Smart Cities Mission | 22 Jan 2025
Key Facts:
|
About the Smart Cities Mission
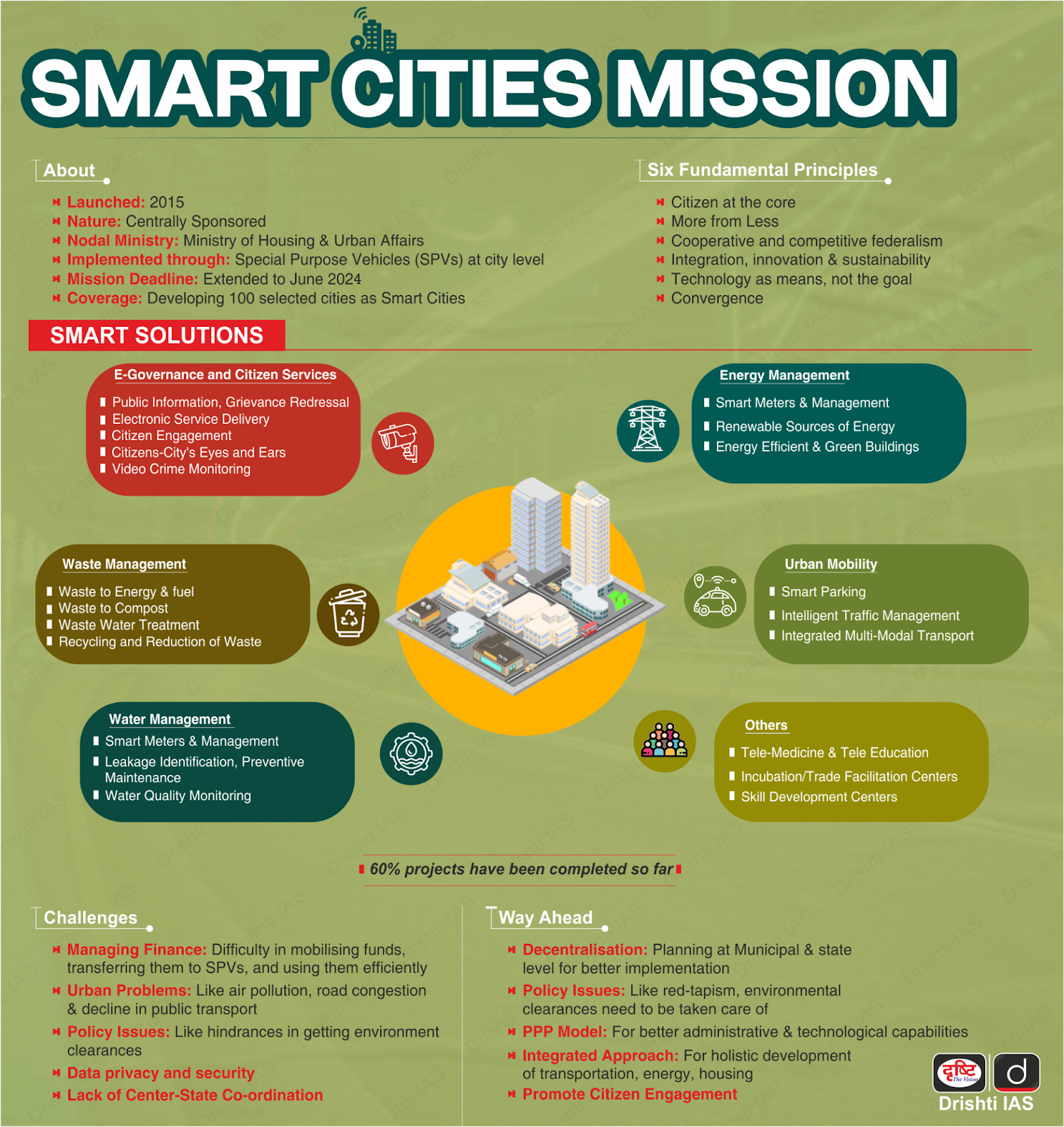
- Smart Cities Mission: The Smart Cities Mission was launched on 25 June 2015 to improve the quality of life in 100 cities.
