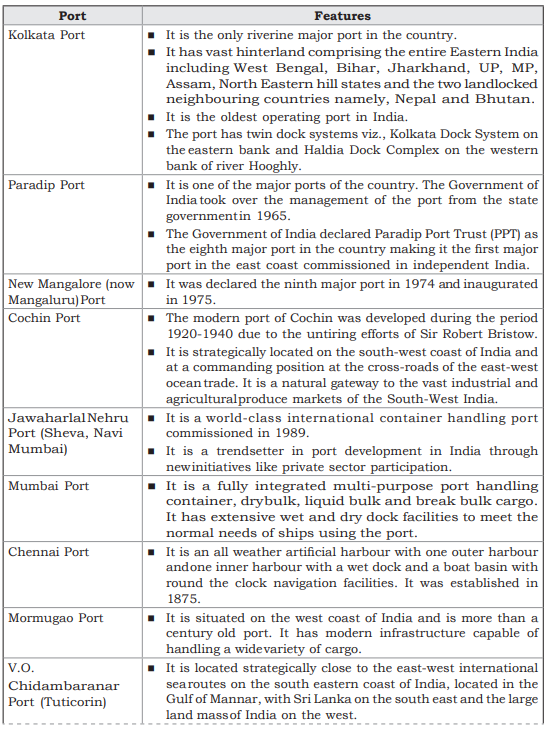
- There are 12 major ports and about 200 non-major ports.
Sagarmala Programme:
- The Government of India has embarked on the ambitious Sagarmala Programme to promote port-led development in the country.
- The vision of the programme is to reduce the logistics cost of EXIM and domestic trade with minimal infrastructure investment.
- The objectives of the Programme include: port modernisation, new port development, port connectivity, coastal community development, etc.
Major Ports:
Inland Water Transport:
|
Civil Aviation
- The Ministry of Civil Aviation is responsible for formulation of national policies and programmes for the development and regulation of the civil aviation sector in the country.
- It is responsible for the administration of the Aircraft Act, 1934, Aircraft Rules, 1937 and various other legislations pertaining to the aviation sector in the country.
- It also supervises implementation by the organizations of special programmes of the government, particularly those intended for weaker sections of society.
National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP), 2016:
- Aims to boost civil aviation growth, leading to tourism promotion, increased employment, and balanced regional development.
- Seeks to democratise flying by enhancing affordability and convenience, while improving ease of doing business through deregulation and e-governance.
- Promotes harmonised development of the entire aviation sector chain, including cargo, MRO, general aviation, aerospace manufacturing, and skill development.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme, UDAN, aims to promote balanced regional growth and affordability by connecting un-served and underserved airports through the revival of existing air strips and airports.
FDI Liberalisation:
- The Government of India has raised the FDI limit from 49% to 100% in scheduled and non scheduled air transport services.
- FDI in scheduled airlines upto 49% is permitted under automatic route and FDI beyond 49% through government approval. For NRIs, 100% FDI will continue to be allowed under automatic route.
Director General of Civil Aviation:
- It is an attached office of the Ministry of Civil Aviation and is headed by Director General (Civil Aviation).
- Primarily responsible for regulation of air transport services to/from/within India and for enforcement of civil air regulations, air safety and airworthiness standards.
- Responsible for licensing of pilots, aircraft maintenance engineers and monitoring of flight crew standards; regulation of civil aircraft; investigation of minor air incidents; supervision of training activities of flying/gliding clubs and other such regulatory functions.
- Co-ordinates all regulatory functions with the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO).
GAGAN
- GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) is an augmentation system to enhance the accuracy and integrity of GPS signals to meet precision approach requirements in civil aviation
- It is being implemented jointly by the Airports Authority of India and ISRO.
Drones or Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS)
- Drone Rules 2021 notified to make India a global hub for the r&d, testing, manufacturing and operation of drones.
- To promote domestic manufacturing of drones, PLI scheme notified for drones and drone components in 2021.
- A Digital Sky Platform launched to regulate the entire gamut of activities pertaining to drone operations.
Digi Yatra:
- Digi Yatra for contactless, seamless processing of passengers at airports launched in 2022.
- It is based on Facial Recognition Technology (FRT).