- It focuses on providing efficient services, modern infrastructure, and sustainable solutions while addressing key urban needs like housing, transport, education, and healthcare.
- Objectives: The objectives of the mission are to provide core infrastructure and a good quality of life, ensure a clean and sustainable environment, and implement smart solutions.
- It aims for sustainable, inclusive development by creating compact areas that serve as replicable models for other cities.
- Funding Mechanism: The mission is primarily funded through a 50:50 cost-sharing model between the central and state governments.
- The central government allocated ₹48,000 crore for five years, with each city receiving ₹100 crore per year. Additional funding is sourced through:
- Convergence with other government schemes.
- Municipal bonds and loans from financial institutions.
- Public Private Partnerships (PPP) to attract private investments- A key feature of the Smart Cities Mission, allowing the private sector to invest in urban infrastructure projects.
- The central government allocated ₹48,000 crore for five years, with each city receiving ₹100 crore per year. Additional funding is sourced through:
- Smart Cities Project Approach: The Mission follows a two-pronged approach to urban development:
- Area-Based Development (ABD): This focuses on transforming specific areas within cities through targeted interventions. Cities implement one of the following models:
- Retrofitting: Upgrading existing infrastructure and services to improve urban efficiency and livability.
- Redevelopment: Replacing old infrastructure with modern facilities and innovative designs.
- Greenfield Development: Building entirely new urban areas with smart features from scratch.
- Pan-City Solutions: These solutions involve the implementation of technology-driven initiatives that span the entire city, enhancing overall efficiency in areas such as transportation, waste management, and governance.
- Area-Based Development (ABD): This focuses on transforming specific areas within cities through targeted interventions. Cities implement one of the following models:
- Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV): To ensure efficient execution of the mission, each city has established a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV).
- The SPV is incorporated as a limited company under the Companies Act, 2013. The State/UT and the Urban Local Body (ULB) jointly hold 50:50 equity in the SPV. The key responsibilities of the SPV include:
- Planning and appraisal of smart city projects.
- Approving and releasing funds for implementation.
- Monitoring and evaluating project performance and impact.
- The SPV is incorporated as a limited company under the Companies Act, 2013. The State/UT and the Urban Local Body (ULB) jointly hold 50:50 equity in the SPV. The key responsibilities of the SPV include:
- Selection of Cities: Cities under the mission were selected through a competitive selection process.
- The criteria considered included factors such as urban population size and the number of statutory towns in each state and union territory.
- The selection process ensured equitable representation across the country, giving equal opportunity to states and UTs in developing smart urban solutions.
- Integrated Control and Command Centres (ICCC): ICCCs have been established in all 100 smart cities to serve as the operational nerve centers. These centers:
- Monitor real-time city operations, including traffic, public safety, water supply, and energy usage.
- Utilize cutting-edge technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and Data Analytics to make informed decisions.
- It played a vital role as COVID-19 war rooms, aiding in pandemic response and resource allocation.
What are the Features of Smart City Mission?
- Smart City Features:
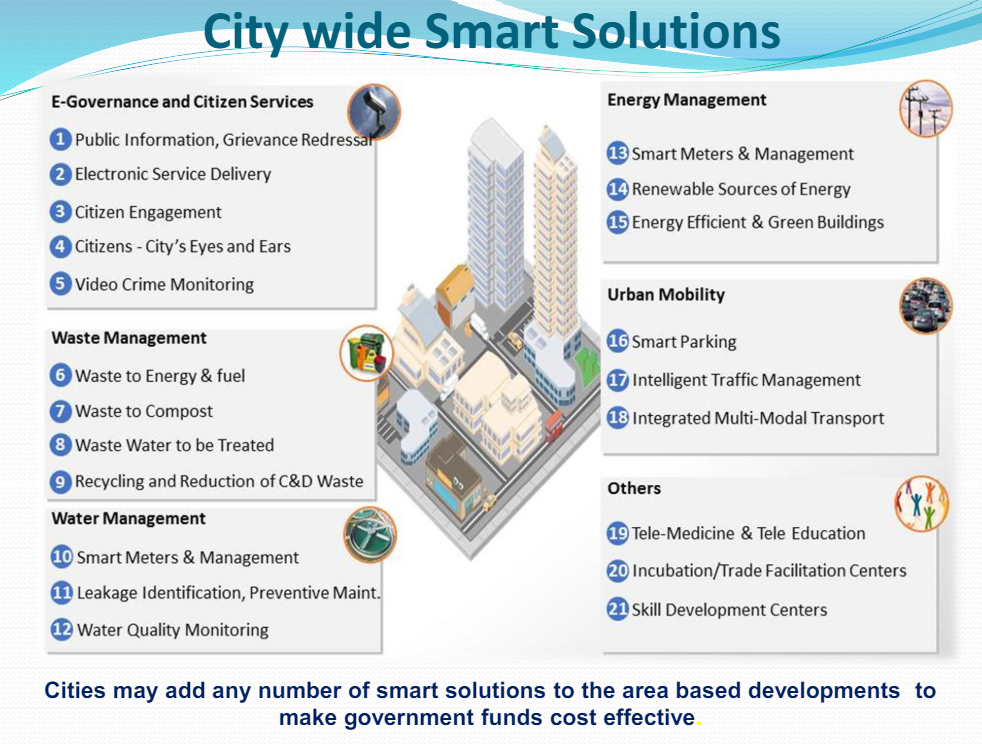
- Efficient Core Infrastructure: Ensuring adequate water supply and 24x7 electricity availability.
- Modern sanitation systems with smart solid waste management solutions.
- Affordable and sustainable housing for all socioeconomic groups.
- Technology Integration: Deployment of smart traffic and transport solutions to manage congestion effectively.
- Establishing a robust IT network to facilitate e-governance and citizen engagement.
- Sustainable Urban Development: Development of green spaces, parks, and eco-friendly zones to improve environmental sustainability.
- Adoption of clean energy solutions to minimize pollution and carbon footprint.
- Social and Economic Inclusion: Promoting mixed land-use policies to encourage walkable neighborhoods.
- Enhancing public safety and security through CCTV surveillance and smart policing.
- Efficient Core Infrastructure: Ensuring adequate water supply and 24x7 electricity availability.
Latest Updates
- As of December 2024, 91% of the total projects have been completed, with 7,380 out of 8,075 projects implemented.
- An investment of ₹1.47 lakh crore has been made to enhance urban infrastructure and services.
- Key Sectoral Achievements:
- Public Safety and Security:Over 84,000 CCTV cameras have been installed for surveillance and crime prevention.
- Smart traffic enforcement systems, including automatic number plate recognition, have been deployed.
- Water Supply Management:
- More than 17,026 km of water pipelines are now monitored using SCADA technology, ensuring leak detection and efficient water usage.
- Waste Management Initiatives: Smart waste collection through RFID-enabled tracking has been implemented in 66 cities.
- Over 9,194 waste management vehicles are now digitally monitored for improved efficiency.
- Urban Mobility Enhancements: Development of 1,740 km of smart roads with intelligent traffic systems.
- Construction of 713 km of cycle tracks to promote eco-friendly transport.
- Education and Healthcare Improvements: Establishment of 9,433 smart classrooms and 41 digital libraries across smart cities.
- Installation of 152 health ATMs and development of 172 e-health centers to improve healthcare accessibility.
- Financial and Time Extensions: The mission has been extended to March 2025 to complete the remaining 10% of projects.
- As of now, ₹46,585 crore has been released, with 93% of the funds utilized effectively.
- Public Safety and Security:Over 84,000 CCTV cameras have been installed for surveillance and crime prevention.